mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2026-01-27 17:22:53 +03:00
[Kandinsky] Improve kandinsky API a bit (#3636)
* Improve docs * up * Update docs/source/en/api/pipelines/kandinsky.mdx * up * up * correct more * further improve * Update docs/source/en/api/pipelines/kandinsky.mdx Co-authored-by: YiYi Xu <yixu310@gmail.com> --------- Co-authored-by: YiYi Xu <yixu310@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
committed by
 GitHub
GitHub
parent
55dbfa0229
commit
32ea2142c0
@@ -19,81 +19,78 @@ The Kandinsky model is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene55
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Colab
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* | - |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* | - |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* | - |
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we will walk you through some cool examples of using the Kandinsky pipelines to create some visually aesthetic artwork.
|
||||
In the following, we will walk you through some examples of how to use the Kandinsky pipelines to create some visually aesthetic artwork.
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
For text-to-image generation, we need to use both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`]. The first step is to encode text prompts with CLIP and then diffuse the CLIP text embeddings to CLIP image embeddings, as first proposed in [DALL-E 2](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-2.pdf). Let's throw a fun prompt at Kandinsky to see what it comes up with :)
|
||||
For text-to-image generation, we need to use both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`].
|
||||
The first step is to encode text prompts with CLIP and then diffuse the CLIP text embeddings to CLIP image embeddings,
|
||||
as first proposed in [DALL-E 2](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-2.pdf).
|
||||
Let's throw a fun prompt at Kandinsky to see what it comes up with.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We will pass both the `prompt` and `negative_prompt` to our prior diffusion pipeline. In contrast to other diffusion pipelines, such as Stable Diffusion, the `prompt` and `negative_prompt` shall be passed separately so that we can retrieve a CLIP image embedding for each prompt input. You can use `guidance_scale`, and `num_inference_steps` arguments to guide this process, just like how you would normally do with all other pipelines in diffusers.
|
||||
First, let's instantiate the prior pipeline and the text-to-image pipeline. Both
|
||||
pipelines are diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
# create prior
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(12)
|
||||
image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt, guidance_scale=1.0, num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator, negative_prompt=negative_prompt
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
negative_prompt, guidance_scale=1.0, num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator, negative_prompt=negative_prompt
|
||||
).images
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once we create the image embedding, we can use [`KandinskyPipeline`] to generate images.
|
||||
Now we pass the prompt through the prior to generate image embeddings. The prior
|
||||
returns both the image embeddings corresponding to the prompt and negative/unconditional image
|
||||
embeddings corresponding to an empty string.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
```py
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(12)
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, generator=generator).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The text-to-image pipeline expects both `image_embeds`, `negative_image_embeds` and the original
|
||||
`prompt` as the text-to-image pipeline uses another text encoder to better guide the second diffusion
|
||||
process of `t2i_pipe`.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the prior returns unconditioned negative image embeddings corresponding to the negative prompt of `""`.
|
||||
For better results, you can also pass a `negative_prompt` to the prior. This will increase the effective batch size
|
||||
of the prior by a factor of 2.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt, generator=generator).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_grid(imgs, rows, cols):
|
||||
assert len(imgs) == rows * cols
|
||||
Next, we can pass the embeddings as well as the prompt to the text-to-image pipeline. Remember that
|
||||
in case you are using a customized negative prompt, that you should pass this one also to the text-to-image pipelines
|
||||
with `negative_prompt=negative_prompt`:
|
||||
|
||||
w, h = imgs[0].size
|
||||
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
|
||||
grid_w, grid_h = grid.size
|
||||
|
||||
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
|
||||
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
|
||||
return grid
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# create diffuser pipeline
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_emb,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=2,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=100,
|
||||
guidance_scale=4.0,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = t2i_pipe(prompt, image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cheeseburger_monster.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One cheeseburger monster coming up! Enjoy!
