You've already forked postgres_exporter
mirror of
https://github.com/prometheus-community/postgres_exporter.git
synced 2025-08-06 17:22:43 +03:00
Refactor repository layout and convert build system to Mage.
This commit implements a massive refactor of the repository, and moves the build system over to use Mage (magefile.org) which should allow seamless building across multiple platforms.
This commit is contained in:
24
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/LICENSE.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
24
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/LICENSE.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
Copyright © 2015, Joe Tsai and The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
|
||||
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or
|
||||
other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to
|
||||
endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior
|
||||
written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
|
||||
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
|
||||
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
|
||||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER BE LIABLE FOR ANY
|
||||
DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
|
||||
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND
|
||||
ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
|
||||
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
75
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
75
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# Collection of compression libraries for Go #
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/dsnet/compress)
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/dsnet/compress)
|
||||
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/dsnet/compress)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction ##
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE: This library is in active development. As such, there are no guarantees about the stability of the API. The author reserves the right to arbitrarily break the API for any reason.**
|
||||
|
||||
This repository hosts a collection of compression related libraries. The goal of this project is to provide pure Go implementations for popular compression algorithms beyond what the Go standard library provides. The goals for these packages are as follows:
|
||||
* Maintainable: That the code remains well documented, well tested, readable, easy to maintain, and easy to verify that it conforms to the specification for the format being implemented.
|
||||
* Performant: To be able to compress and decompress within at least 80% of the rates that the C implementations are able to achieve.
|
||||
* Flexible: That the code provides low-level and fine granularity control over the compression streams similar to what the C APIs would provide.
|
||||
|
||||
Of these three, the first objective is often at odds with the other two objectives and provides interesting challenges. Higher performance can often be achieved by muddling abstraction layers or using non-intuitive low-level primitives. Also, more features and functionality, while useful in some situations, often complicates the API. Thus, this package will attempt to satisfy all the goals, but will defer to favoring maintainability when the performance or flexibility benefits are not significant enough.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Library Status ##
|
||||
|
||||
For the packages available, only some features are currently implemented:
|
||||
|
||||
| Package | Reader | Writer |
|
||||
| ------- | :----: | :----: |
|
||||
| brotli | :white_check_mark: | |
|
||||
| bzip2 | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||||
| flate | :white_check_mark: | |
|
||||
| xflate | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||||
|
||||
This library is in active development. As such, there are no guarantees about the stability of the API. The author reserves the right to arbitrarily break the API for any reason. When the library becomes more mature, it is planned to eventually conform to some strict versioning scheme like [Semantic Versioning](http://semver.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
However, in the meanwhile, this library does provide some basic API guarantees. For the types defined below, the method signatures are guaranteed to not change. Note that the author still reserves the right to change the fields within each ```Reader``` and ```Writer``` structs.
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type ReaderConfig struct { ... }
|
||||
type Reader struct { ... }
|
||||
func NewReader(io.Reader, *ReaderConfig) (*Reader, error) { ... }
|
||||
func (*Reader) Read([]byte) (int, error) { ... }
|
||||
func (*Reader) Close() error { ... }
|
||||
|
||||
type WriterConfig struct { ... }
|
||||
type Writer struct { ... }
|
||||
func NewWriter(io.Writer, *WriterConfig) (*Writer, error) { ... }
|
||||
func (*Writer) Write([]byte) (int, error) { ... }
|
||||
func (*Writer) Close() error { ... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To see what work still remains, see the [Task List](https://github.com/dsnet/compress/wiki/Task-List).
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance ##
|
||||
|
||||
See [Performance Metrics](https://github.com/dsnet/compress/wiki/Performance-Metrics).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently Asked Questions ##
|
||||
|
||||
See [Frequently Asked Questions](https://github.com/dsnet/compress/wiki/Frequently-Asked-Questions).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation ##
|
||||
|
||||
Run the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```go get -u github.com/dsnet/compress```
|
||||
|
||||
This library requires `Go1.7` or higher in order to build.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Packages ##
|
||||
|
||||
| Package | Description |
|
||||
| :------ | :---------- |
|
||||
| [brotli](http://godoc.org/github.com/dsnet/compress/brotli) | Package brotli implements the Brotli format, described in RFC 7932. |
|
||||
| [bzip2](http://godoc.org/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2) | Package bzip2 implements the BZip2 compressed data format. |
|
||||
| [flate](http://godoc.org/github.com/dsnet/compress/flate) | Package flate implements the DEFLATE format, described in RFC 1951. |
|
||||
| [xflate](http://godoc.org/github.com/dsnet/compress/xflate) | Package xflate implements the XFLATE format, an random-access extension to DEFLATE. |
|
||||
74
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/api.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
74
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/api.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package compress is a collection of compression libraries.
|
||||
package compress
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// The Error interface identifies all compression related errors.
|
||||
type Error interface {
|
||||
error
|
||||
CompressError()
|
||||
|
||||
// IsDeprecated reports the use of a deprecated and unsupported feature.
|
||||
IsDeprecated() bool
|
||||
|
||||
// IsCorrupted reports whether the input stream was corrupted.
|
||||
IsCorrupted() bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Error = errors.Error{}
|
||||
|
||||
// ByteReader is an interface accepted by all decompression Readers.
|
||||
// It guarantees that the decompressor never reads more data than is necessary
|
||||
// from the underlying io.Reader.
|
||||
type ByteReader interface {
|
||||
io.Reader
|
||||
io.ByteReader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ ByteReader = (*bufio.Reader)(nil)
|
||||
|
||||
// BufferedReader is an interface accepted by all decompression Readers.
|
||||
// It guarantees that the decompressor never reads more data than is necessary
|
||||
// from the underlying io.Reader. Since BufferedReader allows a decompressor
|
||||
// to peek at bytes further along in the stream without advancing the read
|
||||
// pointer, decompression can experience a significant performance gain when
|
||||
// provided a reader that satisfies this interface. Thus, a decompressor will
|
||||
// prefer this interface over ByteReader for performance reasons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The bufio.Reader satisfies this interface.
|
||||
type BufferedReader interface {
|
||||
io.Reader
|
||||
|
||||
// Buffered returns the number of bytes currently buffered.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This value becomes invalid following the next Read/Discard operation.
|
||||
Buffered() int
|
||||
|
||||
// Peek returns the next n bytes without advancing the reader.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Peek returns fewer than n bytes, it also returns an error explaining
|
||||
// why the peek is short. Peek must support peeking of at least 8 bytes.
|
||||
// If 0 <= n <= Buffered(), Peek is guaranteed to succeed without reading
|
||||
// from the underlying io.Reader.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This result becomes invalid following the next Read/Discard operation.
|
||||
Peek(n int) ([]byte, error)
|
||||
|
||||
// Discard skips the next n bytes, returning the number of bytes discarded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Discard skips fewer than n bytes, it also returns an error.
|
||||
// If 0 <= n <= Buffered(), Discard is guaranteed to succeed without reading
|
||||
// from the underlying io.Reader.
|
||||
Discard(n int) (int, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ BufferedReader = (*bufio.Reader)(nil)
|
||||
110
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/bwt.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
110
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/bwt.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais"
|
||||
|
||||
// The Burrows-Wheeler Transform implementation used here is based on the
|
||||
// Suffix Array by Induced Sorting (SA-IS) methodology by Nong, Zhang, and Chan.
|
||||
// This implementation uses the sais algorithm originally written by Yuta Mori.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The SA-IS algorithm runs in O(n) and outputs a Suffix Array. There is a
|
||||
// mathematical relationship between Suffix Arrays and the Burrows-Wheeler
|
||||
// Transform, such that a SA can be converted to a BWT in O(n) time.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// References:
|
||||
// http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/Compaq-DEC/SRC-RR-124.pdf
|
||||
// https://github.com/cscott/compressjs/blob/master/lib/BWT.js
|
||||
// https://www.quora.com/How-can-I-optimize-burrows-wheeler-transform-and-inverse-transform-to-work-in-O-n-time-O-n-space
|
||||
type burrowsWheelerTransform struct {
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
sa []int
|
||||
perm []uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (bwt *burrowsWheelerTransform) Encode(buf []byte) (ptr int) {
|
||||
if len(buf) == 0 {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(dsnet): Find a way to avoid the duplicate input string method.
|
||||
// We only need to do this because suffix arrays (by definition) only
|
||||
// operate non-wrapped suffixes of a string. On the other hand,
|
||||
// the BWT specifically used in bzip2 operate on a strings that wrap-around
|
||||
// when being sorted.
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 1: Concatenate the input string to itself so that we can use the
|
||||
// suffix array algorithm for bzip2's variant of BWT.
|
||||
n := len(buf)
|
||||
bwt.buf = append(append(bwt.buf[:0], buf...), buf...)
|
||||
if cap(bwt.sa) < 2*n {
|
||||
bwt.sa = make([]int, 2*n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t := bwt.buf[:2*n]
|
||||
sa := bwt.sa[:2*n]
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 2: Compute the suffix array (SA). The input string, t, will not be
|
||||
// modified, while the results will be written to the output, sa.
|
||||
sais.ComputeSA(t, sa)
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 3: Convert the SA to a BWT. Since ComputeSA does not mutate the
|
||||
// input, we have two copies of the input; in buf and buf2. Thus, we write
|
||||
// the transformation to buf, while using buf2.
|
||||
var j int
|
||||
buf2 := t[n:]
|
||||
for _, i := range sa {
|
||||
if i < n {
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
ptr = j
|
||||
i = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf[j] = buf2[i-1]
|
||||
j++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ptr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (bwt *burrowsWheelerTransform) Decode(buf []byte, ptr int) {
|
||||
if len(buf) == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 1: Compute cumm, where cumm[ch] reports the total number of
|
||||
// characters that precede the character ch in the alphabet.
|
||||
var cumm [256]int
|
||||
for _, v := range buf {
|
||||
cumm[v]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
var sum int
|
||||
for i, v := range cumm {
|
||||
cumm[i] = sum
|
||||
sum += v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 2: Compute perm, where perm[ptr] contains a pointer to the next
|
||||
// byte in buf and the next pointer in perm itself.
|
||||
if cap(bwt.perm) < len(buf) {
|
||||
bwt.perm = make([]uint32, len(buf))
|
||||
}
|
||||
perm := bwt.perm[:len(buf)]
|
||||
for i, b := range buf {
|
||||
perm[cumm[b]] = uint32(i)
|
||||
cumm[b]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 3: Follow each pointer in perm to the next byte, starting with the
|
||||
// origin pointer.
|
||||
if cap(bwt.buf) < len(buf) {
|
||||
bwt.buf = make([]byte, len(buf))
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf2 := bwt.buf[:len(buf)]
|
||||
i := perm[ptr]
|
||||
for j := range buf2 {
|
||||
buf2[j] = buf[i]
|
||||
i = perm[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(buf, buf2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
110
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
110
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package bzip2 implements the BZip2 compressed data format.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canonical C implementation:
|
||||
// http://bzip.org
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unofficial format specification:
|
||||
// https://github.com/dsnet/compress/blob/master/doc/bzip2-format.pdf
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"hash/crc32"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// There does not exist a formal specification of the BZip2 format. As such,
|
||||
// much of this work is derived by either reverse engineering the original C
|
||||
// source code or using secondary sources.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Significant amounts of fuzz testing is done to ensure that outputs from
|
||||
// this package is properly decoded by the C library. Furthermore, we test that
|
||||
// both this package and the C library agree about what inputs are invalid.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Compression stack:
|
||||
// Run-length encoding 1 (RLE1)
|
||||
// Burrows-Wheeler transform (BWT)
|
||||
// Move-to-front transform (MTF)
|
||||
// Run-length encoding 2 (RLE2)
|
||||
// Prefix encoding (PE)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// References:
|
||||
// http://bzip.org/
|
||||
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bzip2
|
||||
// https://code.google.com/p/jbzip2/
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
BestSpeed = 1
|
||||
BestCompression = 9
|
||||
DefaultCompression = 6
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
hdrMagic = 0x425a // Hex of "BZ"
|
||||
blkMagic = 0x314159265359 // BCD of PI
|
||||
endMagic = 0x177245385090 // BCD of sqrt(PI)
|
||||
|
||||
blockSize = 100000
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func errorf(c int, f string, a ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
return errors.Error{Code: c, Pkg: "bzip2", Msg: fmt.Sprintf(f, a...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func panicf(c int, f string, a ...interface{}) {
|
||||
errors.Panic(errorf(c, f, a...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errWrap converts a lower-level errors.Error to be one from this package.
|
||||
// The replaceCode passed in will be used to replace the code for any errors
|
||||
// with the errors.Invalid code.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the Reader, set this to errors.Corrupted.
|
||||
// For the Writer, set this to errors.Internal.
|
||||
func errWrap(err error, replaceCode int) error {
|
||||
if cerr, ok := err.(errors.Error); ok {
|
||||
if errors.IsInvalid(cerr) {
|
||||
cerr.Code = replaceCode
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = errorf(cerr.Code, "%s", cerr.Msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var errClosed = errorf(errors.Closed, "")
|
||||
|
||||
// crc computes the CRC-32 used by BZip2.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The CRC-32 computation in bzip2 treats bytes as having bits in big-endian
|
||||
// order. That is, the MSB is read before the LSB. Thus, we can use the
|
||||
// standard library version of CRC-32 IEEE with some minor adjustments.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The byte array is used as an intermediate buffer to swap the bits of every
|
||||
// byte of the input.
|
||||
type crc struct {
|
||||
val uint32
|
||||
buf [256]byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// update computes the CRC-32 of appending buf to c.
|
||||
func (c *crc) update(buf []byte) {
|
||||
cval := internal.ReverseUint32(c.val)
|
||||
for len(buf) > 0 {
|
||||
n := len(buf)
|
||||
if n > len(c.buf) {
|
||||
n = len(c.buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, b := range buf[:n] {
|
||||
c.buf[i] = internal.ReverseLUT[b]
|
||||
}
|
||||
cval = crc32.Update(cval, crc32.IEEETable, c.buf[:n])
|
||||
buf = buf[n:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.val = internal.ReverseUint32(cval)
|
||||
}
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/fuzz_off.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
13
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/fuzz_off.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !gofuzz
|
||||
|
||||
// This file exists to suppress fuzzing details from release builds.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
type fuzzReader struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*fuzzReader) updateChecksum(int64, uint32) {}
|
||||
77
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/fuzz_on.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
77
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/fuzz_on.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build gofuzz
|
||||
|
||||
// This file exists to export internal implementation details for fuzz testing.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
func ForwardBWT(buf []byte) (ptr int) {
|
||||
var bwt burrowsWheelerTransform
|
||||
return bwt.Encode(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func ReverseBWT(buf []byte, ptr int) {
|
||||
var bwt burrowsWheelerTransform
|
||||
bwt.Decode(buf, ptr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type fuzzReader struct {
|
||||
Checksums Checksums
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// updateChecksum updates Checksums.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If a valid pos is provided, it appends the (pos, val) pair to the slice.
|
||||
// Otherwise, it will update the last record with the new value.
|
||||
func (fr *fuzzReader) updateChecksum(pos int64, val uint32) {
|
||||
if pos >= 0 {
|
||||
fr.Checksums = append(fr.Checksums, Checksum{pos, val})
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fr.Checksums[len(fr.Checksums)-1].Value = val
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type Checksum struct {
|
||||
Offset int64 // Bit offset of the checksum
|
||||
Value uint32 // Checksum value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type Checksums []Checksum
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply overwrites all checksum fields in d with the ones in cs.
|
||||
func (cs Checksums) Apply(d []byte) []byte {
|
||||
d = append([]byte(nil), d...)
|
||||
for _, c := range cs {
|
||||
setU32(d, c.Offset, c.Value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func setU32(d []byte, pos int64, val uint32) {
|
||||
for i := uint(0); i < 32; i++ {
|
||||
bpos := uint64(pos) + uint64(i)
|
||||
d[bpos/8] &= ^byte(1 << (7 - bpos%8))
|
||||
d[bpos/8] |= byte(val>>(31-i)) << (7 - bpos%8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Verify checks that all checksum fields in d matches those in cs.
|
||||
func (cs Checksums) Verify(d []byte) bool {
|
||||
for _, c := range cs {
|
||||
if getU32(d, c.Offset) != c.Value {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getU32(d []byte, pos int64) (val uint32) {
|
||||
for i := uint(0); i < 32; i++ {
|
||||
bpos := uint64(pos) + uint64(i)
|
||||
val |= (uint32(d[bpos/8] >> (7 - bpos%8))) << (31 - i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return val
|
||||
}
|
||||
28
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
28
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package sais implements a linear time suffix array algorithm.
|
||||
package sais
|
||||
|
||||
//go:generate go run sais_gen.go byte sais_byte.go
|
||||
//go:generate go run sais_gen.go int sais_int.go
|
||||
|
||||
// This package ports the C sais implementation by Yuta Mori. The ports are
|
||||
// located in sais_byte.go and sais_int.go, which are identical to each other
|
||||
// except for the types. Since Go does not support generics, we use generators to
|
||||
// create the two files.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// References:
|
||||
// https://sites.google.com/site/yuta256/sais
|
||||
// https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221313676_Linear_Time_Suffix_Array_Construction_Using_D-Critical_Substrings
|
||||
// https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224176324_Two_Efficient_Algorithms_for_Linear_Time_Suffix_Array_Construction
|
||||
|
||||
// ComputeSA computes the suffix array of t and places the result in sa.
|
||||
// Both t and sa must be the same length.
|
||||
func ComputeSA(t []byte, sa []int) {
|
||||
if len(sa) != len(t) {
|
||||
panic("mismatching sizes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
computeSA_byte(t, sa, 0, len(t), 256)
|
||||
}
|
||||
661
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/sais_byte.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
661
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/sais_byte.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,661 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Code generated by sais_gen.go. DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2008-2010 Yuta Mori All Rights Reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
|
||||
// obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation
|
||||
// files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without
|
||||
// restriction, including without limitation the rights to use,
|
||||
// copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the
|
||||
// Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following
|
||||
// conditions:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
|
||||
// included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
|
||||
// EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
|
||||
// OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
|
||||
// NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
|
||||
// HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
|
||||
// WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
|
||||
// FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
|
||||
// OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
package sais
|
||||
|
||||
func getCounts_byte(T []byte, C []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var i int
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
C[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
C[T[i]]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getBuckets_byte(C, B []int, k int, end bool) {
|
||||
var i, sum int
|
||||
if end {
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
sum += C[i]
|
||||
B[i] = sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
sum += C[i]
|
||||
B[i] = sum - C[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sortLMS1_byte(T []byte, SA, C, B []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
} else if j < 0 {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i = n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) > c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^(j + 1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func postProcLMS1_byte(T []byte, SA []int, n, m int) int {
|
||||
var i, j, p, q, plen, qlen, name int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
var diff bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Compact all the sorted substrings into the first m items of SA.
|
||||
// 2*m must be not larger than n (provable).
|
||||
for i = 0; SA[i] < 0; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^SA[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < m {
|
||||
for j, i = i, i+1; ; i++ {
|
||||
if p = SA[i]; p < 0 {
|
||||
SA[j] = ^p
|
||||
j++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
if j == m {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Store the length of all substrings.
