Diffusers
Definitions
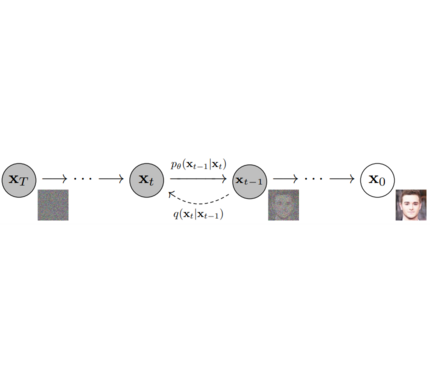
Models: Single neural network that models p_θ(x_t-1|x_t) and is trained to “denoise” to image Examples: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
Schedulers: Algorithm to compute previous image according to alpha, beta schedule and to sample noise. Should be used for both training and inference. Example: Gaussian DDPM, DDIM, PMLS, DEIN
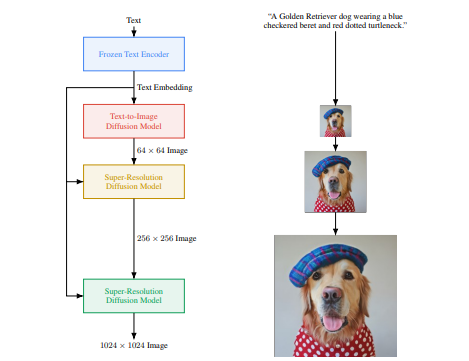
Diffusion Pipeline: End-to-end pipeline that includes multiple diffusion models, possible text encoders, CLIP Example: GLIDE,CompVis/Latent-Diffusion, Imagen, DALL-E
Quickstart
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
cd diffusers && pip install -e .
``
### 1. `diffusers` as a central modular diffusion and sampler library
`diffusers` is more modularized than `transformers`. The idea is that researchers and engineers can use only parts of the library easily for the own use cases.
It could become a central place for all kinds of models, schedulers, training utils and processors that one can mix and match for one's own use case.
Both models and schedulers should be load- and saveable from the Hub.
**Example for [DDPM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239):**
```python
import torch
from diffusers import UNetModel, GaussianDDPMScheduler
import PIL
import numpy as np
import tqdm
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
torch_device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 1. Load models
noise_scheduler = GaussianDDPMScheduler.from_config("fusing/ddpm-lsun-church")
model = UNetModel.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-lsun-church").to(torch_device)
# 2. Sample gaussian noise
image = noise_scheduler.sample_noise((1, model.in_channels, model.resolution, model.resolution), device=torch_device, generator=generator)
# 3. Denoise
num_prediction_steps = len(noise_scheduler)
for t in tqdm.tqdm(reversed(range(num_prediction_steps)), total=num_prediction_steps):
# predict noise residual
with torch.no_grad():
residual = self.unet(image, t)
# predict previous mean of image x_t-1
pred_prev_image = noise_scheduler.compute_prev_image_step(residual, image, t)
# optionally sample variance
variance = 0
if t > 0:
noise = noise_scheduler.sample_noise(image.shape, device=image.device, generator=generator)
variance = noise_scheduler.get_variance(t).sqrt() * noise
# set current image to prev_image: x_t -> x_t-1
image = pred_prev_image + variance
# 5. process image to PIL
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
# 6. save image
image_pil.save("test.png")
Example for DDIM:
import torch
from diffusers import UNetModel, DDIMScheduler
import PIL
import numpy as np
import tqdm
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
torch_device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 1. Load models
noise_scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config("fusing/ddpm-celeba-hq")
model = UNetModel.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-celeba-hq").to(torch_device)
# 2. Sample gaussian noise
image = noise_scheduler.sample_noise((1, model.in_channels, model.resolution, model.resolution), device=torch_device, generator=generator)
# 3. Denoise
num_inference_steps = 50
eta = 0.0 # <- deterministic sampling
for t in tqdm.tqdm(reversed(range(num_inference_steps)), total=num_inference_steps):
# 1. predict noise residual
with torch.no_grad():
residual = self.unet(image, inference_step_times[t])
# 2. predict previous mean of image x_t-1
pred_prev_image = noise_scheduler.compute_prev_image_step(residual, image, t, num_inference_steps, eta)
# 3. optionally sample variance
variance = 0
if eta > 0:
noise = noise_scheduler.sample_noise(image.shape, device=image.device, generator=generator)
variance = noise_scheduler.get_variance(t).sqrt() * eta * noise
# 4. set current image to prev_image: x_t -> x_t-1
image = pred_prev_image + variance
# 5. process image to PIL
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
# 6. save image
image_pil.save("test.png")
2. diffusers as a collection of most important Diffusion systems (GLIDE, Dalle, ...)
models directory in repository hosts the complete code necessary for running a diffusion system as well as to train it. A DiffusionPipeline class allows to easily run the diffusion model in inference:
Example image generation with DDPM
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import PIL.Image
import numpy as np
# load model and scheduler
ddpm = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-lsun-bedroom")
# run pipeline in inference (sample random noise and denoise)
image = ddpm()
# process image to PIL
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
# save image
image_pil.save("test.png")
Library structure:
├── models
│ ├── audio
│ │ └── fastdiff
│ │ ├── modeling_fastdiff.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_fastdiff.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── vision
│ ├── dalle2
│ │ ├── modeling_dalle2.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_dalle2.py
│ ├── ddpm
│ │ ├── example.py
│ │ ├── modeling_ddpm.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_ddpm.py
│ ├── glide
│ │ ├── modeling_glide.py
│ │ ├── modeling_vqvae.py.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_glide.py
│ ├── imagen
│ │ ├── modeling_dalle2.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_dalle2.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── latent_diffusion
│ ├── modeling_latent_diffusion.py
│ ├── README.md
│ └── run_latent_diffusion.py
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
├── setup.cfg
├── setup.py
├── src
│ └── diffusers
│ ├── configuration_utils.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── modeling_utils.py
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── unet_glide.py
│ │ └── unet.py
│ ├── pipeline_utils.py
│ └── schedulers
│ ├── gaussian_ddpm.py
│ ├── __init__.py
├── tests
│ └── test_modeling_utils.py