mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2026-01-27 17:22:53 +03:00
render latex in readme
This commit is contained in:
37
README.md
37
README.md
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ More precisely, 🤗 Diffusers offers:
|
||||
|
||||
## Definitions
|
||||
|
||||
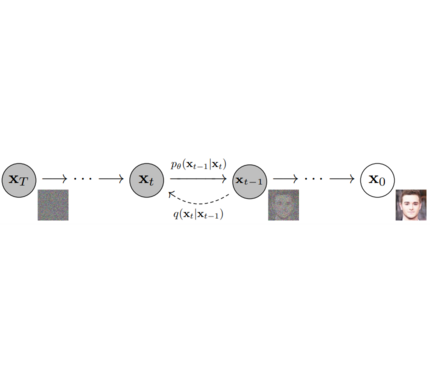
**Models**: Neural network that models **p_θ(x_t-1|x_t)** (see image below) and is trained end-to-end to *denoise* a noisy input to an image.
|
||||
**Models**: Neural network that models $p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t)$ (see image below) and is trained end-to-end to *denoise* a noisy input to an image.
|
||||
*Examples*: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,6 @@ The class provides functionality to compute previous image according to alpha, b
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Philosophy
|
||||
|
||||
- Readability and clarity is prefered over highly optimized code. A strong importance is put on providing readable, intuitive and elementary code desgin. *E.g.*, the provided [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers) are separated from the provided [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) and provide well-commented code that can be read alongside the original paper.
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +58,7 @@ The class provides functionality to compute previous image according to alpha, b
|
||||
pip install diffusers # should install diffusers 0.0.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. `diffusers` as a toolbox for schedulers and models.
|
||||
### 1. `diffusers` as a toolbox for schedulers and models
|
||||
|
||||
`diffusers` is more modularized than `transformers`. The idea is that researchers and engineers can use only parts of the library easily for the own use cases.
|
||||
It could become a central place for all kinds of models, schedulers, training utils and processors that one can mix and match for one's own use case.
|
||||
@@ -137,8 +136,8 @@ unet = UNetModel.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-celeba-hq").to(torch_device)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. Sample gaussian noise
|
||||
image = torch.randn(
|
||||
(1, unet.in_channels, unet.resolution, unet.resolution),
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
(1, unet.in_channels, unet.resolution, unet.resolution),
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
)
|
||||
image = image.to(torch_device)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -147,22 +146,22 @@ num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
eta = 0.0 # <- deterministic sampling
|
||||
|
||||
for t in tqdm.tqdm(reversed(range(num_inference_steps)), total=num_inference_steps):
|
||||
# 1. predict noise residual
|
||||
orig_t = noise_scheduler.get_orig_t(t, num_inference_steps)
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
residual = unet(image, orig_t)
|
||||
# 1. predict noise residual
|
||||
orig_t = noise_scheduler.get_orig_t(t, num_inference_steps)
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
residual = unet(image, orig_t)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. predict previous mean of image x_t-1
|
||||
pred_prev_image = noise_scheduler.step(residual, image, t, num_inference_steps, eta)
|
||||
# 2. predict previous mean of image x_t-1
|
||||
pred_prev_image = noise_scheduler.step(residual, image, t, num_inference_steps, eta)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. optionally sample variance
|
||||
variance = 0
|
||||
if eta > 0:
|
||||
noise = torch.randn(image.shape, generator=generator).to(image.device)
|
||||
variance = noise_scheduler.get_variance(t).sqrt() * eta * noise
|
||||
# 3. optionally sample variance
|
||||
variance = 0
|
||||
if eta > 0:
|
||||
noise = torch.randn(image.shape, generator=generator).to(image.device)
|
||||
variance = noise_scheduler.get_variance(t).sqrt() * eta * noise
|
||||
|
||||
# 4. set current image to prev_image: x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
image = pred_prev_image + variance
|
||||
# 4. set current image to prev_image: x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
image = pred_prev_image + variance
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. process image to PIL
|
||||
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
|
||||
@@ -233,7 +232,7 @@ image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
|
||||
image_pil.save("test.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### **Text to speech with BDDM**
|
||||
#### **Text to speech with BDDM**
|
||||
|
||||
_Follow the instructions [here](https://pytorch.org/hub/nvidia_deeplearningexamples_tacotron2/) to load tacotron2 model._
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Models
|
||||
|
||||
- Models: Neural network that models p_θ(x_t-1|x_t) (see image below) and is trained end-to-end to denoise a noisy input to an image. Examples: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
|
||||
- Models: Neural network that models $p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t)$ (see image below) and is trained end-to-end to denoise a noisy input to an image. Examples: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
|
||||
|
||||
## API
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user