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
SA[m+((i+1)>>1)] = j - i
|
||||
j = i + 1
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the lexicographic names of all substrings.
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
qlen = 0
|
||||
for i, q = 0, n; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
p = SA[i]
|
||||
plen = SA[m+(p>>1)]
|
||||
diff = true
|
||||
if (plen == qlen) && ((q + plen) < n) {
|
||||
for j = 0; (j < plen) && (T[p+j] == T[q+j]); j++ {
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j == plen {
|
||||
diff = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if diff {
|
||||
name++
|
||||
q = p
|
||||
qlen = plen
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[m+(p>>1)] = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sortLMS2_byte(T []byte, SA, C, B, D []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j, t, d int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
t = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i, d = 0, 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
d += 1
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
t = int(c0) << 1
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
t |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if D[t] != d {
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
D[t] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
} else if j < 0 {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = n - 1; 0 <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if SA[i] > 0 {
|
||||
if SA[i] < n {
|
||||
SA[i] += n
|
||||
for j = i - 1; SA[j] < n; j-- {
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[j] -= n
|
||||
i = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i, d = n-1, d+1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
d += 1
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
t = int(c0) << 1
|
||||
if int(T[j]) > c1 {
|
||||
t |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if D[t] != d {
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
D[t] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^(j + 1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func postProcLMS2_byte(SA []int, n, m int) int {
|
||||
var i, j, d, name int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compact all the sorted LMS substrings into the first m items of SA.
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
for i = 0; SA[i] < 0; i++ {
|
||||
j = ^SA[i]
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
name += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < m {
|
||||
for d, i = i, i+1; ; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j < 0 {
|
||||
j = ^j
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
name += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[d] = j
|
||||
d++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
if d == m {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name < m {
|
||||
// Store the lexicographic names.
|
||||
for i, d = m-1, name+1; 0 <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; n <= j {
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
d--
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[m+(j>>1)] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Unset flags.
|
||||
for i = 0; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; n <= j {
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
SA[i] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func induceSA_byte(T []byte, SA, C, B []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
if j > 0 && int(T[j-1]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
j = SA[i]
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
if j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j > 0 && int(T[j-1]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i = n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if (j == 0) || (int(T[j-1]) > c1) {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func computeSA_byte(T []byte, SA []int, fs, n, k int) {
|
||||
const (
|
||||
minBucketSize = 512
|
||||
sortLMS2Limit = 0x3fffffff
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var C, B, D, RA []int
|
||||
var bo int // Offset of B relative to SA
|
||||
var b, i, j, m, p, q, name, newfs int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
var flags uint
|
||||
|
||||
if k <= minBucketSize {
|
||||
C = make([]int, k)
|
||||
if k <= fs {
|
||||
bo = n + fs - k
|
||||
B = SA[bo:]
|
||||
flags = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
flags = 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if k <= fs {
|
||||
C = SA[n+fs-k:]
|
||||
if k <= fs-k {
|
||||
bo = n + fs - 2*k
|
||||
B = SA[bo:]
|
||||
flags = 0
|
||||
} else if k <= 4*minBucketSize {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
flags = 2
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
B = C
|
||||
flags = 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
C = make([]int, k)
|
||||
B = C
|
||||
flags = 4 | 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n <= sortLMS2Limit && 2 <= (n/k) {
|
||||
if flags&1 > 0 {
|
||||
if 2*k <= fs-k {
|
||||
flags |= 32
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flags |= 16
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if flags == 0 && 2*k <= (fs-2*k) {
|
||||
flags |= 32
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 1: Reduce the problem by at least 1/2.
|
||||
// Sort all the LMS-substrings.
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
b = -1
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = n
|
||||
m = 0
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
if b >= 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
B[c1]--
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j = i
|
||||
m++
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if m > 1 {
|
||||
if flags&(16|32) > 0 {
|
||||
if flags&16 > 0 {
|
||||
D = make([]int, 2*k)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
D = SA[bo-2*k:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
B[T[j+1]]++
|
||||
for i, j = 0, 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
j += C[i]
|
||||
if B[i] != j {
|
||||
SA[B[i]] += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
D[i] = 0
|
||||
D[i+k] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
sortLMS2_byte(T, SA, C, B, D, n, k)
|
||||
name = postProcLMS2_byte(SA, n, m)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sortLMS1_byte(T, SA, C, B, n, k)
|
||||
name = postProcLMS1_byte(T, SA, n, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if m == 1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = j + 1
|
||||
name = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 2: Solve the reduced problem.
|
||||
// Recurse if names are not yet unique.
|
||||
if name < m {
|
||||
newfs = n + fs - 2*m
|
||||
if flags&(1|4|8) == 0 {
|
||||
if k+name <= newfs {
|
||||
newfs -= k
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flags |= 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
RA = SA[m+newfs:]
|
||||
for i, j = m+(n>>1)-1, m-1; m <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if SA[i] != 0 {
|
||||
RA[j] = SA[i] - 1
|
||||
j--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
computeSA_int(RA, SA, newfs, m, name)
|
||||
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = m - 1
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
RA[j] = i + 1
|
||||
j--
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = 0; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = RA[SA[i]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&4 > 0 {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
C = B
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&2 > 0 {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 3: Induce the result for the original problem.
|
||||
if flags&8 > 0 {
|
||||
getCounts_byte(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Put all left-most S characters into their buckets.
|
||||
if m > 1 {
|
||||
getBuckets_byte(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
i = m - 1
|
||||
j = n
|
||||
p = SA[m-1]
|
||||
c1 = int(T[p])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c0 = c1
|
||||
q = B[c0]
|
||||
for q < j {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = p
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
p = SA[i]
|
||||
if c1 = int(T[p]); c1 != c0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
induceSA_byte(T, SA, C, B, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
661
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/sais_int.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
661
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/internal/sais/sais_int.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,661 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Code generated by sais_gen.go. DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2008-2010 Yuta Mori All Rights Reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
|
||||
// obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation
|
||||
// files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without
|
||||
// restriction, including without limitation the rights to use,
|
||||
// copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the
|
||||
// Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following
|
||||
// conditions:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
|
||||
// included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
|
||||
// EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
|
||||
// OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
|
||||
// NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
|
||||
// HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
|
||||
// WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
|
||||
// FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
|
||||
// OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
package sais
|
||||
|
||||
func getCounts_int(T []int, C []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var i int
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
C[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
C[T[i]]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getBuckets_int(C, B []int, k int, end bool) {
|
||||
var i, sum int
|
||||
if end {
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
sum += C[i]
|
||||
B[i] = sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for i = 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
sum += C[i]
|
||||
B[i] = sum - C[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sortLMS1_int(T []int, SA, C, B []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
} else if j < 0 {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i = n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) > c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^(j + 1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func postProcLMS1_int(T []int, SA []int, n, m int) int {
|
||||
var i, j, p, q, plen, qlen, name int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
var diff bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Compact all the sorted substrings into the first m items of SA.
|
||||
// 2*m must be not larger than n (provable).
|
||||
for i = 0; SA[i] < 0; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^SA[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < m {
|
||||
for j, i = i, i+1; ; i++ {
|
||||
if p = SA[i]; p < 0 {
|
||||
SA[j] = ^p
|
||||
j++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
if j == m {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Store the length of all substrings.
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
SA[m+((i+1)>>1)] = j - i
|
||||
j = i + 1
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the lexicographic names of all substrings.
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
qlen = 0
|
||||
for i, q = 0, n; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
p = SA[i]
|
||||
plen = SA[m+(p>>1)]
|
||||
diff = true
|
||||
if (plen == qlen) && ((q + plen) < n) {
|
||||
for j = 0; (j < plen) && (T[p+j] == T[q+j]); j++ {
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j == plen {
|
||||
diff = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if diff {
|
||||
name++
|
||||
q = p
|
||||
qlen = plen
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[m+(p>>1)] = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sortLMS2_int(T []int, SA, C, B, D []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j, t, d int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
t = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i, d = 0, 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
d += 1
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
t = int(c0) << 1
|
||||
if int(T[j]) < c1 {
|
||||
t |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if D[t] != d {
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
D[t] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
} else if j < 0 {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = n - 1; 0 <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if SA[i] > 0 {
|
||||
if SA[i] < n {
|
||||
SA[i] += n
|
||||
for j = i - 1; SA[j] < n; j-- {
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[j] -= n
|
||||
i = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i, d = n-1, d+1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
d += 1
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
t = int(c0) << 1
|
||||
if int(T[j]) > c1 {
|
||||
t |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if D[t] != d {
|
||||
j += n
|
||||
D[t] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if t&1 > 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^(j + 1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func postProcLMS2_int(SA []int, n, m int) int {
|
||||
var i, j, d, name int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compact all the sorted LMS substrings into the first m items of SA.
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
for i = 0; SA[i] < 0; i++ {
|
||||
j = ^SA[i]
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
name += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[i] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < m {
|
||||
for d, i = i, i+1; ; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j < 0 {
|
||||
j = ^j
|
||||
if n <= j {
|
||||
name += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[d] = j
|
||||
d++
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
if d == m {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name < m {
|
||||
// Store the lexicographic names.
|
||||
for i, d = m-1, name+1; 0 <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; n <= j {
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
d--
|
||||
}
|
||||
SA[m+(j>>1)] = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Unset flags.
|
||||
for i = 0; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; n <= j {
|
||||
j -= n
|
||||
SA[i] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func induceSA_int(T []int, SA, C, B []int, n, k int) {
|
||||
var b, i, j int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAl.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, false) // Find starts of buckets
|
||||
j = n - 1
|
||||
c1 = int(T[j])
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
if j > 0 && int(T[j-1]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
j = SA[i]
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
if j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j > 0 && int(T[j-1]) < c1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
b++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute SAs.
|
||||
if &C[0] == &B[0] {
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
c1 = 0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
for i = n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if j = SA[i]; j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[j]); c0 != c1 {
|
||||
B[c1] = b
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
b--
|
||||
if (j == 0) || (int(T[j-1]) > c1) {
|
||||
SA[b] = ^j
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
SA[i] = ^j
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func computeSA_int(T []int, SA []int, fs, n, k int) {
|
||||
const (
|
||||
minBucketSize = 512
|
||||
sortLMS2Limit = 0x3fffffff
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var C, B, D, RA []int
|
||||
var bo int // Offset of B relative to SA
|
||||
var b, i, j, m, p, q, name, newfs int
|
||||
var c0, c1 int
|
||||
var flags uint
|
||||
|
||||
if k <= minBucketSize {
|
||||
C = make([]int, k)
|
||||
if k <= fs {
|
||||
bo = n + fs - k
|
||||
B = SA[bo:]
|
||||
flags = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
flags = 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if k <= fs {
|
||||
C = SA[n+fs-k:]
|
||||
if k <= fs-k {
|
||||
bo = n + fs - 2*k
|
||||
B = SA[bo:]
|
||||
flags = 0
|
||||
} else if k <= 4*minBucketSize {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
flags = 2
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
B = C
|
||||
flags = 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
C = make([]int, k)
|
||||
B = C
|
||||
flags = 4 | 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n <= sortLMS2Limit && 2 <= (n/k) {
|
||||
if flags&1 > 0 {
|
||||
if 2*k <= fs-k {
|
||||
flags |= 32
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flags |= 16
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if flags == 0 && 2*k <= (fs-2*k) {
|
||||
flags |= 32
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 1: Reduce the problem by at least 1/2.
|
||||
// Sort all the LMS-substrings.
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
for i = 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
b = -1
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = n
|
||||
m = 0
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
if b >= 0 {
|
||||
SA[b] = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
B[c1]--
|
||||
b = B[c1]
|
||||
j = i
|
||||
m++
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if m > 1 {
|
||||
if flags&(16|32) > 0 {
|
||||
if flags&16 > 0 {
|
||||
D = make([]int, 2*k)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
D = SA[bo-2*k:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
B[T[j+1]]++
|
||||
for i, j = 0, 0; i < k; i++ {
|
||||
j += C[i]
|
||||
if B[i] != j {
|
||||
SA[B[i]] += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
D[i] = 0
|
||||
D[i+k] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
sortLMS2_int(T, SA, C, B, D, n, k)
|
||||
name = postProcLMS2_int(SA, n, m)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sortLMS1_int(T, SA, C, B, n, k)
|
||||
name = postProcLMS1_int(T, SA, n, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if m == 1 {
|
||||
SA[b] = j + 1
|
||||
name = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
name = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 2: Solve the reduced problem.
|
||||
// Recurse if names are not yet unique.
|
||||
if name < m {
|
||||
newfs = n + fs - 2*m
|
||||
if flags&(1|4|8) == 0 {
|
||||
if k+name <= newfs {
|
||||
newfs -= k
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flags |= 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
RA = SA[m+newfs:]
|
||||
for i, j = m+(n>>1)-1, m-1; m <= i; i-- {
|
||||
if SA[i] != 0 {
|
||||
RA[j] = SA[i] - 1
|
||||
j--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
computeSA_int(RA, SA, newfs, m, name)
|
||||
|
||||
i = n - 1
|
||||
j = m - 1
|
||||
c0 = int(T[n-1])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 > c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
RA[j] = i + 1
|
||||
j--
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c1 = c0
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c0 = int(T[i]); c0 < c1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i = 0; i < m; i++ {
|
||||
SA[i] = RA[SA[i]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&4 > 0 {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
C = B
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&2 > 0 {
|
||||
B = make([]int, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stage 3: Induce the result for the original problem.
|
||||
if flags&8 > 0 {
|
||||
getCounts_int(T, C, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Put all left-most S characters into their buckets.
|
||||
if m > 1 {
|
||||
getBuckets_int(C, B, k, true) // Find ends of buckets
|
||||
i = m - 1
|
||||
j = n
|
||||
p = SA[m-1]
|
||||
c1 = int(T[p])
|
||||
for {
|
||||
c0 = c1
|
||||
q = B[c0]
|
||||
for q < j {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = p
|
||||
if i--; i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
p = SA[i]
|
||||
if c1 = int(T[p]); c1 != c0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j > 0 {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
SA[j] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
induceSA_int(T, SA, C, B, n, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
131
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/mtf_rle2.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
131
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/mtf_rle2.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
|
||||
// moveToFront implements both the MTF and RLE stages of bzip2 at the same time.
|
||||
// Any runs of zeros in the encoded output will be replaced by a sequence of
|
||||
// RUNA and RUNB symbols are encode the length of the run.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The RLE encoding used can actually be encoded to and decoded from using
|
||||
// normal two's complement arithmetic. The methodology for doing so is below.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Assuming the following:
|
||||
// num: The value being encoded by RLE encoding.
|
||||
// run: A sequence of RUNA and RUNB symbols represented as a binary integer,
|
||||
// where RUNA is the 0 bit, RUNB is the 1 bit, and least-significant RUN
|
||||
// symbols are at the least-significant bit positions.
|
||||
// cnt: The number of RUNA and RUNB symbols.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Then the RLE encoding used by bzip2 has this mathematical property:
|
||||
// num+1 == (1<<cnt) | run
|
||||
type moveToFront struct {
|
||||
dictBuf [256]uint8
|
||||
dictLen int
|
||||
|
||||
vals []byte
|
||||
syms []uint16
|
||||
blkSize int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (mtf *moveToFront) Init(dict []uint8, blkSize int) {
|
||||
if len(dict) > len(mtf.dictBuf) {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Internal, "alphabet too large")
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(mtf.dictBuf[:], dict)
|
||||
mtf.dictLen = len(dict)
|
||||
mtf.blkSize = blkSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (mtf *moveToFront) Encode(vals []byte) (syms []uint16) {
|
||||
dict := mtf.dictBuf[:mtf.dictLen]
|
||||
syms = mtf.syms[:0]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(vals) > mtf.blkSize {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Internal, "exceeded block size")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var lastNum uint32
|
||||
for _, val := range vals {
|
||||
// Normal move-to-front transform.
|
||||
var idx uint8 // Reverse lookup idx in dict
|
||||
for di, dv := range dict {
|
||||
if dv == val {
|
||||
idx = uint8(di)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(dict[1:], dict[:idx])
|
||||
dict[0] = val
|
||||
|
||||
// Run-length encoding augmentation.
|
||||
if idx == 0 {
|
||||
lastNum++
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lastNum > 0 {
|
||||
for rc := lastNum + 1; rc != 1; rc >>= 1 {
|
||||
syms = append(syms, uint16(rc&1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastNum = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
syms = append(syms, uint16(idx)+1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lastNum > 0 {
|
||||
for rc := lastNum + 1; rc != 1; rc >>= 1 {
|
||||
syms = append(syms, uint16(rc&1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
mtf.syms = syms
|
||||
return syms
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (mtf *moveToFront) Decode(syms []uint16) (vals []byte) {
|
||||
dict := mtf.dictBuf[:mtf.dictLen]
|
||||
vals = mtf.vals[:0]
|
||||
|
||||
var lastCnt uint
|
||||
var lastRun uint32
|
||||
for _, sym := range syms {
|
||||
// Run-length encoding augmentation.
|
||||
if sym < 2 {
|
||||
lastRun |= uint32(sym) << lastCnt
|
||||
lastCnt++
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lastCnt > 0 {
|
||||
cnt := int((1<<lastCnt)|lastRun) - 1
|
||||
if len(vals)+cnt > mtf.blkSize || lastCnt > 24 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "run-length decoding exceeded block size")
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := cnt; i > 0; i-- {
|
||||
vals = append(vals, dict[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastCnt, lastRun = 0, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Normal move-to-front transform.
|
||||
val := dict[sym-1] // Forward lookup val in dict
|
||||
copy(dict[1:], dict[:sym-1])
|
||||
dict[0] = val
|
||||
|
||||
if len(vals) >= mtf.blkSize {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "run-length decoding exceeded block size")
|
||||
}
|
||||
vals = append(vals, val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lastCnt > 0 {
|
||||
cnt := int((1<<lastCnt)|lastRun) - 1
|
||||
if len(vals)+cnt > mtf.blkSize || lastCnt > 24 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "run-length decoding exceeded block size")
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := cnt; i > 0; i-- {
|
||||
vals = append(vals, dict[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
mtf.vals = vals
|
||||
return vals
|
||||
}
|
||||
374
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/prefix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
374
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/prefix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,374 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
minNumTrees = 2
|
||||
maxNumTrees = 6
|
||||
|
||||
maxPrefixBits = 20 // Maximum bit-width of a prefix code
|
||||
maxNumSyms = 256 + 2 // Maximum number of symbols in the alphabet
|
||||
numBlockSyms = 50 // Number of bytes in a block
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// encSel and decSel are used to handle the prefix encoding for tree selectors.