|
||||
@@ -164,22 +161,15 @@ prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(30)
|
||||
image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt, guidance_scale=4.0, num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator, negative_prompt=negative_prompt
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
negative_prompt, guidance_scale=4.0, num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator, negative_prompt=negative_prompt
|
||||
).images
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt, generator=generator).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=original_image,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_emb,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_embeds,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=500,
|
||||
strength=0.3,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -193,7 +183,7 @@ out.images[0].save("fantasy_land.png")
|
||||
|
||||
You can use [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] to edit images. In this example, we will add a hat to the portrait of a cat.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyInpaintPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -205,7 +195,7 @@ pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(prompt, return_dict=False)
|
||||
prior_output = pipe_prior(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
@@ -222,8 +212,7 @@ out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_emb,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb,
|
||||
**prior_output,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=150,
|
||||
@@ -246,7 +235,6 @@ from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
@@ -263,22 +251,80 @@ img2 = load_image(
|
||||
|
||||
# add all the conditions we want to interpolate, can be either text or image
|
||||
images_texts = ["a cat", img1, img2]
|
||||
|
||||
# specify the weights for each condition in images_texts
|
||||
weights = [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
# We can leave the prompt empty
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
prior_out = pipe_prior.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
"", image_embeds=image_emb, negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb, height=768, width=768, num_inference_steps=150
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("starry_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
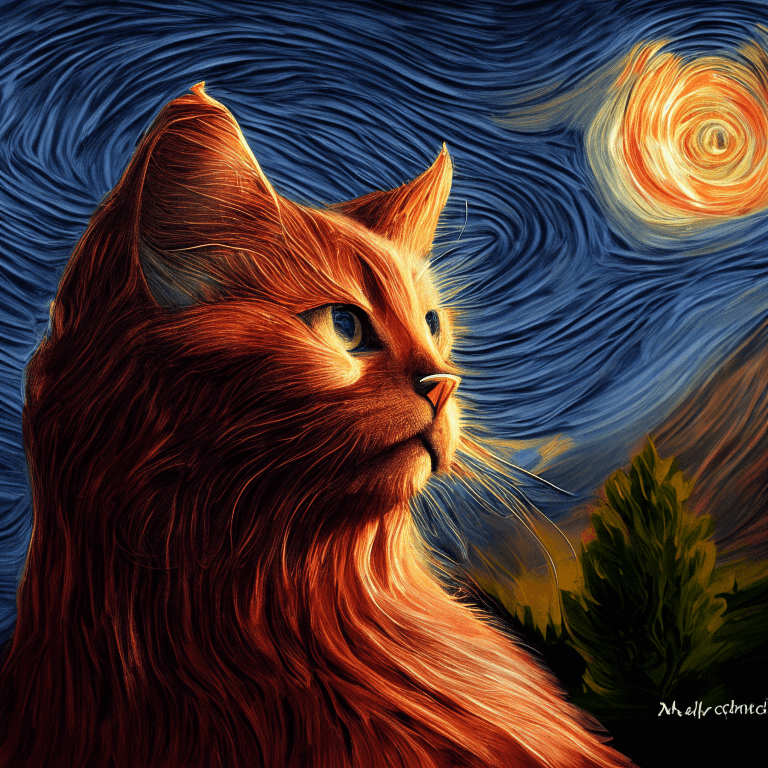
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Running Kandinsky in inference requires running both a first prior pipeline: [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`]
|
||||
and a second image decoding pipeline which is one of [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The bulk of the computation time will always be the second image decoding pipeline, so when looking
|
||||
into optimizing the model, one should look into the second image decoding pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
When running with PyTorch < 2.0, we strongly recommend making use of [`xformers`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)
|
||||
to speed-up the optimization. This can be done by simply running:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running on PyTorch >= 2.0, PyTorch's SDPA attention will automatically be used. For more information on
|
||||
PyTorch's SDPA, feel free to have a look at [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
|
||||
To have explicit control , you can also manually set the pipeline to use PyTorch's 2.0 efficient attention:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The slowest and most memory intense attention processor is the default `AttnAddedKVProcessor` processor.
|
||||
We do **not** recommend using it except for testing purposes or cases where very high determistic behaviour is desired.
|
||||
You can set it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch >= 2.0, you can also use Kandinsky with `torch.compile` which depending
|
||||
on your hardware can signficantly speed-up your inference time once the model is compiled.
|
||||
To use Kandinsksy with `torch.compile`, you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet = torch.compile(t2i_pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation you should see a very fast inference time. For more information,
|
||||
feel free to have a look at [Our PyTorch 2.0 benchmark](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
@@ -292,15 +338,14 @@ image.save("starry_cat.png")
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -304,12 +304,12 @@ class KandinskyPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
prompt: Union[str, List[str]],
|
||||
image_embeds: Union[torch.FloatTensor, List[torch.FloatTensor]],
|
||||
negative_image_embeds: Union[torch.FloatTensor, List[torch.FloatTensor]],
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
height: int = 512,
|
||||
width: int = 512,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: int = 100,
|
||||
guidance_scale: float = 4.0,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
|
||||
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
|
||||
@@ -325,6 +325,9 @@ class KandinskyPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for text prompt, that will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` or `List[torch.FloatTensor]`):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for negative text prompt, will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
The height in pixels of the generated image.