|
||||
// The prefix encoding is as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Code TreeIdx
|
||||
// 0 <=> 0
|
||||
// 10 <=> 1
|
||||
// 110 <=> 2
|
||||
// 1110 <=> 3
|
||||
// 11110 <=> 4
|
||||
// 111110 <=> 5
|
||||
// 111111 <=> 6 Invalid tree index, so should fail
|
||||
//
|
||||
var encSel, decSel = func() (e prefix.Encoder, d prefix.Decoder) {
|
||||
var selCodes [maxNumTrees + 1]prefix.PrefixCode
|
||||
for i := range selCodes {
|
||||
selCodes[i] = prefix.PrefixCode{Sym: uint32(i), Len: uint32(i + 1)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
selCodes[maxNumTrees] = prefix.PrefixCode{Sym: maxNumTrees, Len: maxNumTrees}
|
||||
prefix.GeneratePrefixes(selCodes[:])
|
||||
e.Init(selCodes[:])
|
||||
d.Init(selCodes[:])
|
||||
return
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
type prefixReader struct{ prefix.Reader }
|
||||
|
||||
func (pr *prefixReader) Init(r io.Reader) {
|
||||
pr.Reader.Init(r, true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pr *prefixReader) ReadBitsBE64(nb uint) uint64 {
|
||||
if nb <= 32 {
|
||||
v := uint32(pr.ReadBits(nb))
|
||||
return uint64(internal.ReverseUint32N(v, nb))
|
||||
}
|
||||
v0 := internal.ReverseUint32(uint32(pr.ReadBits(32)))
|
||||
v1 := internal.ReverseUint32(uint32(pr.ReadBits(nb - 32)))
|
||||
v := uint64(v0)<<32 | uint64(v1)
|
||||
return v >> (64 - nb)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pr *prefixReader) ReadPrefixCodes(codes []prefix.PrefixCodes, trees []prefix.Decoder) {
|
||||
for i, pc := range codes {
|
||||
clen := int(pr.ReadBitsBE64(5))
|
||||
sum := 1 << maxPrefixBits
|
||||
for sym := range pc {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if clen < 1 || clen > maxPrefixBits {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid prefix bit-length: %d", clen)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b, ok := pr.TryReadBits(1)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
b = pr.ReadBits(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b, ok = pr.TryReadBits(1)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
b = pr.ReadBits(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
clen -= int(b*2) - 1 // +1 or -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc[sym] = prefix.PrefixCode{Sym: uint32(sym), Len: uint32(clen)}
|
||||
sum -= (1 << maxPrefixBits) >> uint(clen)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if sum == 0 {
|
||||
// Fast path, but only handles complete trees.
|
||||
if err := prefix.GeneratePrefixes(pc); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err) // Using complete trees; should never fail
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Slow path, but handles anything.
|
||||
pc = handleDegenerateCodes(pc) // Never fails, but may fail later
|
||||
codes[i] = pc
|
||||
}
|
||||
trees[i].Init(pc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type prefixWriter struct{ prefix.Writer }
|
||||
|
||||
func (pw *prefixWriter) Init(w io.Writer) {
|
||||
pw.Writer.Init(w, true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pw *prefixWriter) WriteBitsBE64(v uint64, nb uint) {
|
||||
if nb <= 32 {
|
||||
v := internal.ReverseUint32N(uint32(v), nb)
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(uint(v), nb)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
v <<= (64 - nb)
|
||||
v0 := internal.ReverseUint32(uint32(v >> 32))
|
||||
v1 := internal.ReverseUint32(uint32(v))
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(uint(v0), 32)
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(uint(v1), nb-32)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pw *prefixWriter) WritePrefixCodes(codes []prefix.PrefixCodes, trees []prefix.Encoder) {
|
||||
for i, pc := range codes {
|
||||
if err := prefix.GeneratePrefixes(pc); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err) // Using complete trees; should never fail
|
||||
}
|
||||
trees[i].Init(pc)
|
||||
|
||||
clen := int(pc[0].Len)
|
||||
pw.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(clen), 5)
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
for int(c.Len) < clen {
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(3, 2) // 11
|
||||
clen--
|
||||
}
|
||||
for int(c.Len) > clen {
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(1, 2) // 10
|
||||
clen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(0, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// handleDegenerateCodes converts a degenerate tree into a canonical tree.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, when the input is an under-subscribed tree:
|
||||
// input: []PrefixCode{
|
||||
// {Sym: 0, Len: 3},
|
||||
// {Sym: 1, Len: 4},
|
||||
// {Sym: 2, Len: 3},
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// output: []PrefixCode{
|
||||
// {Sym: 0, Len: 3, Val: 0}, // 000
|
||||
// {Sym: 1, Len: 4, Val: 2}, // 0010
|
||||
// {Sym: 2, Len: 3, Val: 4}, // 100
|
||||
// {Sym: 258, Len: 4, Val: 10}, // 1010
|
||||
// {Sym: 259, Len: 3, Val: 6}, // 110
|
||||
// {Sym: 260, Len: 1, Val: 1}, // 1
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, when the input is an over-subscribed tree:
|
||||
// input: []PrefixCode{
|
||||
// {Sym: 0, Len: 1},
|
||||
// {Sym: 1, Len: 3},
|
||||
// {Sym: 2, Len: 4},
|
||||
// {Sym: 3, Len: 3},
|
||||
// {Sym: 4, Len: 2},
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// output: []PrefixCode{
|
||||
// {Sym: 0, Len: 1, Val: 0}, // 0
|
||||
// {Sym: 1, Len: 3, Val: 3}, // 011
|
||||
// {Sym: 3, Len: 3, Val: 7}, // 111
|
||||
// {Sym: 4, Len: 2, Val: 1}, // 01
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func handleDegenerateCodes(codes prefix.PrefixCodes) prefix.PrefixCodes {
|
||||
// Since there is no formal definition for the BZip2 format, there is no
|
||||
// specification that says that the code lengths must form a complete
|
||||
// prefix tree (IE: it is neither over-subscribed nor under-subscribed).
|
||||
// Thus, the original C implementation becomes the reference for how prefix
|
||||
// decoding is done in these edge cases. Unfortunately, the C version does
|
||||
// not error when an invalid tree is used, but rather allows decoding to
|
||||
// continue and only errors if some bit pattern happens to cause an error.
|
||||
// Thus, it is possible for an invalid tree to end up decoding an input
|
||||
// "properly" so long as invalid bit patterns are not present. In order to
|
||||
// replicate this non-specified behavior, we use a ported version of the
|
||||
// C code to generate the codes as a valid canonical tree by substituting
|
||||
// invalid nodes with invalid symbols.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
// This program, "bzip2", the associated library "libbzip2", and all
|
||||
// documentation, are copyright (C) 1996-2010 Julian R Seward. All
|
||||
// rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
|
||||
// are met:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 2. The origin of this software must not be misrepresented; you must
|
||||
// not claim that you wrote the original software. If you use this
|
||||
// software in a product, an acknowledgment in the product
|
||||
// documentation would be appreciated but is not required.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 3. Altered source versions must be plainly marked as such, and must
|
||||
// not be misrepresented as being the original software.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 4. The name of the author may not be used to endorse or promote
|
||||
// products derived from this software without specific prior written
|
||||
// permission.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS
|
||||
// OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
|
||||
// WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
|
||||
// ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY
|
||||
// DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
|
||||
// DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE
|
||||
// GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
|
||||
// INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
|
||||
// WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
|
||||
// NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
|
||||
// SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Julian Seward, jseward@bzip.org
|
||||
// bzip2/libbzip2 version 1.0.6 of 6 September 2010
|
||||
// ====================================================
|
||||
var (
|
||||
limits [maxPrefixBits + 2]int32
|
||||
bases [maxPrefixBits + 2]int32
|
||||
perms [maxNumSyms]int32
|
||||
|
||||
minLen = uint32(maxPrefixBits)
|
||||
maxLen = uint32(0)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
statusOkay = iota
|
||||
statusInvalid
|
||||
statusNeedBits
|
||||
statusMaxBits
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// createTables is the BZ2_hbCreateDecodeTables function from the C code.
|
||||
createTables := func(codes []prefix.PrefixCode) {
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
if c.Len > maxLen {
|
||||
maxLen = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c.Len < minLen {
|
||||
minLen = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var pp int
|
||||
for i := minLen; i <= maxLen; i++ {
|
||||
for j, c := range codes {
|
||||
if c.Len == i {
|
||||
perms[pp] = int32(j)
|
||||
pp++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var vec int32
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
bases[c.Len+1]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 1; i < len(bases); i++ {
|
||||
bases[i] += bases[i-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := minLen; i <= maxLen; i++ {
|
||||
vec += bases[i+1] - bases[i]
|
||||
limits[i] = vec - 1
|
||||
vec <<= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := minLen + 1; i <= maxLen; i++ {
|
||||
bases[i] = ((limits[i-1] + 1) << 1) - bases[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getSymbol is the GET_MTF_VAL macro from the C code.
|
||||
getSymbol := func(c prefix.PrefixCode) (uint32, int) {
|
||||
v := internal.ReverseUint32(c.Val)
|
||||
n := c.Len
|
||||
|
||||
zn := minLen
|
||||
if zn > n {
|
||||
return 0, statusNeedBits
|
||||
}
|
||||
zvec := int32(v >> (32 - zn))
|
||||
v <<= zn
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if zn > maxLen {
|
||||
return 0, statusMaxBits
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zvec <= limits[zn] {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
zn++
|
||||
if zn > n {
|
||||
return 0, statusNeedBits
|
||||
}
|
||||
zvec = (zvec << 1) | int32(v>>31)
|
||||
v <<= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zvec-bases[zn] < 0 || zvec-bases[zn] >= maxNumSyms {
|
||||
return 0, statusInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
return uint32(perms[zvec-bases[zn]]), statusOkay
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 1: Create the prefix trees using the C algorithm.
|
||||
createTables(codes)
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 2: Starting with the shortest bit pattern, explore the whole tree.
|
||||
// If tree is under-subscribed, the worst-case runtime is O(1<<maxLen).
|
||||
// If tree is over-subscribed, the worst-case runtime is O(maxNumSyms).
|
||||
var pcodesArr [2 * maxNumSyms]prefix.PrefixCode
|
||||
pcodes := pcodesArr[:maxNumSyms]
|
||||
var exploreCode func(prefix.PrefixCode) bool
|
||||
exploreCode = func(c prefix.PrefixCode) (term bool) {
|
||||
sym, status := getSymbol(c)
|
||||
switch status {
|
||||
case statusOkay:
|
||||
// This code is valid, so insert it.
|
||||
c.Sym = sym
|
||||
pcodes[sym] = c
|
||||
term = true
|
||||
case statusInvalid:
|
||||
// This code is invalid, so insert an invalid symbol.
|
||||
c.Sym = uint32(len(pcodes))
|
||||
pcodes = append(pcodes, c)
|
||||
term = true
|
||||
case statusNeedBits:
|
||||
// This code is too short, so explore both children.
|
||||
c.Len++
|
||||
c0, c1 := c, c
|
||||
c1.Val |= 1 << (c.Len - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
b0 := exploreCode(c0)
|
||||
b1 := exploreCode(c1)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case !b0 && b1:
|
||||
c0.Sym = uint32(len(pcodes))
|
||||
pcodes = append(pcodes, c0)
|
||||
case !b1 && b0:
|
||||
c1.Sym = uint32(len(pcodes))
|
||||
pcodes = append(pcodes, c1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
term = b0 || b1
|
||||
case statusMaxBits:
|
||||
// This code is too long, so report it upstream.
|
||||
term = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return term // Did this code terminate?
|
||||
}
|
||||
exploreCode(prefix.PrefixCode{})
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 3: Copy new sparse codes to old output codes.
|
||||
codes = codes[:0]
|
||||
for _, c := range pcodes {
|
||||
if c.Len > 0 {
|
||||
codes = append(codes, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return codes
|
||||
}
|
||||
274
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
274
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,274 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Reader struct {
|
||||
InputOffset int64 // Total number of bytes read from underlying io.Reader
|
||||
OutputOffset int64 // Total number of bytes emitted from Read
|
||||
|
||||
rd prefixReader
|
||||
err error
|
||||
level int // The current compression level
|
||||
rdHdrFtr int // Number of times we read the stream header and footer
|
||||
blkCRC uint32 // CRC-32 IEEE of each block (as stored)
|
||||
endCRC uint32 // Checksum of all blocks using bzip2's custom method
|
||||
|
||||
crc crc
|
||||
mtf moveToFront
|
||||
bwt burrowsWheelerTransform
|
||||
rle runLengthEncoding
|
||||
|
||||
// These fields are allocated with Reader and re-used later.
|
||||
treeSels []uint8
|
||||
codes2D [maxNumTrees][maxNumSyms]prefix.PrefixCode
|
||||
codes1D [maxNumTrees]prefix.PrefixCodes
|
||||
trees1D [maxNumTrees]prefix.Decoder
|
||||
syms []uint16
|
||||
|
||||
fuzzReader // Exported functionality when fuzz testing
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type ReaderConfig struct {
|
||||
_ struct{} // Blank field to prevent unkeyed struct literals
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewReader(r io.Reader, conf *ReaderConfig) (*Reader, error) {
|
||||
zr := new(Reader)
|
||||
zr.Reset(r)
|
||||
return zr, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zr *Reader) Reset(r io.Reader) error {
|
||||
*zr = Reader{
|
||||
rd: zr.rd,
|
||||
|
||||
mtf: zr.mtf,
|
||||
bwt: zr.bwt,
|
||||
rle: zr.rle,
|
||||
|
||||
treeSels: zr.treeSels,
|
||||
trees1D: zr.trees1D,
|
||||
syms: zr.syms,
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.rd.Init(r)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zr *Reader) Read(buf []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
cnt, err := zr.rle.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != rleDone && zr.err == nil {
|
||||
zr.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cnt > 0 {
|
||||
zr.crc.update(buf[:cnt])
|
||||
zr.OutputOffset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
return cnt, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zr.err != nil || len(buf) == 0 {
|
||||
return 0, zr.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read the next chunk.
|
||||
zr.rd.Offset = zr.InputOffset
|
||||
func() {
|
||||
defer errors.Recover(&zr.err)
|
||||
if zr.rdHdrFtr%2 == 0 {
|
||||
// Check if we are already at EOF.
|
||||
if err := zr.rd.PullBits(1); err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.ErrUnexpectedEOF && zr.rdHdrFtr > 0 {
|
||||
err = io.EOF // EOF is okay if we read at least one stream
|
||||
}
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read stream header.
|
||||
if zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(16) != hdrMagic {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid stream magic")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ver := zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(8); ver != 'h' {
|
||||
if ver == '0' {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Deprecated, "bzip1 format is not supported")
|
||||
}
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid version: %q", ver)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lvl := int(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(8)) - '0'
|
||||
if lvl < BestSpeed || lvl > BestCompression {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid block size: %d", lvl*blockSize)
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.level = lvl
|
||||
zr.rdHdrFtr++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Check and update the CRC.
|
||||
if internal.GoFuzz {
|
||||
zr.updateChecksum(-1, zr.crc.val) // Update with value
|
||||
zr.blkCRC = zr.crc.val // Suppress CRC failures
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zr.blkCRC != zr.crc.val {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "mismatching block checksum")
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.endCRC = (zr.endCRC<<1 | zr.endCRC>>31) ^ zr.blkCRC
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf := zr.decodeBlock()
|
||||
zr.rle.Init(buf)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
if zr.InputOffset, err = zr.rd.Flush(); zr.err == nil {
|
||||
zr.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zr.err != nil {
|
||||
zr.err = errWrap(zr.err, errors.Corrupted)
|
||||
return 0, zr.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zr *Reader) Close() error {
|
||||
if zr.err == io.EOF || zr.err == errClosed {
|
||||
zr.rle.Init(nil) // Make sure future reads fail
|
||||
zr.err = errClosed
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return zr.err // Return the persistent error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zr *Reader) decodeBlock() []byte {
|
||||
if magic := zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(48); magic != blkMagic {
|
||||
if magic == endMagic {
|
||||
endCRC := uint32(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(32))
|
||||
if internal.GoFuzz {
|
||||
zr.updateChecksum(zr.rd.BitsRead()-32, zr.endCRC)
|
||||
endCRC = zr.endCRC // Suppress CRC failures
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zr.endCRC != endCRC {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "mismatching stream checksum")
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.endCRC = 0
|
||||
zr.rd.ReadPads()
|
||||
zr.rdHdrFtr++
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid block or footer magic")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
zr.crc.val = 0
|
||||
zr.blkCRC = uint32(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(32))
|
||||
if internal.GoFuzz {
|
||||
zr.updateChecksum(zr.rd.BitsRead()-32, 0) // Record offset only
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(1) != 0 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Deprecated, "block randomization is not supported")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read BWT related fields.
|
||||
ptr := int(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(24)) // BWT origin pointer
|
||||
|
||||
// Read MTF related fields.
|
||||
var dictArr [256]uint8
|
||||
dict := dictArr[:0]
|
||||
bmapHi := uint16(zr.rd.ReadBits(16))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 256; i, bmapHi = i+16, bmapHi>>1 {
|
||||
if bmapHi&1 > 0 {
|
||||
bmapLo := uint16(zr.rd.ReadBits(16))
|
||||
for j := 0; j < 16; j, bmapLo = j+1, bmapLo>>1 {
|
||||
if bmapLo&1 > 0 {
|
||||
dict = append(dict, uint8(i+j))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 1: Prefix encoding.
|
||||
syms := zr.decodePrefix(len(dict))
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 2: Move-to-front transform and run-length encoding.
|
||||
zr.mtf.Init(dict, zr.level*blockSize)
|
||||
buf := zr.mtf.Decode(syms)
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 3: Burrows-Wheeler transformation.
|
||||
if ptr >= len(buf) {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "origin pointer (0x%06x) exceeds block size: %d", ptr, len(buf))
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.bwt.Decode(buf, ptr)
|
||||
|
||||
return buf
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zr *Reader) decodePrefix(numSyms int) (syms []uint16) {
|
||||
numSyms += 2 // Remove 0 symbol, add RUNA, RUNB, and EOF symbols
|
||||
if numSyms < 3 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "not enough prefix symbols: %d", numSyms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read information about the trees and tree selectors.
|
||||
var mtf internal.MoveToFront
|
||||
numTrees := int(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(3))
|
||||
if numTrees < minNumTrees || numTrees > maxNumTrees {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid number of prefix trees: %d", numTrees)
|
||||
}
|
||||
numSels := int(zr.rd.ReadBitsBE64(15))
|
||||
if cap(zr.treeSels) < numSels {
|
||||
zr.treeSels = make([]uint8, numSels)
|
||||
}
|
||||
treeSels := zr.treeSels[:numSels]
|
||||
for i := range treeSels {
|
||||
sym, ok := zr.rd.TryReadSymbol(&decSel)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
sym = zr.rd.ReadSymbol(&decSel)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if int(sym) >= numTrees {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid prefix tree selector: %d", sym)
|
||||
}
|
||||
treeSels[i] = uint8(sym)
|
||||
}
|
||||
mtf.Decode(treeSels)
|
||||
zr.treeSels = treeSels
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize prefix codes.
|
||||
for i := range zr.codes2D[:numTrees] {
|
||||
zr.codes1D[i] = zr.codes2D[i][:numSyms]
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.rd.ReadPrefixCodes(zr.codes1D[:numTrees], zr.trees1D[:numTrees])
|
||||
|
||||
// Read prefix encoded symbols of compressed data.
|
||||
var tree *prefix.Decoder
|
||||
var blkLen, selIdx int
|
||||
syms = zr.syms[:0]
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if blkLen == 0 {
|
||||
blkLen = numBlockSyms
|
||||
if selIdx >= len(treeSels) {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "not enough prefix tree selectors")
|
||||
}
|
||||
tree = &zr.trees1D[treeSels[selIdx]]
|
||||
selIdx++
|
||||
}
|
||||
blkLen--
|
||||
sym, ok := zr.rd.TryReadSymbol(tree)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
sym = zr.rd.ReadSymbol(tree)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if int(sym) == numSyms-1 {
|
||||
break // EOF marker
|
||||
}
|
||||
if int(sym) >= numSyms {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "invalid prefix symbol: %d", sym)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(syms) >= zr.level*blockSize {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Corrupted, "number of prefix symbols exceeds block size")
|
||||
}
|
||||
syms = append(syms, uint16(sym))
|
||||
}
|
||||
zr.syms = syms
|
||||
return syms
|
||||
}
|
||||
101
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/rle1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
101
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/rle1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
|
||||
// rleDone is a special "error" to indicate that the RLE stage is done.
|
||||
var rleDone = errorf(errors.Unknown, "RLE1 stage is completed")
|
||||
|
||||
// runLengthEncoding implements the first RLE stage of bzip2. Every sequence
|
||||
// of 4..255 duplicated bytes is replaced by only the first 4 bytes, and a
|
||||
// single byte representing the repeat length. Similar to the C bzip2
|
||||
// implementation, the encoder will always terminate repeat sequences with a
|
||||
// count (even if it is the end of the buffer), and it will also never produce
|
||||
// run lengths of 256..259. The decoder can handle the latter case.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, if the input was:
|
||||
// input: "AAAAAAABBBBCCCD"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Then the output will be:
|
||||
// output: "AAAA\x03BBBB\x00CCCD"
|
||||
type runLengthEncoding struct {
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
idx int
|
||||
lastVal byte
|
||||
lastCnt int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rle *runLengthEncoding) Init(buf []byte) {
|
||||
*rle = runLengthEncoding{buf: buf}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rle *runLengthEncoding) Write(buf []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
for i, b := range buf {
|
||||
if rle.lastVal != b {
|
||||
rle.lastCnt = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.lastCnt++
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case rle.lastCnt < 4:
|
||||
if rle.idx >= len(rle.buf) {
|
||||
return i, rleDone
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.buf[rle.idx] = b
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
case rle.lastCnt == 4:
|
||||
if rle.idx+1 >= len(rle.buf) {
|
||||
return i, rleDone
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.buf[rle.idx] = b
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
rle.buf[rle.idx] = 0
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
case rle.lastCnt < 256:
|
||||
rle.buf[rle.idx-1]++
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if rle.idx >= len(rle.buf) {
|
||||
return i, rleDone
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.lastCnt = 1
|
||||
rle.buf[rle.idx] = b
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.lastVal = b
|
||||
}
|
||||
return len(buf), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rle *runLengthEncoding) Read(buf []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
for i := range buf {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case rle.lastCnt == -4:
|
||||
if rle.idx >= len(rle.buf) {
|
||||
return i, errorf(errors.Corrupted, "missing terminating run-length repeater")
|
||||
}
|
||||
rle.lastCnt = int(rle.buf[rle.idx])
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
if rle.lastCnt > 0 {
|
||||
break // Break the switch
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough // Count was zero, continue the work
|
||||
case rle.lastCnt <= 0:
|
||||
if rle.idx >= len(rle.buf) {
|
||||
return i, rleDone
|
||||
}
|
||||
b := rle.buf[rle.idx]
|
||||
rle.idx++
|
||||
if b != rle.lastVal {
|
||||
rle.lastCnt = 0
|
||||
rle.lastVal = b
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf[i] = rle.lastVal
|
||||
rle.lastCnt--
|
||||
}
|
||||
return len(buf), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rle *runLengthEncoding) Bytes() []byte { return rle.buf[:rle.idx] }
|
||||
307
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/writer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
307
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2/writer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package bzip2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Writer struct {
|
||||
InputOffset int64 // Total number of bytes issued to Write
|
||||
OutputOffset int64 // Total number of bytes written to underlying io.Writer
|
||||
|
||||
wr prefixWriter
|
||||
err error
|
||||
level int // The current compression level
|
||||
wrHdr bool // Have we written the stream header?
|
||||
blkCRC uint32 // CRC-32 IEEE of each block
|
||||
endCRC uint32 // Checksum of all blocks using bzip2's custom method
|
||||
|
||||
crc crc
|
||||
rle runLengthEncoding
|
||||
bwt burrowsWheelerTransform
|
||||
mtf moveToFront
|
||||
|
||||
// These fields are allocated with Writer and re-used later.
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
treeSels []uint8
|
||||
treeSelsMTF []uint8
|
||||
codes2D [maxNumTrees][maxNumSyms]prefix.PrefixCode
|
||||
codes1D [maxNumTrees]prefix.PrefixCodes
|
||||
trees1D [maxNumTrees]prefix.Encoder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type WriterConfig struct {
|
||||
Level int
|
||||
|
||||
_ struct{} // Blank field to prevent unkeyed struct literals
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewWriter(w io.Writer, conf *WriterConfig) (*Writer, error) {
|
||||
var lvl int
|
||||
if conf != nil {
|
||||
lvl = conf.Level
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lvl == 0 {
|
||||
lvl = DefaultCompression
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lvl < BestSpeed || lvl > BestCompression {
|
||||
return nil, errorf(errors.Invalid, "compression level: %d", lvl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw := new(Writer)
|
||||
zw.level = lvl
|
||||
zw.Reset(w)
|
||||
return zw, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) Reset(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
*zw = Writer{
|
||||
wr: zw.wr,
|
||||
level: zw.level,
|
||||
|
||||
rle: zw.rle,
|
||||
bwt: zw.bwt,
|
||||
mtf: zw.mtf,
|
||||
|
||||
buf: zw.buf,
|
||||
treeSels: zw.treeSels,
|
||||
treeSelsMTF: zw.treeSelsMTF,
|
||||
trees1D: zw.trees1D,
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.wr.Init(w)
|
||||
if len(zw.buf) != zw.level*blockSize {
|
||||
zw.buf = make([]byte, zw.level*blockSize)
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.rle.Init(zw.buf)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) Write(buf []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
if zw.err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, zw.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cnt := len(buf)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
wrCnt, err := zw.rle.Write(buf)
|
||||
if err != rleDone && zw.err == nil {
|
||||
zw.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.crc.update(buf[:wrCnt])
|
||||
buf = buf[wrCnt:]
|
||||
if len(buf) == 0 {
|
||||
zw.InputOffset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
return cnt, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zw.err = zw.flush(); zw.err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, zw.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) flush() error {
|
||||
vals := zw.rle.Bytes()
|
||||
if len(vals) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.wr.Offset = zw.OutputOffset
|
||||
func() {
|
||||
defer errors.Recover(&zw.err)
|
||||
if !zw.wrHdr {
|
||||
// Write stream header.
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(hdrMagic, 16)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64('h', 8)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64('0'+zw.level), 8)
|
||||
zw.wrHdr = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.encodeBlock(vals)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if zw.OutputOffset, err = zw.wr.Flush(); zw.err == nil {
|
||||
zw.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zw.err != nil {
|
||||
zw.err = errWrap(zw.err, errors.Internal)
|
||||
return zw.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.endCRC = (zw.endCRC<<1 | zw.endCRC>>31) ^ zw.blkCRC
|
||||
zw.blkCRC = 0
|
||||
zw.rle.Init(zw.buf)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) Close() error {
|
||||
if zw.err == errClosed {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flush RLE buffer if there is left-over data.
|
||||
if zw.err = zw.flush(); zw.err != nil {
|
||||
return zw.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write stream footer.
|
||||
zw.wr.Offset = zw.OutputOffset
|
||||
func() {
|
||||
defer errors.Recover(&zw.err)
|
||||
if !zw.wrHdr {
|
||||
// Write stream header.
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(hdrMagic, 16)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64('h', 8)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64('0'+zw.level), 8)
|
||||
zw.wrHdr = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(endMagic, 48)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(zw.endCRC), 32)
|
||||
zw.wr.WritePads(0)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if zw.OutputOffset, err = zw.wr.Flush(); zw.err == nil {
|
||||
zw.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if zw.err != nil {
|
||||
zw.err = errWrap(zw.err, errors.Internal)
|
||||
return zw.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
zw.err = errClosed
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) encodeBlock(buf []byte) {
|
||||
zw.blkCRC = zw.crc.val
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(blkMagic, 48)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(zw.blkCRC), 32)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(0, 1)
|
||||
zw.crc.val = 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 1: Burrows-Wheeler transformation.
|
||||
ptr := zw.bwt.Encode(buf)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(ptr), 24)
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 2: Move-to-front transform and run-length encoding.
|
||||
var dictMap [256]bool
|
||||
for _, c := range buf {
|
||||
dictMap[c] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var dictArr [256]uint8
|
||||
var bmapLo [16]uint16
|
||||
dict := dictArr[:0]
|
||||
bmapHi := uint16(0)
|
||||
for i, b := range dictMap {
|
||||
if b {
|
||||
c := uint8(i)
|
||||
dict = append(dict, c)
|
||||
bmapHi |= 1 << (c >> 4)
|
||||
bmapLo[c>>4] |= 1 << (c & 0xf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBits(uint(bmapHi), 16)
|
||||
for _, m := range bmapLo {
|
||||
if m > 0 {
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBits(uint(m), 16)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
zw.mtf.Init(dict, len(buf))
|
||||
syms := zw.mtf.Encode(buf)
|
||||
|
||||
// Step 3: Prefix encoding.
|
||||
zw.encodePrefix(syms, len(dict))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zw *Writer) encodePrefix(syms []uint16, numSyms int) {
|
||||
numSyms += 2 // Remove 0 symbol, add RUNA, RUNB, and EOB symbols
|
||||
if numSyms < 3 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Internal, "unable to encode EOB marker")
|
||||
}
|
||||
syms = append(syms, uint16(numSyms-1)) // EOB marker
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute number of prefix trees needed.
|
||||
numTrees := maxNumTrees
|
||||
for i, lim := range []int{200, 600, 1200, 2400} {
|
||||
if len(syms) < lim {
|
||||
numTrees = minNumTrees + i
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute number of block selectors.
|
||||
numSels := (len(syms) + numBlockSyms - 1) / numBlockSyms
|
||||
if cap(zw.treeSels) < numSels {
|
||||
zw.treeSels = make([]uint8, numSels)
|
||||
}
|
||||
treeSels := zw.treeSels[:numSels]
|
||||
for i := range treeSels {
|
||||
treeSels[i] = uint8(i % numTrees)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize prefix codes.
|
||||
for i := range zw.codes2D[:numTrees] {
|
||||
pc := zw.codes2D[i][:numSyms]
|
||||
for j := range pc {
|
||||
pc[j] = prefix.PrefixCode{Sym: uint32(j)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.codes1D[i] = pc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// First cut at assigning prefix trees to each group.
|
||||
var codes prefix.PrefixCodes
|
||||
var blkLen, selIdx int
|
||||
for _, sym := range syms {
|
||||
if blkLen == 0 {
|
||||
blkLen = numBlockSyms
|
||||
codes = zw.codes2D[treeSels[selIdx]][:numSyms]
|
||||
selIdx++
|
||||
}
|
||||
blkLen--
|
||||
codes[sym].Cnt++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(dsnet): Use K-means to cluster groups to each prefix tree.
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate lengths and prefixes based on symbol frequencies.
|
||||
for i := range zw.trees1D[:numTrees] {
|
||||
pc := prefix.PrefixCodes(zw.codes2D[i][:numSyms])
|
||||
pc.SortByCount()
|
||||
if err := prefix.GenerateLengths(pc, maxPrefixBits); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc.SortBySymbol()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write out information about the trees and tree selectors.
|
||||
var mtf internal.MoveToFront
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(numTrees), 3)
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteBitsBE64(uint64(numSels), 15)
|
||||
zw.treeSelsMTF = append(zw.treeSelsMTF[:0], treeSels...)
|
||||
mtf.Encode(zw.treeSelsMTF)
|
||||
for _, sym := range zw.treeSelsMTF {
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteSymbol(uint(sym), &encSel)
|
||||
}
|
||||
zw.wr.WritePrefixCodes(zw.codes1D[:numTrees], zw.trees1D[:numTrees])
|
||||
|
||||
// Write out prefix encoded symbols of compressed data.
|
||||
var tree *prefix.Encoder
|
||||
blkLen, selIdx = 0, 0
|
||||
for _, sym := range syms {
|
||||
if blkLen == 0 {
|
||||
blkLen = numBlockSyms
|
||||
tree = &zw.trees1D[treeSels[selIdx]]
|
||||
selIdx++
|
||||
}
|
||||
blkLen--
|
||||
ok := zw.wr.TryWriteSymbol(uint(sym), tree)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
zw.wr.WriteSymbol(uint(sym), tree)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
107
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
107
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/common.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package internal is a collection of common compression algorithms.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For performance reasons, these packages lack strong error checking and
|
||||
// require that the caller to ensure that strict invariants are kept.
|
||||
package internal
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// IdentityLUT returns the input key itself.
|
||||
IdentityLUT = func() (lut [256]byte) {
|
||||
for i := range lut {
|
||||
lut[i] = uint8(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lut
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseLUT returns the input key with its bits reversed.
|
||||
ReverseLUT = func() (lut [256]byte) {
|
||||
for i := range lut {
|
||||
b := uint8(i)
|
||||
b = (b&0xaa)>>1 | (b&0x55)<<1
|
||||
b = (b&0xcc)>>2 | (b&0x33)<<2
|
||||
b = (b&0xf0)>>4 | (b&0x0f)<<4
|
||||
lut[i] = b
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lut
|
||||
}()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseUint32 reverses all bits of v.
|
||||
func ReverseUint32(v uint32) (x uint32) {
|
||||
x |= uint32(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>0)]) << 24
|
||||
x |= uint32(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>8)]) << 16
|
||||
x |= uint32(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>16)]) << 8
|
||||
x |= uint32(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>24)]) << 0
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseUint32N reverses the lower n bits of v.
|
||||
func ReverseUint32N(v uint32, n uint) (x uint32) {
|
||||
return ReverseUint32(v << (32 - n))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseUint64 reverses all bits of v.
|
||||
func ReverseUint64(v uint64) (x uint64) {
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>0)]) << 56
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>8)]) << 48
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>16)]) << 40
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>24)]) << 32
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>32)]) << 24
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>40)]) << 16
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>48)]) << 8
|
||||
x |= uint64(ReverseLUT[byte(v>>56)]) << 0
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseUint64N reverses the lower n bits of v.
|
||||
func ReverseUint64N(v uint64, n uint) (x uint64) {
|
||||
return ReverseUint64(v << (64 - n))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveToFront is a data structure that allows for more efficient move-to-front
|
||||
// transformations. This specific implementation assumes that the alphabet is
|
||||
// densely packed within 0..255.
|
||||
type MoveToFront struct {
|
||||
dict [256]uint8 // Mapping from indexes to values
|
||||
tail int // Number of tail bytes that are already ordered
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *MoveToFront) Encode(vals []uint8) {
|
||||
copy(m.dict[:], IdentityLUT[:256-m.tail]) // Reset dict to be identity
|
||||
|
||||
var max int
|
||||
for i, val := range vals {
|
||||
var idx uint8 // Reverse lookup idx in dict
|
||||
for di, dv := range m.dict {
|
||||
if dv == val {
|
||||
idx = uint8(di)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
vals[i] = idx
|
||||
|
||||
max |= int(idx)
|
||||
copy(m.dict[1:], m.dict[:idx])
|
||||
m.dict[0] = val
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.tail = 256 - max - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *MoveToFront) Decode(idxs []uint8) {
|
||||
copy(m.dict[:], IdentityLUT[:256-m.tail]) // Reset dict to be identity
|
||||
|
||||
var max int
|
||||
for i, idx := range idxs {
|
||||
val := m.dict[idx] // Forward lookup val in dict
|
||||
idxs[i] = val
|
||||
|
||||
max |= int(idx)
|
||||
copy(m.dict[1:], m.dict[:idx])
|
||||
m.dict[0] = val
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.tail = 256 - max - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/debug.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/debug.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build debug,!gofuzz
|
||||
|
||||
package internal
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Debug = true
|
||||
GoFuzz = false
|
||||
)
|
||||
120
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
120
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package errors implements functions to manipulate compression errors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In idiomatic Go, it is an anti-pattern to use panics as a form of error
|
||||
// reporting in the API. Instead, the expected way to transmit errors is by
|
||||
// returning an error value. Unfortunately, the checking of "err != nil" in
|
||||
// tight loops commonly found in compression causes non-negligible performance
|
||||
// degradation. While this may not be idiomatic, the internal packages of this
|
||||
// repository rely on panics as a normal means to convey errors. In order to
|
||||
// ensure that these panics do not leak across the public API, the public
|
||||
// packages must recover from these panics and present an error value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Panic and Recover functions in this package provide a safe way to
|
||||
// recover from errors only generated from within this repository.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
// func Foo() (err error) {
|
||||
// defer errors.Recover(&err)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if rand.Intn(2) == 0 {
|
||||
// // Unexpected panics will not be caught by Recover.
|
||||
// io.Closer(nil).Close()
|
||||
// } else {
|
||||
// // Errors thrown by Panic will be caught by Recover.
|
||||
// errors.Panic(errors.New("whoopsie"))
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
package errors
|
||||
|
||||
import "strings"
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Unknown indicates that there is no classification for this error.
|
||||
Unknown = iota
|
||||
|
||||
// Internal indicates that this error is due to an internal bug.
|
||||
// Users should file a issue report if this type of error is encountered.
|
||||
Internal
|
||||
|
||||
// Invalid indicates that this error is due to the user misusing the API
|
||||
// and is indicative of a bug on the user's part.
|
||||
Invalid
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated indicates the use of a deprecated and unsupported feature.
|
||||
Deprecated
|
||||
|
||||
// Corrupted indicates that the input stream is corrupted.
|
||||
Corrupted
|
||||
|
||||
// Closed indicates that the handlers are closed.