|
||||
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
@@ -340,9 +343,6 @@ class KandinskyPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The number of images to generate per prompt.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
|
||||
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
|
||||
to make generation deterministic.
|
||||
@@ -418,7 +418,8 @@ class KandinskyPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
timestep=t,
|
||||
encoder_hidden_states=text_encoder_hidden_states,
|
||||
added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_kwargs,
|
||||
).sample
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
|
||||
noise_pred, variance_pred = noise_pred.split(latents.shape[1], dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -368,13 +368,13 @@ class KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
image: Union[torch.FloatTensor, PIL.Image.Image, List[torch.FloatTensor], List[PIL.Image.Image]],
|
||||
image_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
height: int = 512,
|
||||
width: int = 512,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: int = 100,
|
||||
strength: float = 0.3,
|
||||
guidance_scale: float = 7.0,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
|
||||
return_dict: bool = True,
|
||||
@@ -392,6 +392,9 @@ class KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for text prompt, that will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` or `List[torch.FloatTensor]`):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for negative text prompt, will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
The height in pixels of the generated image.
|
||||
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
@@ -413,9 +416,6 @@ class KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The number of images to generate per prompt.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
|
||||
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
|
||||
to make generation deterministic.
|
||||
@@ -512,7 +512,8 @@ class KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
timestep=t,
|
||||
encoder_hidden_states=text_encoder_hidden_states,
|
||||
added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_kwargs,
|
||||
).sample
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
|
||||
noise_pred, _ = noise_pred.split(latents.shape[1], dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -466,12 +466,12 @@ class KandinskyInpaintPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
mask_image: Union[torch.FloatTensor, PIL.Image.Image, np.ndarray],
|
||||
image_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
height: int = 512,
|
||||
width: int = 512,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: int = 100,
|
||||
guidance_scale: float = 4.0,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
|
||||
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
|
||||
@@ -498,6 +498,9 @@ class KandinskyInpaintPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for text prompt, that will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` or `List[torch.FloatTensor]`):
|
||||
The clip image embeddings for negative text prompt, will be used to condition the image generation.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
The height in pixels of the generated image.
|
||||
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 512):
|
||||
@@ -513,9 +516,6 @@ class KandinskyInpaintPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The number of images to generate per prompt.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
|
||||
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
|
||||
to make generation deterministic.
|
||||
@@ -629,7 +629,8 @@ class KandinskyInpaintPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
timestep=t,
|
||||
encoder_hidden_states=text_encoder_hidden_states,
|
||||
added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_kwargs,
|
||||
).sample
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
|
||||
noise_pred, variance_pred = noise_pred.split(latents.shape[1], dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -116,14 +116,14 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipelineOutput(BaseOutput):
|
||||
Output class for KandinskyPriorPipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
images (`torch.FloatTensor`)
|
||||
image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`)
|
||||
clip image embeddings for text prompt
|
||||
zero_embeds (`List[PIL.Image.Image]` or `np.ndarray`)
|
||||
negative_image_embeds (`List[PIL.Image.Image]` or `np.ndarray`)
|
||||
clip image embeddings for unconditional tokens
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
images: Union[torch.FloatTensor, np.ndarray]
|
||||
zero_embeds: Union[torch.FloatTensor, np.ndarray]
|
||||
image_embeds: Union[torch.FloatTensor, np.ndarray]
|
||||
negative_image_embeds: Union[torch.FloatTensor, np.ndarray]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
image_embeddings = []
|
||||
for cond, weight in zip(images_and_prompts, weights):
|
||||
if isinstance(cond, str):
|
||||
image_emb = self.__call__(
|
||||
image_emb = self(
|
||||
cond,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
latents=latents,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prior_prompt,
|
||||
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
).image_embeds
|
||||
|
||||
elif isinstance(cond, (PIL.Image.Image, torch.Tensor)):
|
||||
if isinstance(cond, PIL.Image.Image):
|
||||
@@ -261,7 +261,7 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
|
||||
image_emb = torch.cat(image_embeddings).sum(dim=0, keepdim=True)
|
||||
|
||||
out_zero = self.__call__(
|
||||
out_zero = self(
|
||||
negative_prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
|
||||
@@ -270,9 +270,9 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prior_prompt,
|
||||
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
|
||||
)
|
||||
zero_image_emb = out_zero.zero_embeds if negative_prompt == "" else out_zero.images
|
||||
zero_image_emb = out_zero.negative_image_embeds if negative_prompt == "" else out_zero.image_embeds
|
||||
|
||||
return image_emb, zero_image_emb
|
||||
return KandinskyPriorPipelineOutput(image_embeds=image_emb, negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb)
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_latents(self, shape, dtype, device, generator, latents, scheduler):
|
||||
if latents is None:
|
||||
@@ -435,11 +435,11 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
prompt: Union[str, List[str]],
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: int = 25,
|
||||
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
|
||||
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
guidance_scale: float = 4.0,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pt", # pt only
|
||||
return_dict: bool = True,
|
||||
@@ -450,6 +450,9 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts to guide the image generation.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The number of images to generate per prompt.