|
||||
Closed
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var codeMap = map[int]string{
|
||||
Unknown: "unknown error",
|
||||
Internal: "internal error",
|
||||
Invalid: "invalid argument",
|
||||
Deprecated: "deprecated format",
|
||||
Corrupted: "corrupted input",
|
||||
Closed: "closed handler",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type Error struct {
|
||||
Code int // The error type
|
||||
Pkg string // Name of the package where the error originated
|
||||
Msg string // Descriptive message about the error (optional)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e Error) Error() string {
|
||||
var ss []string
|
||||
for _, s := range []string{e.Pkg, codeMap[e.Code], e.Msg} {
|
||||
if s != "" {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.Join(ss, ": ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e Error) CompressError() {}
|
||||
func (e Error) IsInternal() bool { return e.Code == Internal }
|
||||
func (e Error) IsInvalid() bool { return e.Code == Invalid }
|
||||
func (e Error) IsDeprecated() bool { return e.Code == Deprecated }
|
||||
func (e Error) IsCorrupted() bool { return e.Code == Corrupted }
|
||||
func (e Error) IsClosed() bool { return e.Code == Closed }
|
||||
|
||||
func IsInternal(err error) bool { return isCode(err, Internal) }
|
||||
func IsInvalid(err error) bool { return isCode(err, Invalid) }
|
||||
func IsDeprecated(err error) bool { return isCode(err, Deprecated) }
|
||||
func IsCorrupted(err error) bool { return isCode(err, Corrupted) }
|
||||
func IsClosed(err error) bool { return isCode(err, Closed) }
|
||||
|
||||
func isCode(err error, code int) bool {
|
||||
if cerr, ok := err.(Error); ok && cerr.Code == code {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errWrap is used by Panic and Recover to ensure that only errors raised by
|
||||
// Panic are recovered by Recover.
|
||||
type errWrap struct{ e *error }
|
||||
|
||||
func Recover(err *error) {
|
||||
switch ex := recover().(type) {
|
||||
case nil:
|
||||
// Do nothing.
|
||||
case errWrap:
|
||||
*err = *ex.e
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(ex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Panic(err error) {
|
||||
panic(errWrap{&err})
|
||||
}
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/gofuzz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/gofuzz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build gofuzz
|
||||
|
||||
package internal
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Debug = true
|
||||
GoFuzz = true
|
||||
)
|
||||
159
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/debug.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
159
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/debug.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build debug
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lenBase2(n uint) int {
|
||||
return int(math.Ceil(math.Log2(float64(n + 1))))
|
||||
}
|
||||
func padBase2(v, n uint, m int) string {
|
||||
s := fmt.Sprintf("%b", 1<<n|v)[1:]
|
||||
if pad := m - len(s); pad > 0 {
|
||||
return strings.Repeat(" ", pad) + s
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lenBase10(n int) int {
|
||||
return int(math.Ceil(math.Log10(float64(n + 1))))
|
||||
}
|
||||
func padBase10(n, m int) string {
|
||||
s := fmt.Sprintf("%d", n)
|
||||
if pad := m - len(s); pad > 0 {
|
||||
return strings.Repeat(" ", pad) + s
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rc RangeCodes) String() string {
|
||||
var maxLen, maxBase int
|
||||
for _, c := range rc {
|
||||
maxLen = max(maxLen, int(c.Len))
|
||||
maxBase = max(maxBase, int(c.Base))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var ss []string
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "{")
|
||||
for i, c := range rc {
|
||||
base := padBase10(int(c.Base), lenBase10(maxBase))
|
||||
if c.Len > 0 {
|
||||
base += fmt.Sprintf("-%d", c.End()-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\t%s: {len: %s, range: %s},",
|
||||
padBase10(int(i), lenBase10(len(rc)-1)),
|
||||
padBase10(int(c.Len), lenBase10(maxLen)),
|
||||
base,
|
||||
))
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "}")
|
||||
return strings.Join(ss, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) String() string {
|
||||
var maxSym, maxLen, maxCnt int
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
maxSym = max(maxSym, int(c.Sym))
|
||||
maxLen = max(maxLen, int(c.Len))
|
||||
maxCnt = max(maxCnt, int(c.Cnt))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var ss []string
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "{")
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
var cntStr string
|
||||
if maxCnt > 0 {
|
||||
cnt := int(32*float32(c.Cnt)/float32(maxCnt) + 0.5)
|
||||
cntStr = fmt.Sprintf("%s |%s",
|
||||
padBase10(int(c.Cnt), lenBase10(maxCnt)),
|
||||
strings.Repeat("#", cnt),
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\t%s: %s, %s",
|
||||
padBase10(int(c.Sym), lenBase10(maxSym)),
|
||||
padBase2(uint(c.Val), uint(c.Len), maxLen),
|
||||
cntStr,
|
||||
))
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "}")
|
||||
return strings.Join(ss, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pd Decoder) String() string {
|
||||
var ss []string
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "{")
|
||||
if len(pd.chunks) > 0 {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "\tchunks: {")
|
||||
for i, c := range pd.chunks {
|
||||
label := "sym"
|
||||
if uint(c&countMask) > uint(pd.chunkBits) {
|
||||
label = "idx"
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\t\t%s: {%s: %s, len: %s}",
|
||||
padBase2(uint(i), uint(pd.chunkBits), int(pd.chunkBits)),
|
||||
label, padBase10(int(c>>countBits), 3),
|
||||
padBase10(int(c&countMask), 2),
|
||||
))
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "\t},")
|
||||
|
||||
for j, links := range pd.links {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tlinks[%d]: {", j))
|
||||
linkBits := lenBase2(uint(pd.linkMask))
|
||||
for i, c := range links {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\t\t%s: {sym: %s, len: %s},",
|
||||
padBase2(uint(i), uint(linkBits), int(linkBits)),
|
||||
padBase10(int(c>>countBits), 3),
|
||||
padBase10(int(c&countMask), 2),
|
||||
))
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "\t},")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tchunkMask: %b,", pd.chunkMask))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tlinkMask: %b,", pd.linkMask))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tchunkBits: %d,", pd.chunkBits))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tMinBits: %d,", pd.MinBits))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tNumSyms: %d,", pd.NumSyms))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "}")
|
||||
return strings.Join(ss, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (pe Encoder) String() string {
|
||||
var maxLen int
|
||||
for _, c := range pe.chunks {
|
||||
maxLen = max(maxLen, int(c&countMask))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var ss []string
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "{")
|
||||
if len(pe.chunks) > 0 {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "\tchunks: {")
|
||||
for i, c := range pe.chunks {
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\t\t%s: %s,",
|
||||
padBase10(i, 3),
|
||||
padBase2(uint(c>>countBits), uint(c&countMask), maxLen),
|
||||
))
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "\t},")
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tchunkMask: %b,", pe.chunkMask))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, fmt.Sprintf("\tNumSyms: %d,", pe.NumSyms))
|
||||
ss = append(ss, "}")
|
||||
return strings.Join(ss, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
136
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/decoder.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
136
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/decoder.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// The algorithm used to decode variable length codes is based on the lookup
|
||||
// method in zlib. If the code is less-than-or-equal to maxChunkBits,
|
||||
// then the symbol can be decoded using a single lookup into the chunks table.
|
||||
// Otherwise, the links table will be used for a second level lookup.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The chunks slice is keyed by the contents of the bit buffer ANDed with
|
||||
// the chunkMask to avoid a out-of-bounds lookup. The value of chunks is a tuple
|
||||
// that is decoded as follow:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var length = chunks[bitBuffer&chunkMask] & countMask
|
||||
// var symbol = chunks[bitBuffer&chunkMask] >> countBits
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the decoded length is larger than chunkBits, then an overflow link table
|
||||
// must be used for further decoding. In this case, the symbol is actually the
|
||||
// index into the links tables. The second-level links table returned is
|
||||
// processed in the same way as the chunks table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if length > chunkBits {
|
||||
// var index = symbol // Previous symbol is index into links tables
|
||||
// length = links[index][bitBuffer>>chunkBits & linkMask] & countMask
|
||||
// symbol = links[index][bitBuffer>>chunkBits & linkMask] >> countBits
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See the following:
|
||||
// http://www.gzip.org/algorithm.txt
|
||||
|
||||
type Decoder struct {
|
||||
chunks []uint32 // First-level lookup map
|
||||
links [][]uint32 // Second-level lookup map
|
||||
chunkMask uint32 // Mask the length of the chunks table
|
||||
linkMask uint32 // Mask the length of the link table
|
||||
chunkBits uint32 // Bit-length of the chunks table
|
||||
|
||||
MinBits uint32 // The minimum number of bits to safely make progress
|
||||
NumSyms uint32 // Number of symbols
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init initializes Decoder according to the codes provided.
|
||||
func (pd *Decoder) Init(codes PrefixCodes) {
|
||||
// Handle special case trees.
|
||||
if len(codes) <= 1 {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case len(codes) == 0: // Empty tree (should error if used later)
|
||||
*pd = Decoder{chunks: pd.chunks[:0], links: pd.links[:0], NumSyms: 0}
|
||||
case len(codes) == 1 && codes[0].Len == 0: // Single code tree (bit-length of zero)
|
||||
pd.chunks = append(pd.chunks[:0], codes[0].Sym<<countBits|0)
|
||||
*pd = Decoder{chunks: pd.chunks[:1], links: pd.links[:0], NumSyms: 1}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("invalid codes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !sort.IsSorted(prefixCodesBySymbol(codes)) {
|
||||
panic("input codes is not sorted")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !(codes.checkLengths() && codes.checkPrefixes()) {
|
||||
panic("detected incomplete or overlapping codes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var minBits, maxBits uint32 = valueBits, 0
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
if minBits > c.Len {
|
||||
minBits = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
if maxBits < c.Len {
|
||||
maxBits = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocate chunks table as needed.
|
||||
const maxChunkBits = 9 // This can be tuned for better performance
|
||||
pd.NumSyms = uint32(len(codes))
|
||||
pd.MinBits = minBits
|
||||
pd.chunkBits = maxBits
|
||||
if pd.chunkBits > maxChunkBits {
|
||||
pd.chunkBits = maxChunkBits
|
||||
}
|
||||
numChunks := 1 << pd.chunkBits
|
||||
pd.chunks = allocUint32s(pd.chunks, numChunks)
|
||||
pd.chunkMask = uint32(numChunks - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocate links tables as needed.
|
||||
pd.links = pd.links[:0]
|
||||
pd.linkMask = 0
|
||||
if pd.chunkBits < maxBits {
|
||||
numLinks := 1 << (maxBits - pd.chunkBits)
|
||||
pd.linkMask = uint32(numLinks - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
var linkIdx uint32
|
||||
for i := range pd.chunks {
|
||||
pd.chunks[i] = 0 // Logic below relies on zero value as uninitialized
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
if c.Len > pd.chunkBits && pd.chunks[c.Val&pd.chunkMask] == 0 {
|
||||
pd.chunks[c.Val&pd.chunkMask] = (linkIdx << countBits) | (pd.chunkBits + 1)
|
||||
linkIdx++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pd.links = extendSliceUint32s(pd.links, int(linkIdx))
|
||||
linksFlat := allocUint32s(pd.links[0], numLinks*int(linkIdx))
|
||||
for i, j := 0, 0; i < len(pd.links); i, j = i+1, j+numLinks {
|
||||
pd.links[i] = linksFlat[j : j+numLinks]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill out chunks and links tables with values.
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
chunk := c.Sym<<countBits | c.Len
|
||||
if c.Len <= pd.chunkBits {
|
||||
skip := 1 << uint(c.Len)
|
||||
for j := int(c.Val); j < len(pd.chunks); j += skip {
|
||||
pd.chunks[j] = chunk
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
linkIdx := pd.chunks[c.Val&pd.chunkMask] >> countBits
|
||||
links := pd.links[linkIdx]
|
||||
skip := 1 << uint(c.Len-pd.chunkBits)
|
||||
for j := int(c.Val >> pd.chunkBits); j < len(links); j += skip {
|
||||
links[j] = chunk
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
66
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/encoder.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
66
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/encoder.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Encoder struct {
|
||||
chunks []uint32 // First-level lookup map
|
||||
chunkMask uint32 // Mask the length of the chunks table
|
||||
|
||||
NumSyms uint32 // Number of symbols
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init initializes Encoder according to the codes provided.
|
||||
func (pe *Encoder) Init(codes PrefixCodes) {
|
||||
// Handle special case trees.
|
||||
if len(codes) <= 1 {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case len(codes) == 0: // Empty tree (should error if used later)
|
||||
*pe = Encoder{chunks: pe.chunks[:0], NumSyms: 0}
|
||||
case len(codes) == 1 && codes[0].Len == 0: // Single code tree (bit-length of zero)
|
||||
pe.chunks = append(pe.chunks[:0], codes[0].Val<<countBits|0)
|
||||
*pe = Encoder{chunks: pe.chunks[:1], NumSyms: 1}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("invalid codes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !sort.IsSorted(prefixCodesBySymbol(codes)) {
|
||||
panic("input codes is not sorted")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !(codes.checkLengths() && codes.checkPrefixes()) {
|
||||
panic("detected incomplete or overlapping codes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Enough chunks to contain all the symbols.
|
||||
numChunks := 1
|
||||
for n := len(codes) - 1; n > 0; n >>= 1 {
|
||||
numChunks <<= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
pe.NumSyms = uint32(len(codes))
|
||||
|
||||
retry:
|
||||
// Allocate and reset chunks.
|
||||
pe.chunks = allocUint32s(pe.chunks, numChunks)
|
||||
pe.chunkMask = uint32(numChunks - 1)
|
||||
for i := range pe.chunks {
|
||||
pe.chunks[i] = 0 // Logic below relies on zero value as uninitialized
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Insert each symbol, checking that there are no conflicts.
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
if pe.chunks[c.Sym&pe.chunkMask] > 0 {
|
||||
// Collision found our "hash" table, so grow and try again.
|
||||
numChunks <<= 1
|
||||
goto retry
|
||||
}
|
||||
pe.chunks[c.Sym&pe.chunkMask] = c.Val<<countBits | c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
400
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/prefix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
400
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/prefix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,400 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package prefix implements bit readers and writers that use prefix encoding.
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func errorf(c int, f string, a ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
return errors.Error{Code: c, Pkg: "prefix", Msg: fmt.Sprintf(f, a...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func panicf(c int, f string, a ...interface{}) {
|
||||
errors.Panic(errorf(c, f, a...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
countBits = 5 // Number of bits to store the bit-length of the code
|
||||
valueBits = 27 // Number of bits to store the code value
|
||||
|
||||
countMask = (1 << countBits) - 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// PrefixCode is a representation of a prefix code, which is conceptually a
|
||||
// mapping from some arbitrary symbol to some bit-string.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Sym and Cnt fields are typically provided by the user,
|
||||
// while the Len and Val fields are generated by this package.
|
||||
type PrefixCode struct {
|
||||
Sym uint32 // The symbol being mapped
|
||||
Cnt uint32 // The number times this symbol is used
|
||||
Len uint32 // Bit-length of the prefix code
|
||||
Val uint32 // Value of the prefix code (must be in 0..(1<<Len)-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
type PrefixCodes []PrefixCode
|
||||
|
||||
type prefixCodesBySymbol []PrefixCode
|
||||
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesBySymbol) Len() int { return len(c) }
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesBySymbol) Less(i, j int) bool { return c[i].Sym < c[j].Sym }
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesBySymbol) Swap(i, j int) { c[i], c[j] = c[j], c[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
type prefixCodesByCount []PrefixCode
|
||||
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesByCount) Len() int { return len(c) }
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesByCount) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return c[i].Cnt < c[j].Cnt || (c[i].Cnt == c[j].Cnt && c[i].Sym < c[j].Sym)
|
||||
}
|
||||
func (c prefixCodesByCount) Swap(i, j int) { c[i], c[j] = c[j], c[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) SortBySymbol() { sort.Sort(prefixCodesBySymbol(pc)) }
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) SortByCount() { sort.Sort(prefixCodesByCount(pc)) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Length computes the total bit-length using the Len and Cnt fields.
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) Length() (nb uint) {
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
nb += uint(c.Len * c.Cnt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nb
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkLengths reports whether the codes form a complete prefix tree.
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) checkLengths() bool {
|
||||
sum := 1 << valueBits
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
sum -= (1 << valueBits) >> uint(c.Len)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum == 0 || len(pc) == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkPrefixes reports whether all codes have non-overlapping prefixes.
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) checkPrefixes() bool {
|
||||
for i, c1 := range pc {
|
||||
for j, c2 := range pc {
|
||||
mask := uint32(1)<<c1.Len - 1
|
||||
if i != j && c1.Len <= c2.Len && c1.Val&mask == c2.Val&mask {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkCanonical reports whether all codes are canonical.
|
||||
// That is, they have the following properties:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1. All codes of a given bit-length are consecutive values.
|
||||
// 2. Shorter codes lexicographically precede longer codes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The codes must have unique symbols and be sorted by the symbol
|
||||
// The Len and Val fields in each code must be populated.
|
||||
func (pc PrefixCodes) checkCanonical() bool {
|
||||
// Rule 1.
|
||||
var vals [valueBits + 1]PrefixCode
|
||||
for _, c := range pc {
|
||||
if c.Len > 0 {
|
||||
c.Val = internal.ReverseUint32N(c.Val, uint(c.Len))
|
||||
if vals[c.Len].Cnt > 0 && vals[c.Len].Val+1 != c.Val {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
vals[c.Len].Val = c.Val
|
||||
vals[c.Len].Cnt++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rule 2.
|
||||
var last PrefixCode
|
||||
for _, v := range vals {
|
||||
if v.Cnt > 0 {
|
||||
curVal := v.Val - v.Cnt + 1
|
||||
if last.Cnt != 0 && last.Val >= curVal {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
last = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GenerateLengths assigns non-zero bit-lengths to all codes. Codes with high
|
||||
// frequency counts will be assigned shorter codes to reduce bit entropy.
|
||||
// This function is used primarily by compressors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The input codes must have the Cnt field populated, be sorted by count.
|
||||
// Even if a code has a count of 0, a non-zero bit-length will be assigned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The result will have the Len field populated. The algorithm used guarantees
|
||||
// that Len <= maxBits and that it is a complete prefix tree. The resulting
|
||||
// codes will remain sorted by count.
|
||||
func GenerateLengths(codes PrefixCodes, maxBits uint) error {
|
||||
if len(codes) <= 1 {
|
||||
if len(codes) == 1 {
|
||||
codes[0].Len = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Verify that the codes are in ascending order by count.
|
||||
cntLast := codes[0].Cnt
|
||||
for _, c := range codes[1:] {
|
||||
if c.Cnt < cntLast {
|
||||
return errorf(errors.Invalid, "non-monotonically increasing symbol counts")
|
||||
}
|
||||
cntLast = c.Cnt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Construct a Huffman tree used to generate the bit-lengths.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Huffman tree is a binary tree where each symbol lies as a leaf node
|
||||
// on this tree. The length of the prefix code to assign is the depth of
|
||||
// that leaf from the root. The Huffman algorithm, which runs in O(n),
|
||||
// is used to generate the tree. It assumes that codes are sorted in
|
||||
// increasing order of frequency.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The algorithm is as follows:
|
||||
// 1. Start with two queues, F and Q, where F contains all of the starting
|
||||
// symbols sorted such that symbols with lowest counts come first.
|
||||
// 2. While len(F)+len(Q) > 1:
|
||||
// 2a. Dequeue the node from F or Q that has the lowest weight as N0.