|
||||
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 100):
|
||||
@@ -462,9 +465,6 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
Pre-generated noisy latents, sampled from a Gaussian distribution, to be used as inputs for image
|
||||
generation. Can be used to tweak the same generation with different prompts. If not provided, a latents
|
||||
tensor will ge generated by sampling using the supplied random `generator`.
|
||||
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored
|
||||
if `guidance_scale` is less than `1`).
|
||||
guidance_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 4.0):
|
||||
Guidance scale as defined in [Classifier-Free Diffusion Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.12598).
|
||||
`guidance_scale` is defined as `w` of equation 2. of [Imagen
|
||||
@@ -484,14 +484,24 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(prompt, str):
|
||||
batch_size = 1
|
||||
elif isinstance(prompt, list):
|
||||
batch_size = len(prompt)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prompt = [prompt]
|
||||
elif not isinstance(prompt, list):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`prompt` has to be of type `str` or `list` but is {type(prompt)}")
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(negative_prompt, str):
|
||||
negative_prompt = [negative_prompt]
|
||||
elif not isinstance(negative_prompt, list) and negative_prompt is not None:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`negative_prompt` has to be of type `str` or `list` but is {type(negative_prompt)}")
|
||||
|
||||
# if the negative prompt is defined we double the batch size to
|
||||
# directly retrieve the negative prompt embedding
|
||||
if negative_prompt is not None:
|
||||
prompt = prompt + negative_prompt
|
||||
negative_prompt = 2 * negative_prompt
|
||||
|
||||
device = self._execution_device
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size = len(prompt)
|
||||
batch_size = batch_size * num_images_per_prompt
|
||||
|
||||
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
|
||||
@@ -548,7 +558,12 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
latents = self.prior.post_process_latents(latents)
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeddings = latents
|
||||
zero_embeds = self.get_zero_embed(latents.shape[0], device=latents.device)
|
||||
|
||||
# if negative prompt has been defined, we retrieve split the image embedding into two
|
||||
if negative_prompt is None:
|
||||
zero_embeds = self.get_zero_embed(latents.shape[0], device=latents.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image_embeddings, zero_embeds = image_embeddings.chunk(2)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_type not in ["pt", "np"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Only the output types `pt` and `np` are supported not output_type={output_type}")
|
||||
@@ -560,4 +575,4 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return (image_embeddings, zero_embeds)
|
||||
|
||||
return KandinskyPriorPipelineOutput(images=image_embeddings, zero_embeds=zero_embeds)
|
||||
return KandinskyPriorPipelineOutput(image_embeds=image_embeddings, negative_image_embeds=zero_embeds)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -258,12 +258,12 @@ class KandinskyPipelineIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
prompt = "red cat, 4k photo"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=5,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
zero_image_emb = pipe_prior("", num_inference_steps=5).images
|
||||
negative_prompt="",
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
output = pipeline(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -276,12 +276,12 @@ class KandinskyImg2ImgPipelineIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=5,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
zero_image_emb = pipe_prior("", num_inference_steps=5).images
|
||||
negative_prompt="",
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -286,12 +286,12 @@ class KandinskyInpaintPipelineIntegrationTests(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=5,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
zero_image_emb = pipe_prior("").images
|
||||
negative_prompt="",
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -194,7 +194,7 @@ class KandinskyPriorPipelineFastTests(PipelineTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
pipe.set_progress_bar_config(disable=None)
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(**self.get_dummy_inputs(device))
|
||||
image = output.images
|
||||
image = output.image_embeds
|
||||
|
||||
image_from_tuple = pipe(
|
||||
**self.get_dummy_inputs(device),
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -650,7 +650,7 @@ class PipelineTesterMixin:
|
||||
if key in self.batch_params:
|
||||
inputs[key] = batch_size * [inputs[key]]
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(**inputs, num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt).images
|
||||
images = pipe(**inputs, num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
assert images.shape[0] == batch_size * num_images_per_prompt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user