|
||||
// 2b. Dequeue the node from F or Q that has the lowest weight as N1.
|
||||
// 2c. Create a new node N that has N0 and N1 as its children.
|
||||
// 2d. Enqueue N into the back of Q.
|
||||
// 3. The tree's root node is Q[0].
|
||||
type node struct {
|
||||
cnt uint32
|
||||
|
||||
// n0 or c0 represent the left child of this node.
|
||||
// Since Go does not have unions, only one of these will be set.
|
||||
// Similarly, n1 or c1 represent the right child of this node.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If n0 or n1 is set, then it represents a "pointer" to another
|
||||
// node in the Huffman tree. Since Go's pointer analysis cannot reason
|
||||
// that these node pointers do not escape (golang.org/issue/13493),
|
||||
// we use an index to a node in the nodes slice as a pseudo-pointer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If c0 or c1 is set, then it represents a leaf "node" in the
|
||||
// Huffman tree. The leaves are the PrefixCode values themselves.
|
||||
n0, n1 int // Index to child nodes
|
||||
c0, c1 *PrefixCode
|
||||
}
|
||||
var nodeIdx int
|
||||
var nodeArr [1024]node // Large enough to handle most cases on the stack
|
||||
nodes := nodeArr[:]
|
||||
if len(nodes) < len(codes) {
|
||||
nodes = make([]node, len(codes)) // Number of internal nodes < number of leaves
|
||||
}
|
||||
freqs, queue := codes, nodes[:0]
|
||||
for len(freqs)+len(queue) > 1 {
|
||||
// These are the two smallest nodes at the front of freqs and queue.
|
||||
var n node
|
||||
if len(queue) == 0 || (len(freqs) > 0 && freqs[0].Cnt <= queue[0].cnt) {
|
||||
n.c0, freqs = &freqs[0], freqs[1:]
|
||||
n.cnt += n.c0.Cnt
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n.cnt += queue[0].cnt
|
||||
n.n0 = nodeIdx // nodeIdx is same as &queue[0] - &nodes[0]
|
||||
nodeIdx++
|
||||
queue = queue[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(queue) == 0 || (len(freqs) > 0 && freqs[0].Cnt <= queue[0].cnt) {
|
||||
n.c1, freqs = &freqs[0], freqs[1:]
|
||||
n.cnt += n.c1.Cnt
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n.cnt += queue[0].cnt
|
||||
n.n1 = nodeIdx // nodeIdx is same as &queue[0] - &nodes[0]
|
||||
nodeIdx++
|
||||
queue = queue[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
queue = append(queue, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
rootIdx := nodeIdx
|
||||
|
||||
// Search the whole binary tree, noting when we hit each leaf node.
|
||||
// We do not care about the exact Huffman tree structure, but rather we only
|
||||
// care about depth of each of the leaf nodes. That is, the depth determines
|
||||
// how long each symbol is in bits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Since the number of leaves is n, there is at most n internal nodes.
|
||||
// Thus, this algorithm runs in O(n).
|
||||
var fixBits bool
|
||||
var explore func(int, uint)
|
||||
explore = func(rootIdx int, level uint) {
|
||||
root := &nodes[rootIdx]
|
||||
|
||||
// Explore left branch.
|
||||
if root.c0 == nil {
|
||||
explore(root.n0, level+1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fixBits = fixBits || (level > maxBits)
|
||||
root.c0.Len = uint32(level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Explore right branch.
|
||||
if root.c1 == nil {
|
||||
explore(root.n1, level+1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fixBits = fixBits || (level > maxBits)
|
||||
root.c1.Len = uint32(level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
explore(rootIdx, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// Fix the bit-lengths if we violate the maxBits requirement.
|
||||
if fixBits {
|
||||
// Create histogram for number of symbols with each bit-length.
|
||||
var symBitsArr [valueBits + 1]uint32
|
||||
symBits := symBitsArr[:] // symBits[nb] indicates number of symbols using nb bits
|
||||
for _, c := range codes {
|
||||
for int(c.Len) >= len(symBits) {
|
||||
symBits = append(symBits, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
symBits[c.Len]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fudge the tree such that the largest bit-length is <= maxBits.
|
||||
// This is accomplish by effectively doing a tree rotation. That is, we
|
||||
// increase the bit-length of some higher frequency code, so that the
|
||||
// bit-lengths of lower frequency codes can be decreased.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Visually, this looks like the following transform:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Level Before After
|
||||
// __ ___
|
||||
// / \ / \
|
||||
// n-1 X / \ /\ /\
|
||||
// n X /\ X X X X
|
||||
// n+1 X X
|
||||
//
|
||||
var treeRotate func(uint)
|
||||
treeRotate = func(nb uint) {
|
||||
if symBits[nb-1] == 0 {
|
||||
treeRotate(nb - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
symBits[nb-1] -= 1 // Push this node to the level below
|
||||
symBits[nb] += 3 // This level gets one node from above, two from below
|
||||
symBits[nb+1] -= 2 // Push two nodes to the level above
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := uint(len(symBits)) - 1; i > maxBits; i-- {
|
||||
for symBits[i] > 0 {
|
||||
treeRotate(i - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Assign bit-lengths to each code. Since codes is sorted in increasing
|
||||
// order of frequency, that means that the most frequently used symbols
|
||||
// should have the shortest bit-lengths. Thus, we copy symbols to codes
|
||||
// from the back of codes first.
|
||||
cs := codes
|
||||
for nb, cnt := range symBits {
|
||||
if cnt > 0 {
|
||||
pos := len(cs) - int(cnt)
|
||||
cs2 := cs[pos:]
|
||||
for i := range cs2 {
|
||||
cs2[i].Len = uint32(nb)
|
||||
}
|
||||
cs = cs[:pos]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(cs) != 0 {
|
||||
panic("not all codes were used up")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !codes.checkLengths() {
|
||||
panic("incomplete prefix tree detected")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GeneratePrefixes assigns a prefix value to all codes according to the
|
||||
// bit-lengths. This function is used by both compressors and decompressors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The input codes must have the Sym and Len fields populated and be
|
||||
// sorted by symbol. The bit-lengths of each code must be properly allocated,
|
||||
// such that it forms a complete tree.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The result will have the Val field populated and will produce a canonical
|
||||
// prefix tree. The resulting codes will remain sorted by symbol.
|
||||
func GeneratePrefixes(codes PrefixCodes) error {
|
||||
if len(codes) <= 1 {
|
||||
if len(codes) == 1 {
|
||||
if codes[0].Len != 0 {
|
||||
return errorf(errors.Invalid, "degenerate prefix tree with one node")
|
||||
}
|
||||
codes[0].Val = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute basic statistics on the symbols.
|
||||
var bitCnts [valueBits + 1]uint
|
||||
c0 := codes[0]
|
||||
bitCnts[c0.Len]++
|
||||
minBits, maxBits, symLast := c0.Len, c0.Len, c0.Sym
|
||||
for _, c := range codes[1:] {
|
||||
if c.Sym <= symLast {
|
||||
return errorf(errors.Invalid, "non-unique or non-monotonically increasing symbols")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if minBits > c.Len {
|
||||
minBits = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
if maxBits < c.Len {
|
||||
maxBits = c.Len
|
||||
}
|
||||
bitCnts[c.Len]++ // Histogram of bit counts
|
||||
symLast = c.Sym // Keep track of last symbol
|
||||
}
|
||||
if minBits == 0 {
|
||||
return errorf(errors.Invalid, "invalid prefix bit-length")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the next code for a symbol of a given bit length.
|
||||
var nextCodes [valueBits + 1]uint
|
||||
var code uint
|
||||
for i := minBits; i <= maxBits; i++ {
|
||||
code <<= 1
|
||||
nextCodes[i] = code
|
||||
code += bitCnts[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if code != 1<<maxBits {
|
||||
return errorf(errors.Invalid, "degenerate prefix tree")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Assign the code to each symbol.
|
||||
for i, c := range codes {
|
||||
codes[i].Val = internal.ReverseUint32N(uint32(nextCodes[c.Len]), uint(c.Len))
|
||||
nextCodes[c.Len]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !codes.checkPrefixes() {
|
||||
panic("overlapping prefixes detected")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if internal.Debug && !codes.checkCanonical() {
|
||||
panic("non-canonical prefixes detected")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func allocUint32s(s []uint32, n int) []uint32 {
|
||||
if cap(s) >= n {
|
||||
return s[:n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return make([]uint32, n, n*3/2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func extendSliceUint32s(s [][]uint32, n int) [][]uint32 {
|
||||
if cap(s) >= n {
|
||||
return s[:n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss := make([][]uint32, n, n*3/2)
|
||||
copy(ss, s[:cap(s)])
|
||||
return ss
|
||||
}
|
||||
93
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/range.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
93
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/range.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
type RangeCode struct {
|
||||
Base uint32 // Starting base offset of the range
|
||||
Len uint32 // Bit-length of a subsequent integer to add to base offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
type RangeCodes []RangeCode
|
||||
|
||||
type RangeEncoder struct {
|
||||
rcs RangeCodes
|
||||
lut [1024]uint32
|
||||
minBase uint
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// End reports the non-inclusive ending range.
|
||||
func (rc RangeCode) End() uint32 { return rc.Base + (1 << rc.Len) }
|
||||
|
||||
// MakeRangeCodes creates a RangeCodes, where each region is assumed to be
|
||||
// contiguously stacked, without any gaps, with bit-lengths taken from bits.
|
||||
func MakeRangeCodes(minBase uint, bits []uint) (rc RangeCodes) {
|
||||
for _, nb := range bits {
|
||||
rc = append(rc, RangeCode{Base: uint32(minBase), Len: uint32(nb)})
|
||||
minBase += 1 << nb
|
||||
}
|
||||
return rc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Base reports the inclusive starting range for all ranges.
|
||||
func (rcs RangeCodes) Base() uint32 { return rcs[0].Base }
|
||||
|
||||
// End reports the non-inclusive ending range for all ranges.
|
||||
func (rcs RangeCodes) End() uint32 { return rcs[len(rcs)-1].End() }
|
||||
|
||||
// checkValid reports whether the RangeCodes is valid. In order to be valid,
|
||||
// the following must hold true:
|
||||
// rcs[i-1].Base <= rcs[i].Base
|
||||
// rcs[i-1].End <= rcs[i].End
|
||||
// rcs[i-1].End >= rcs[i].Base
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Practically speaking, each range must be increasing and must not have any
|
||||
// gaps in between. It is okay for ranges to overlap.
|
||||
func (rcs RangeCodes) checkValid() bool {
|
||||
if len(rcs) == 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
pre := rcs[0]
|
||||
for _, cur := range rcs[1:] {
|
||||
preBase, preEnd := pre.Base, pre.End()
|
||||
curBase, curEnd := cur.Base, cur.End()
|
||||
if preBase > curBase || preEnd > curEnd || preEnd < curBase {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
pre = cur
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (re *RangeEncoder) Init(rcs RangeCodes) {
|
||||
if !rcs.checkValid() {
|
||||
panic("invalid range codes")
|
||||
}
|
||||
*re = RangeEncoder{rcs: rcs, minBase: uint(rcs.Base())}
|
||||
for sym, rc := range rcs {
|
||||
base := int(rc.Base) - int(re.minBase)
|
||||
end := int(rc.End()) - int(re.minBase)
|
||||
if base >= len(re.lut) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if end > len(re.lut) {
|
||||
end = len(re.lut)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := base; i < end; i++ {
|
||||
re.lut[i] = uint32(sym)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (re *RangeEncoder) Encode(offset uint) (sym uint) {
|
||||
if idx := int(offset - re.minBase); idx < len(re.lut) {
|
||||
return uint(re.lut[idx])
|
||||
}
|
||||
sym = uint(re.lut[len(re.lut)-1])
|
||||
retry:
|
||||
if int(sym) >= len(re.rcs) || re.rcs[sym].Base > uint32(offset) {
|
||||
return sym - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
sym++
|
||||
goto retry // Avoid for-loop so that this function can be inlined
|
||||
}
|
||||
335
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
335
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,335 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal"
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Reader implements a prefix decoder. If the input io.Reader satisfies the
|
||||
// compress.ByteReader or compress.BufferedReader interface, then it also
|
||||
// guarantees that it will never read more bytes than is necessary.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For high performance, provide an io.Reader that satisfies the
|
||||
// compress.BufferedReader interface. If the input does not satisfy either
|
||||
// compress.ByteReader or compress.BufferedReader, then it will be internally
|
||||
// wrapped with a bufio.Reader.
|
||||
type Reader struct {
|
||||
Offset int64 // Number of bytes read from the underlying io.Reader
|
||||
|
||||
rd io.Reader
|
||||
byteRd compress.ByteReader // Set if rd is a ByteReader
|
||||
bufRd compress.BufferedReader // Set if rd is a BufferedReader
|
||||
|
||||
bufBits uint64 // Buffer to hold some bits
|
||||
numBits uint // Number of valid bits in bufBits
|
||||
bigEndian bool // Do we treat input bytes as big endian?
|
||||
|
||||
// These fields are only used if rd is a compress.BufferedReader.
|
||||
bufPeek []byte // Buffer for the Peek data
|
||||
discardBits int // Number of bits to discard from reader
|
||||
fedBits uint // Number of bits fed in last call to PullBits
|
||||
|
||||
// These fields are used to reduce allocations.
|
||||
bb *buffer
|
||||
br *bytesReader
|
||||
sr *stringReader
|
||||
bu *bufio.Reader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init initializes the bit Reader to read from r. If bigEndian is true, then
|
||||
// bits will be read starting from the most-significant bits of a byte
|
||||
// (as done in bzip2), otherwise it will read starting from the
|
||||
// least-significant bits of a byte (such as for deflate and brotli).
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) Init(r io.Reader, bigEndian bool) {
|
||||
*pr = Reader{
|
||||
rd: r,
|
||||
bigEndian: bigEndian,
|
||||
|
||||
bb: pr.bb,
|
||||
br: pr.br,
|
||||
sr: pr.sr,
|
||||
bu: pr.bu,
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch rr := r.(type) {
|
||||
case *bytes.Buffer:
|
||||
if pr.bb == nil {
|
||||
pr.bb = new(buffer)
|
||||
}
|
||||
*pr.bb = buffer{Buffer: rr}
|
||||
pr.bufRd = pr.bb
|
||||
case *bytes.Reader:
|
||||
if pr.br == nil {
|
||||
pr.br = new(bytesReader)
|
||||
}
|
||||
*pr.br = bytesReader{Reader: rr}
|
||||
pr.bufRd = pr.br
|
||||
case *strings.Reader:
|
||||
if pr.sr == nil {
|
||||
pr.sr = new(stringReader)
|
||||
}
|
||||
*pr.sr = stringReader{Reader: rr}
|
||||
pr.bufRd = pr.sr
|
||||
case compress.BufferedReader:
|
||||
pr.bufRd = rr
|
||||
case compress.ByteReader:
|
||||
pr.byteRd = rr
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if pr.bu == nil {
|
||||
pr.bu = bufio.NewReader(nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bu.Reset(r)
|
||||
pr.rd, pr.bufRd = pr.bu, pr.bu
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BitsRead reports the total number of bits emitted from any Read method.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) BitsRead() int64 {
|
||||
offset := 8*pr.Offset - int64(pr.numBits)
|
||||
if pr.bufRd != nil {
|
||||
discardBits := pr.discardBits + int(pr.fedBits-pr.numBits)
|
||||
offset = 8*pr.Offset + int64(discardBits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsBufferedReader reports whether the underlying io.Reader is also a
|
||||
// compress.BufferedReader.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) IsBufferedReader() bool {
|
||||
return pr.bufRd != nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadPads reads 0-7 bits from the bit buffer to achieve byte-alignment.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) ReadPads() uint {
|
||||
nb := pr.numBits % 8
|
||||
val := uint(pr.bufBits & uint64(1<<nb-1))
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= nb
|
||||
pr.numBits -= nb
|
||||
return val
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read reads bytes into buf.
|
||||
// The bit-ordering mode does not affect this method.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) Read(buf []byte) (cnt int, err error) {
|
||||
if pr.numBits > 0 {
|
||||
if pr.numBits%8 != 0 {
|
||||
return 0, errorf(errors.Invalid, "non-aligned bit buffer")
|
||||
}
|
||||
for cnt = 0; len(buf) > cnt && pr.numBits > 0; cnt++ {
|
||||
if pr.bigEndian {
|
||||
buf[cnt] = internal.ReverseLUT[byte(pr.bufBits)]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
buf[cnt] = byte(pr.bufBits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= 8
|
||||
pr.numBits -= 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cnt, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := pr.Flush(); err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
cnt, err = pr.rd.Read(buf)
|
||||
pr.Offset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
return cnt, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadOffset reads an offset value using the provided RangeCodes indexed by
|
||||
// the symbol read.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) ReadOffset(pd *Decoder, rcs RangeCodes) uint {
|
||||
rc := rcs[pr.ReadSymbol(pd)]
|
||||
return uint(rc.Base) + pr.ReadBits(uint(rc.Len))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TryReadBits attempts to read nb bits using the contents of the bit buffer
|
||||
// alone. It returns the value and whether it succeeded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method is designed to be inlined for performance reasons.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) TryReadBits(nb uint) (uint, bool) {
|
||||
if pr.numBits < nb {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
val := uint(pr.bufBits & uint64(1<<nb-1))
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= nb
|
||||
pr.numBits -= nb
|
||||
return val, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadBits reads nb bits in from the underlying reader.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) ReadBits(nb uint) uint {
|
||||
if err := pr.PullBits(nb); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
val := uint(pr.bufBits & uint64(1<<nb-1))
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= nb
|
||||
pr.numBits -= nb
|
||||
return val
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TryReadSymbol attempts to decode the next symbol using the contents of the
|
||||
// bit buffer alone. It returns the decoded symbol and whether it succeeded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method is designed to be inlined for performance reasons.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) TryReadSymbol(pd *Decoder) (uint, bool) {
|
||||
if pr.numBits < uint(pd.MinBits) || len(pd.chunks) == 0 {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
chunk := pd.chunks[uint32(pr.bufBits)&pd.chunkMask]
|
||||
nb := uint(chunk & countMask)
|
||||
if nb > pr.numBits || nb > uint(pd.chunkBits) {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= nb
|
||||
pr.numBits -= nb
|
||||
return uint(chunk >> countBits), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadSymbol reads the next symbol using the provided prefix Decoder.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) ReadSymbol(pd *Decoder) uint {
|
||||
if len(pd.chunks) == 0 {
|
||||
panicf(errors.Invalid, "decode with empty prefix tree")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
nb := uint(pd.MinBits)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if err := pr.PullBits(nb); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
chunk := pd.chunks[uint32(pr.bufBits)&pd.chunkMask]
|
||||
nb = uint(chunk & countMask)
|
||||
if nb > uint(pd.chunkBits) {
|
||||
linkIdx := chunk >> countBits
|
||||
chunk = pd.links[linkIdx][uint32(pr.bufBits>>pd.chunkBits)&pd.linkMask]
|
||||
nb = uint(chunk & countMask)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nb <= pr.numBits {
|
||||
pr.bufBits >>= nb
|
||||
pr.numBits -= nb
|
||||
return uint(chunk >> countBits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flush updates the read offset of the underlying ByteReader.
|
||||
// If reader is a compress.BufferedReader, then this calls Discard to update
|
||||
// the read offset.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) Flush() (int64, error) {
|
||||
if pr.bufRd == nil {
|
||||
return pr.Offset, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Update the number of total bits to discard.
|
||||
pr.discardBits += int(pr.fedBits - pr.numBits)
|
||||
pr.fedBits = pr.numBits
|
||||
|
||||
// Discard some bytes to update read offset.
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
nd := (pr.discardBits + 7) / 8 // Round up to nearest byte
|
||||
nd, err = pr.bufRd.Discard(nd)
|
||||
pr.discardBits -= nd * 8 // -7..0
|
||||
pr.Offset += int64(nd)
|
||||
|
||||
// These are invalid after Discard.
|
||||
pr.bufPeek = nil
|
||||
return pr.Offset, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PullBits ensures that at least nb bits exist in the bit buffer.
|
||||
// If the underlying reader is a compress.BufferedReader, then this will fill
|
||||
// the bit buffer with as many bits as possible, relying on Peek and Discard to
|
||||
// properly advance the read offset. Otherwise, it will use ReadByte to fill the
|
||||
// buffer with just the right number of bits.
|
||||
func (pr *Reader) PullBits(nb uint) error {
|
||||
if pr.bufRd != nil {
|
||||
pr.discardBits += int(pr.fedBits - pr.numBits)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if len(pr.bufPeek) == 0 {
|
||||
pr.fedBits = pr.numBits // Don't discard bits just added
|
||||
if _, err := pr.Flush(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Peek no more bytes than necessary.
|
||||
// The computation for cntPeek computes the minimum number of
|
||||
// bytes to Peek to fill nb bits.
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
cntPeek := int(nb+(-nb&7)) / 8
|
||||
if cntPeek < pr.bufRd.Buffered() {
|
||||
cntPeek = pr.bufRd.Buffered()
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufPeek, err = pr.bufRd.Peek(cntPeek)
|
||||
pr.bufPeek = pr.bufPeek[int(pr.numBits/8):] // Skip buffered bits
|
||||
if len(pr.bufPeek) == 0 {
|
||||
if pr.numBits >= nb {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = io.ErrUnexpectedEOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n := int(64-pr.numBits) / 8 // Number of bytes to copy to bit buffer
|
||||
if len(pr.bufPeek) >= 8 {
|
||||
// Starting with Go 1.7, the compiler should use a wide integer
|
||||
// load here if the architecture supports it.
|
||||
u := binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(pr.bufPeek)
|
||||
if pr.bigEndian {
|
||||
// Swap all the bits within each byte.
|
||||
u = (u&0xaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa)>>1 | (u&0x5555555555555555)<<1
|
||||
u = (u&0xcccccccccccccccc)>>2 | (u&0x3333333333333333)<<2
|
||||
u = (u&0xf0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0)>>4 | (u&0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0f)<<4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pr.bufBits |= u << pr.numBits
|
||||
pr.numBits += uint(n * 8)
|
||||
pr.bufPeek = pr.bufPeek[n:]
|
||||
break
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if n > len(pr.bufPeek) {
|
||||
n = len(pr.bufPeek)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, c := range pr.bufPeek[:n] {
|
||||
if pr.bigEndian {
|
||||
c = internal.ReverseLUT[c]
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufBits |= uint64(c) << pr.numBits
|
||||
pr.numBits += 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufPeek = pr.bufPeek[n:]
|
||||
if pr.numBits > 56 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.fedBits = pr.numBits
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for pr.numBits < nb {
|
||||
c, err := pr.byteRd.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = io.ErrUnexpectedEOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if pr.bigEndian {
|
||||
c = internal.ReverseLUT[c]
|
||||
}
|
||||
pr.bufBits |= uint64(c) << pr.numBits
|
||||
pr.numBits += 8
|
||||
pr.Offset++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
146
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/wrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
146
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/wrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// For some of the common Readers, we wrap and extend them to satisfy the
|
||||
// compress.BufferedReader interface to improve performance.
|
||||
|
||||
type buffer struct {
|
||||
*bytes.Buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type bytesReader struct {
|
||||
*bytes.Reader
|
||||
pos int64
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
arr [512]byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type stringReader struct {
|
||||
*strings.Reader
|
||||
pos int64
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
arr [512]byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *buffer) Buffered() int {
|
||||
return r.Len()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *buffer) Peek(n int) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
b := r.Bytes()
|
||||
if len(b) < n {
|
||||
return b, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b[:n], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *buffer) Discard(n int) (int, error) {
|
||||
b := r.Next(n)
|
||||
if len(b) < n {
|
||||
return len(b), io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *bytesReader) Buffered() int {
|
||||
r.update()
|
||||
if r.Len() > len(r.buf) {
|
||||
return len(r.buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r.Len()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *bytesReader) Peek(n int) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
if n > len(r.arr) {
|
||||
return nil, io.ErrShortBuffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return sub-slice of local buffer if possible.
|
||||
r.update()
|
||||
if len(r.buf) >= n {
|
||||
return r.buf[:n], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill entire local buffer, and return appropriate sub-slice.
|
||||
cnt, err := r.ReadAt(r.arr[:], r.pos)
|
||||
r.buf = r.arr[:cnt]
|
||||
if cnt < n {
|
||||
return r.arr[:cnt], err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r.arr[:n], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *bytesReader) Discard(n int) (int, error) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if n > r.Len() {
|
||||
n, err = r.Len(), io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.Seek(int64(n), io.SeekCurrent)
|
||||
return n, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// update reslices the internal buffer to be consistent with the read offset.
|
||||
func (r *bytesReader) update() {
|
||||
pos, _ := r.Seek(0, io.SeekCurrent)
|
||||
if off := pos - r.pos; off >= 0 && off < int64(len(r.buf)) {
|
||||
r.buf, r.pos = r.buf[off:], pos
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.buf, r.pos = nil, pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *stringReader) Buffered() int {
|
||||
r.update()
|
||||
if r.Len() > len(r.buf) {
|
||||
return len(r.buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r.Len()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *stringReader) Peek(n int) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
if n > len(r.arr) {
|
||||
return nil, io.ErrShortBuffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return sub-slice of local buffer if possible.
|
||||
r.update()
|
||||
if len(r.buf) >= n {
|
||||
return r.buf[:n], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill entire local buffer, and return appropriate sub-slice.
|
||||
cnt, err := r.ReadAt(r.arr[:], r.pos)
|
||||
r.buf = r.arr[:cnt]
|
||||
if cnt < n {
|
||||
return r.arr[:cnt], err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r.arr[:n], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *stringReader) Discard(n int) (int, error) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if n > r.Len() {
|
||||
n, err = r.Len(), io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.Seek(int64(n), io.SeekCurrent)
|
||||
return n, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// update reslices the internal buffer to be consistent with the read offset.
|
||||
func (r *stringReader) update() {
|
||||
pos, _ := r.Seek(0, io.SeekCurrent)
|
||||
if off := pos - r.pos; off >= 0 && off < int64(len(r.buf)) {
|
||||
r.buf, r.pos = r.buf[off:], pos
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.buf, r.pos = nil, pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
166
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/writer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
166
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/writer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
package prefix
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Writer implements a prefix encoder. For performance reasons, Writer will not
|
||||
// write bytes immediately to the underlying stream.
|
||||
type Writer struct {
|
||||
Offset int64 // Number of bytes written to the underlying io.Writer
|
||||
|
||||
wr io.Writer
|
||||
bufBits uint64 // Buffer to hold some bits
|
||||
numBits uint // Number of valid bits in bufBits
|
||||
bigEndian bool // Are bits written in big-endian order?
|
||||
|
||||
buf [512]byte
|
||||
cntBuf int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init initializes the bit Writer to write to w. If bigEndian is true, then
|
||||
// bits will be written starting from the most-significant bits of a byte
|
||||
// (as done in bzip2), otherwise it will write starting from the
|
||||
// least-significant bits of a byte (such as for deflate and brotli).
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) Init(w io.Writer, bigEndian bool) {
|
||||
*pw = Writer{wr: w, bigEndian: bigEndian}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BitsWritten reports the total number of bits issued to any Write method.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) BitsWritten() int64 {
|
||||
return 8*pw.Offset + 8*int64(pw.cntBuf) + int64(pw.numBits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WritePads writes 0-7 bits to the bit buffer to achieve byte-alignment.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) WritePads(v uint) {
|
||||
nb := -pw.numBits & 7
|
||||
pw.bufBits |= uint64(v) << pw.numBits
|
||||
pw.numBits += nb
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write writes bytes from buf.
|
||||
// The bit-ordering mode does not affect this method.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) Write(buf []byte) (cnt int, err error) {
|
||||
if pw.numBits > 0 || pw.cntBuf > 0 {
|
||||
if pw.numBits%8 != 0 {
|
||||
return 0, errorf(errors.Invalid, "non-aligned bit buffer")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := pw.Flush(); err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cnt, err = pw.wr.Write(buf)
|
||||
pw.Offset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
return cnt, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteOffset writes ofs in a (sym, extra) fashion using the provided prefix
|
||||
// Encoder and RangeEncoder.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) WriteOffset(ofs uint, pe *Encoder, re *RangeEncoder) {
|
||||
sym := re.Encode(ofs)
|
||||
pw.WriteSymbol(sym, pe)
|
||||
rc := re.rcs[sym]
|
||||
pw.WriteBits(ofs-uint(rc.Base), uint(rc.Len))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TryWriteBits attempts to write nb bits using the contents of the bit buffer
|
||||
// alone. It reports whether it succeeded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method is designed to be inlined for performance reasons.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) TryWriteBits(v, nb uint) bool {
|
||||
if 64-pw.numBits < nb {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
pw.bufBits |= uint64(v) << pw.numBits
|
||||
pw.numBits += nb
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteBits writes nb bits of v to the underlying writer.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) WriteBits(v, nb uint) {
|
||||
if _, err := pw.PushBits(); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pw.bufBits |= uint64(v) << pw.numBits
|
||||
pw.numBits += nb
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TryWriteSymbol attempts to encode the next symbol using the contents of the
|
||||
// bit buffer alone. It reports whether it succeeded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method is designed to be inlined for performance reasons.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) TryWriteSymbol(sym uint, pe *Encoder) bool {
|
||||
chunk := pe.chunks[uint32(sym)&pe.chunkMask]
|
||||
nb := uint(chunk & countMask)
|
||||
if 64-pw.numBits < nb {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
pw.bufBits |= uint64(chunk>>countBits) << pw.numBits
|
||||
pw.numBits += nb
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteSymbol writes the symbol using the provided prefix Encoder.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) WriteSymbol(sym uint, pe *Encoder) {
|
||||
if _, err := pw.PushBits(); err != nil {
|
||||
errors.Panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
chunk := pe.chunks[uint32(sym)&pe.chunkMask]
|
||||
nb := uint(chunk & countMask)
|
||||
pw.bufBits |= uint64(chunk>>countBits) << pw.numBits
|
||||
pw.numBits += nb
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flush flushes all complete bytes from the bit buffer to the byte buffer, and
|
||||
// then flushes all bytes in the byte buffer to the underlying writer.
|
||||
// After this call, the bit Writer is will only withhold 7 bits at most.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) Flush() (int64, error) {
|
||||
if pw.numBits < 8 && pw.cntBuf == 0 {
|
||||
return pw.Offset, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := pw.PushBits(); err != nil {
|
||||
return pw.Offset, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
cnt, err := pw.wr.Write(pw.buf[:pw.cntBuf])
|
||||
pw.cntBuf -= cnt
|
||||
pw.Offset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
return pw.Offset, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PushBits pushes as many bytes as possible from the bit buffer to the byte
|
||||
// buffer, reporting the number of bits pushed.
|
||||
func (pw *Writer) PushBits() (uint, error) {
|
||||
if pw.cntBuf >= len(pw.buf)-8 {
|
||||
cnt, err := pw.wr.Write(pw.buf[:pw.cntBuf])
|
||||
pw.cntBuf -= cnt
|
||||
pw.Offset += int64(cnt)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
u := pw.bufBits
|
||||
if pw.bigEndian {
|
||||
// Swap all the bits within each byte.
|
||||
u = (u&0xaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa)>>1 | (u&0x5555555555555555)<<1
|
||||
u = (u&0xcccccccccccccccc)>>2 | (u&0x3333333333333333)<<2
|
||||
u = (u&0xf0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0)>>4 | (u&0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0f)<<4
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Starting with Go 1.7, the compiler should use a wide integer
|
||||
// store here if the architecture supports it.
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(pw.buf[pw.cntBuf:], u)
|
||||
|
||||
nb := pw.numBits / 8 // Number of bytes to copy from bit buffer
|
||||
pw.cntBuf += int(nb)
|
||||
pw.bufBits >>= 8 * nb
|
||||
pw.numBits -= 8 * nb
|
||||
return 8 * nb, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/release.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/release.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !debug,!gofuzz
|
||||
|
||||
package internal
|
||||
|
||||
// Debug indicates whether the debug build tag was set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If set, programs may choose to print with more human-readable
|
||||
// debug information and also perform sanity checks that would otherwise be too
|
||||
// expensive to run in a release build.
|
||||
const Debug = false
|
||||
|
||||
// GoFuzz indicates whether the gofuzz build tag was set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If set, programs may choose to disable certain checks (like checksums) that
|
||||
// would be nearly impossible for gofuzz to properly get right.
|
||||
// If GoFuzz is set, it implies that Debug is set as well.
|
||||
const GoFuzz = false
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zbench.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
12
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zbench.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2017, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
# license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
# zbench wraps internal/tool/bench and is useful for comparing benchmarks from
|
||||
# the implementations in this repository relative to other implementations.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See internal/tool/bench/main.go for more details.
|
||||
cd $(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")/internal/tool/bench
|
||||
go run $(go list -f '{{ join .GoFiles "\n" }}') "$@"
|
||||
10
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zfuzz.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
10
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zfuzz.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2017, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
# license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
# zfuzz wraps internal/tool/fuzz and is useful for fuzz testing each of
|
||||
# the implementations in this repository.
|
||||
cd $(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")/internal/tool/fuzz
|
||||
./fuzz.sh "$@"
|
||||
54
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zprof.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
54
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/zprof.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2017, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
# license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $# == 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo "Usage: $0 PKG_PATH TEST_ARGS..."
|
||||
echo ""
|
||||
echo "Runs coverage and performance benchmarks for a given package."
|
||||
echo "The results are stored in the _zprof_ directory."
|
||||
echo ""
|
||||
echo "Example:"
|
||||
echo " $0 flate -test.bench=Decode/Twain/Default"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)"
|
||||
PKG_PATH=$1
|
||||
PKG_NAME=$(basename $PKG_PATH)
|
||||
shift
|
||||
|
||||
TMPDIR=$(mktemp -d)
|
||||
trap "rm -rf $TMPDIR $PKG_PATH/$PKG_NAME.test" SIGINT SIGTERM EXIT
|
||||
|
||||
(
|
||||
cd $DIR/$PKG_PATH
|
||||
|
||||
# Print the go version.
|
||||
go version
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform coverage profiling.
|
||||
go test github.com/dsnet/compress/$PKG_PATH -coverprofile $TMPDIR/cover.profile
|
||||
if [ $? != 0 ]; then exit 1; fi
|
||||
go tool cover -html $TMPDIR/cover.profile -o cover.html
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform performance profiling.
|
||||
if [ $# != 0 ]; then
|
||||
go test -c github.com/dsnet/compress/$PKG_PATH
|
||||
if [ $? != 0 ]; then exit 1; fi
|
||||
./$PKG_NAME.test -test.cpuprofile $TMPDIR/cpu.profile -test.memprofile $TMPDIR/mem.profile -test.run - "$@"
|
||||
PPROF="go tool pprof"
|
||||
$PPROF -output=cpu.svg -web $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/cpu.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
$PPROF -output=cpu.html -weblist=. $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/cpu.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
$PPROF -output=mem_objects.svg -alloc_objects -web $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/mem.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
$PPROF -output=mem_objects.html -alloc_objects -weblist=. $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/mem.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
$PPROF -output=mem_space.svg -alloc_space -web $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/mem.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
$PPROF -output=mem_space.html -alloc_space -weblist=. $PKG_NAME.test $TMPDIR/mem.profile 2> /dev/null
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
rm -rf $DIR/_zprof_/$PKG_NAME
|
||||
mkdir -p $DIR/_zprof_/$PKG_NAME
|
||||
mv *.html *.svg $DIR/_zprof_/$PKG_NAME 2> /dev/null
|
||||
)
|
||||
50
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/ztest.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
50
vendor/github.com/dsnet/compress/ztest.sh
generated
vendored
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Copyright 2017, Joe Tsai. All rights reserved.
|
||||
# Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
# license that can be found in the LICENSE.md file.
|
||||
|
||||
cd $(go list -f '{{ .Dir }}' github.com/dsnet/compress)
|
||||
|
||||
BOLD="\x1b[1mRunning: "
|
||||
PASS="\x1b[32mPASS"
|
||||
FAIL="\x1b[31mFAIL"
|
||||
RESET="\x1b[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "${BOLD}fmt${RESET}"
|
||||
RET_FMT=$(find . -name "*.go" | egrep -v "/(_.*_|\..*|testdata)/" | xargs gofmt -d)
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_FMT" ]]; then echo "$RET_FMT"; echo; fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "${BOLD}test${RESET}"
|
||||
RET_TEST=$(go test -race ./... | egrep -v "^(ok|[?])\s+")
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_TEST" ]]; then echo "$RET_TEST"; echo; fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "${BOLD}staticcheck${RESET}"
|
||||
RET_SCHK=$(staticcheck \
|
||||
-ignore "
|
||||
github.com/dsnet/compress/internal/prefix/*.go:SA4016
|
||||
github.com/dsnet/compress/brotli/*.go:SA4016
|
||||
" ./... 2>&1)
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_SCHK" ]]; then echo "$RET_SCHK"; echo; fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "${BOLD}vet${RESET}"
|
||||
RET_VET=$(go vet ./... 2>&1 |
|
||||
egrep -v "^flate/dict_decoder.go:(.*)WriteByte" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^exit status")
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_VET" ]]; then echo "$RET_VET"; echo; fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "${BOLD}lint${RESET}"
|
||||
RET_LINT=$(golint ./... 2>&1 |
|
||||
egrep -v "should have comment(.*)or be unexported" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^(.*)type name will be used as(.*)by other packages" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^brotli/transform.go:(.*)replace i [+]= 1 with i[+]{2}" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^internal/prefix/prefix.go:(.*)replace symBits(.*) [-]= 1 with symBits(.*)[-]{2}" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^xflate/common.go:(.*)NoCompression should be of the form" |
|
||||
egrep -v "^exit status")
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_LINT" ]]; then echo "$RET_LINT"; echo; fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ ! -z "$RET_FMT" ]] || [ ! -z "$RET_TEST" ] || [[ ! -z "$RET_VET" ]] || [[ ! -z "$RET_SCHK" ]] || [[ ! -z "$RET_LINT" ]] || [[ ! -z "$RET_SPELL" ]]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${FAIL}${RESET}"; exit 1
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo -e "${PASS}${RESET}"; exit 0
|
||||
fi
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/AUTHORS
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/AUTHORS
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# This is the official list of Snappy-Go authors for copyright purposes.
|
||||
# This file is distinct from the CONTRIBUTORS files.
|
||||
# See the latter for an explanation.
|
||||
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file as
|
||||
# Name or Organization <email address>
|
||||
# The email address is not required for organizations.
|
||||
|
||||
# Please keep the list sorted.
|
||||
|
||||
Damian Gryski <dgryski@gmail.com>
|
||||
Google Inc.
|
||||
Jan Mercl <0xjnml@gmail.com>
|
||||
Rodolfo Carvalho <rhcarvalho@gmail.com>
|
||||
Sebastien Binet <seb.binet@gmail.com>
|
||||
37
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/CONTRIBUTORS
generated
vendored
Normal file
37
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/CONTRIBUTORS
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
# This is the official list of people who can contribute
|
||||
# (and typically have contributed) code to the Snappy-Go repository.
|
||||
# The AUTHORS file lists the copyright holders; this file
|
||||
# lists people. For example, Google employees are listed here
|
||||
# but not in AUTHORS, because Google holds the copyright.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The submission process automatically checks to make sure
|
||||
# that people submitting code are listed in this file (by email address).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file only after verifying that
|
||||
# the individual or the individual's organization has agreed to
|
||||
# the appropriate Contributor License Agreement, found here:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://code.google.com/legal/individual-cla-v1.0.html
|
||||
# http://code.google.com/legal/corporate-cla-v1.0.html
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The agreement for individuals can be filled out on the web.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# When adding J Random Contributor's name to this file,
|
||||
# either J's name or J's organization's name should be
|
||||
# added to the AUTHORS file, depending on whether the
|
||||
# individual or corporate CLA was used.
|
||||
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file like so:
|
||||
# Name <email address>
|
||||
|
||||
# Please keep the list sorted.
|
||||
|
||||
Damian Gryski <dgryski@gmail.com>
|
||||
Jan Mercl <0xjnml@gmail.com>
|
||||
Kai Backman <kaib@golang.org>
|
||||
Marc-Antoine Ruel <maruel@chromium.org>
|
||||
Nigel Tao <nigeltao@golang.org>
|
||||
Rob Pike <r@golang.org>
|
||||
Rodolfo Carvalho <rhcarvalho@gmail.com>
|
||||
Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
|
||||
Sebastien Binet <seb.binet@gmail.com>
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2011 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
|
||||
met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
|
||||
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
|
||||
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
|
||||
this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
|
||||
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
|
||||
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
|
||||
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
|
||||
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
107
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/README
generated
vendored
Normal file
107
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/README
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
The Snappy compression format in the Go programming language.
|
||||
|
||||
To download and install from source:
|
||||
$ go get github.com/golang/snappy
|
||||
|
||||
Unless otherwise noted, the Snappy-Go source files are distributed
|
||||
under the BSD-style license found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarks.
|
||||
|
||||
The golang/snappy benchmarks include compressing (Z) and decompressing (U) ten
|
||||
or so files, the same set used by the C++ Snappy code (github.com/google/snappy
|
||||
and note the "google", not "golang"). On an "Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3770 CPU @
|
||||
3.40GHz", Go's GOARCH=amd64 numbers as of 2016-05-29:
|
||||
|
||||
"go test -test.bench=."
|
||||
|
||||
_UFlat0-8 2.19GB/s ± 0% html
|
||||
_UFlat1-8 1.41GB/s ± 0% urls
|
||||
_UFlat2-8 23.5GB/s ± 2% jpg
|
||||
_UFlat3-8 1.91GB/s ± 0% jpg_200
|
||||
_UFlat4-8 14.0GB/s ± 1% pdf
|
||||
_UFlat5-8 1.97GB/s ± 0% html4
|
||||
_UFlat6-8 814MB/s ± 0% txt1
|
||||
_UFlat7-8 785MB/s ± 0% txt2
|
||||
_UFlat8-8 857MB/s ± 0% txt3
|
||||
_UFlat9-8 719MB/s ± 1% txt4
|
||||
_UFlat10-8 2.84GB/s ± 0% pb
|
||||
_UFlat11-8 1.05GB/s ± 0% gaviota
|
||||
|
||||
_ZFlat0-8 1.04GB/s ± 0% html
|
||||
_ZFlat1-8 534MB/s ± 0% urls
|
||||
_ZFlat2-8 15.7GB/s ± 1% jpg
|
||||
_ZFlat3-8 740MB/s ± 3% jpg_200
|
||||
_ZFlat4-8 9.20GB/s ± 1% pdf
|
||||
_ZFlat5-8 991MB/s ± 0% html4
|
||||
_ZFlat6-8 379MB/s ± 0% txt1
|
||||
_ZFlat7-8 352MB/s ± 0% txt2
|
||||
_ZFlat8-8 396MB/s ± 1% txt3
|
||||
_ZFlat9-8 327MB/s ± 1% txt4
|
||||
_ZFlat10-8 1.33GB/s ± 1% pb
|
||||
_ZFlat11-8 605MB/s ± 1% gaviota
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"go test -test.bench=. -tags=noasm"
|
||||
|
||||
_UFlat0-8 621MB/s ± 2% html
|
||||
_UFlat1-8 494MB/s ± 1% urls
|
||||
_UFlat2-8 23.2GB/s ± 1% jpg
|
||||
_UFlat3-8 1.12GB/s ± 1% jpg_200
|
||||
_UFlat4-8 4.35GB/s ± 1% pdf
|
||||
_UFlat5-8 609MB/s ± 0% html4
|
||||
_UFlat6-8 296MB/s ± 0% txt1
|
||||
_UFlat7-8 288MB/s ± 0% txt2
|
||||
_UFlat8-8 309MB/s ± 1% txt3
|
||||
_UFlat9-8 280MB/s ± 1% txt4
|
||||
_UFlat10-8 753MB/s ± 0% pb
|
||||
_UFlat11-8 400MB/s ± 0% gaviota
|
||||
|
||||
_ZFlat0-8 409MB/s ± 1% html
|
||||
_ZFlat1-8 250MB/s ± 1% urls
|
||||
_ZFlat2-8 12.3GB/s ± 1% jpg
|
||||
_ZFlat3-8 132MB/s ± 0% jpg_200
|
||||
_ZFlat4-8 2.92GB/s ± 0% pdf
|
||||
_ZFlat5-8 405MB/s ± 1% html4
|
||||
_ZFlat6-8 179MB/s ± 1% txt1
|
||||
_ZFlat7-8 170MB/s ± 1% txt2
|
||||
_ZFlat8-8 189MB/s ± 1% txt3
|
||||
_ZFlat9-8 164MB/s ± 1% txt4
|
||||
_ZFlat10-8 479MB/s ± 1% pb
|
||||
_ZFlat11-8 270MB/s ± 1% gaviota
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For comparison (Go's encoded output is byte-for-byte identical to C++'s), here
|
||||
are the numbers from C++ Snappy's
|
||||
|
||||
make CXXFLAGS="-O2 -DNDEBUG -g" clean snappy_unittest.log && cat snappy_unittest.log
|
||||
|
||||
BM_UFlat/0 2.4GB/s html
|
||||
BM_UFlat/1 1.4GB/s urls
|
||||
BM_UFlat/2 21.8GB/s jpg
|
||||
BM_UFlat/3 1.5GB/s jpg_200
|
||||
BM_UFlat/4 13.3GB/s pdf
|
||||
BM_UFlat/5 2.1GB/s html4
|
||||
BM_UFlat/6 1.0GB/s txt1
|
||||
BM_UFlat/7 959.4MB/s txt2
|
||||
BM_UFlat/8 1.0GB/s txt3
|
||||
BM_UFlat/9 864.5MB/s txt4
|
||||
BM_UFlat/10 2.9GB/s pb
|
||||
BM_UFlat/11 1.2GB/s gaviota
|
||||
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/0 944.3MB/s html (22.31 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/1 501.6MB/s urls (47.78 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/2 14.3GB/s jpg (99.95 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/3 538.3MB/s jpg_200 (73.00 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/4 8.3GB/s pdf (83.30 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/5 903.5MB/s html4 (22.52 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/6 336.0MB/s txt1 (57.88 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/7 312.3MB/s txt2 (61.91 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/8 353.1MB/s txt3 (54.99 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/9 289.9MB/s txt4 (66.26 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/10 1.2GB/s pb (19.68 %)
|
||||
BM_ZFlat/11 527.4MB/s gaviota (37.72 %)
|
||||
237
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
237
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// ErrCorrupt reports that the input is invalid.
|
||||
ErrCorrupt = errors.New("snappy: corrupt input")
|
||||
// ErrTooLarge reports that the uncompressed length is too large.
|
||||
ErrTooLarge = errors.New("snappy: decoded block is too large")
|
||||
// ErrUnsupported reports that the input isn't supported.
|
||||
ErrUnsupported = errors.New("snappy: unsupported input")
|
||||
|
||||
errUnsupportedLiteralLength = errors.New("snappy: unsupported literal length")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DecodedLen returns the length of the decoded block.
|
||||
func DecodedLen(src []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
v, _, err := decodedLen(src)
|
||||
return v, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// decodedLen returns the length of the decoded block and the number of bytes
|
||||
// that the length header occupied.
|
||||
func decodedLen(src []byte) (blockLen, headerLen int, err error) {
|
||||
v, n := binary.Uvarint(src)
|
||||
if n <= 0 || v > 0xffffffff {
|
||||
return 0, 0, ErrCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const wordSize = 32 << (^uint(0) >> 32 & 1)
|
||||
if wordSize == 32 && v > 0x7fffffff {
|
||||
return 0, 0, ErrTooLarge
|
||||
}
|
||||
return int(v), n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
decodeErrCodeCorrupt = 1
|
||||
decodeErrCodeUnsupportedLiteralLength = 2
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode returns the decoded form of src. The returned slice may be a sub-
|
||||
// slice of dst if dst was large enough to hold the entire decoded block.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a newly allocated slice will be returned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The dst and src must not overlap. It is valid to pass a nil dst.
|
||||
func Decode(dst, src []byte) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
dLen, s, err := decodedLen(src)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dLen <= len(dst) {
|
||||
dst = dst[:dLen]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dst = make([]byte, dLen)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch decode(dst, src[s:]) {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return dst, nil
|
||||
case decodeErrCodeUnsupportedLiteralLength:
|
||||
return nil, errUnsupportedLiteralLength
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, ErrCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewReader returns a new Reader that decompresses from r, using the framing
|
||||
// format described at
|
||||
// https://github.com/google/snappy/blob/master/framing_format.txt
|
||||
func NewReader(r io.Reader) *Reader {
|
||||
return &Reader{
|
||||
r: r,
|
||||
decoded: make([]byte, maxBlockSize),
|
||||
buf: make([]byte, maxEncodedLenOfMaxBlockSize+checksumSize),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reader is an io.Reader that can read Snappy-compressed bytes.
|
||||
type Reader struct {
|
||||
r io.Reader
|
||||
err error
|
||||
decoded []byte
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
// decoded[i:j] contains decoded bytes that have not yet been passed on.
|
||||
i, j int
|
||||
readHeader bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset discards any buffered data, resets all state, and switches the Snappy
|
||||
// reader to read from r. This permits reusing a Reader rather than allocating
|
||||
// a new one.
|
||||
func (r *Reader) Reset(reader io.Reader) {
|
||||
r.r = reader
|
||||
r.err = nil
|
||||
r.i = 0
|
||||
r.j = 0
|
||||
r.readHeader = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *Reader) readFull(p []byte, allowEOF bool) (ok bool) {
|
||||
if _, r.err = io.ReadFull(r.r, p); r.err != nil {
|
||||
if r.err == io.ErrUnexpectedEOF || (r.err == io.EOF && !allowEOF) {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read satisfies the io.Reader interface.
|
||||
func (r *Reader) Read(p []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
if r.err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if r.i < r.j {
|
||||
n := copy(p, r.decoded[r.i:r.j])
|
||||
r.i += n
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !r.readFull(r.buf[:4], true) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
chunkType := r.buf[0]
|
||||
if !r.readHeader {
|
||||
if chunkType != chunkTypeStreamIdentifier {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.readHeader = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
chunkLen := int(r.buf[1]) | int(r.buf[2])<<8 | int(r.buf[3])<<16
|
||||
if chunkLen > len(r.buf) {
|
||||
r.err = ErrUnsupported
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The chunk types are specified at
|
||||
// https://github.com/google/snappy/blob/master/framing_format.txt
|
||||
switch chunkType {
|
||||
case chunkTypeCompressedData:
|
||||
// Section 4.2. Compressed data (chunk type 0x00).
|
||||
if chunkLen < checksumSize {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf := r.buf[:chunkLen]
|
||||
if !r.readFull(buf, false) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
checksum := uint32(buf[0]) | uint32(buf[1])<<8 | uint32(buf[2])<<16 | uint32(buf[3])<<24
|
||||
buf = buf[checksumSize:]
|
||||
|
||||
n, err := DecodedLen(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
r.err = err
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > len(r.decoded) {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := Decode(r.decoded, buf); err != nil {
|
||||
r.err = err
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if crc(r.decoded[:n]) != checksum {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.i, r.j = 0, n
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
case chunkTypeUncompressedData:
|
||||
// Section 4.3. Uncompressed data (chunk type 0x01).
|
||||
if chunkLen < checksumSize {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf := r.buf[:checksumSize]
|
||||
if !r.readFull(buf, false) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
checksum := uint32(buf[0]) | uint32(buf[1])<<8 | uint32(buf[2])<<16 | uint32(buf[3])<<24
|
||||
// Read directly into r.decoded instead of via r.buf.
|
||||
n := chunkLen - checksumSize
|
||||
if n > len(r.decoded) {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !r.readFull(r.decoded[:n], false) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if crc(r.decoded[:n]) != checksum {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.i, r.j = 0, n
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
case chunkTypeStreamIdentifier:
|
||||
// Section 4.1. Stream identifier (chunk type 0xff).
|
||||
if chunkLen != len(magicBody) {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !r.readFull(r.buf[:len(magicBody)], false) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(magicBody); i++ {
|
||||
if r.buf[i] != magicBody[i] {
|
||||
r.err = ErrCorrupt
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if chunkType <= 0x7f {
|
||||
// Section 4.5. Reserved unskippable chunks (chunk types 0x02-0x7f).
|
||||
r.err = ErrUnsupported
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Section 4.4 Padding (chunk type 0xfe).
|
||||
// Section 4.6. Reserved skippable chunks (chunk types 0x80-0xfd).
|
||||
if !r.readFull(r.buf[:chunkLen], false) {
|
||||
return 0, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
14
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_amd64.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
14
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_amd64.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !appengine
|
||||
// +build gc
|
||||
// +build !noasm
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
// decode has the same semantics as in decode_other.go.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:noescape
|
||||
func decode(dst, src []byte) int
|
||||
490
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_amd64.s
generated
vendored
Normal file
490
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_amd64.s
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,490 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !appengine
|
||||
// +build gc
|
||||
// +build !noasm
|
||||
|
||||
#include "textflag.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// The asm code generally follows the pure Go code in decode_other.go, except
|
||||
// where marked with a "!!!".
|
||||
|
||||
// func decode(dst, src []byte) int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All local variables fit into registers. The non-zero stack size is only to
|
||||
// spill registers and push args when issuing a CALL. The register allocation:
|
||||
// - AX scratch
|
||||
// - BX scratch
|
||||
// - CX length or x
|
||||
// - DX offset
|
||||
// - SI &src[s]
|
||||
// - DI &dst[d]
|
||||
// + R8 dst_base
|
||||
// + R9 dst_len
|
||||
// + R10 dst_base + dst_len
|
||||
// + R11 src_base
|
||||
// + R12 src_len
|
||||
// + R13 src_base + src_len
|
||||
// - R14 used by doCopy
|
||||
// - R15 used by doCopy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The registers R8-R13 (marked with a "+") are set at the start of the
|
||||
// function, and after a CALL returns, and are not otherwise modified.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The d variable is implicitly DI - R8, and len(dst)-d is R10 - DI.
|
||||
// The s variable is implicitly SI - R11, and len(src)-s is R13 - SI.
|
||||
TEXT ·decode(SB), NOSPLIT, $48-56
|
||||
// Initialize SI, DI and R8-R13.
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), R8
|
||||
MOVQ dst_len+8(FP), R9
|
||||
MOVQ R8, DI
|
||||
MOVQ R8, R10
|
||||
ADDQ R9, R10
|
||||
MOVQ src_base+24(FP), R11
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+32(FP), R12
|
||||
MOVQ R11, SI
|
||||
MOVQ R11, R13
|
||||
ADDQ R12, R13
|
||||
|
||||
loop:
|
||||
// for s < len(src)
|
||||
CMPQ SI, R13
|
||||
JEQ end
|
||||
|
||||
// CX = uint32(src[s])
|
||||
//
|
||||
// switch src[s] & 0x03
|
||||
MOVBLZX (SI), CX
|
||||
MOVL CX, BX
|
||||
ANDL $3, BX
|
||||
CMPL BX, $1
|
||||
JAE tagCopy
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
// The code below handles literal tags.
|
||||
|
||||
// case tagLiteral:
|
||||
// x := uint32(src[s] >> 2)
|
||||
// switch
|
||||
SHRL $2, CX
|
||||
CMPL CX, $60
|
||||
JAE tagLit60Plus
|
||||
|
||||
// case x < 60:
|
||||
// s++
|
||||
INCQ SI
|
||||
|
||||
doLit:
|
||||
// This is the end of the inner "switch", when we have a literal tag.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We assume that CX == x and x fits in a uint32, where x is the variable
|
||||
// used in the pure Go decode_other.go code.
|
||||
|
||||
// length = int(x) + 1
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unlike the pure Go code, we don't need to check if length <= 0 because
|
||||
// CX can hold 64 bits, so the increment cannot overflow.
|
||||
INCQ CX
|
||||
|
||||
// Prepare to check if copying length bytes will run past the end of dst or
|
||||
// src.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// AX = len(dst) - d
|
||||
// BX = len(src) - s
|
||||
MOVQ R10, AX
|
||||
SUBQ DI, AX
|
||||
MOVQ R13, BX
|
||||
SUBQ SI, BX
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Try a faster technique for short (16 or fewer bytes) copies.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if length > 16 || len(dst)-d < 16 || len(src)-s < 16 {
|
||||
// goto callMemmove // Fall back on calling runtime·memmove.
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The C++ snappy code calls this TryFastAppend. It also checks len(src)-s
|
||||
// against 21 instead of 16, because it cannot assume that all of its input
|
||||
// is contiguous in memory and so it needs to leave enough source bytes to
|
||||
// read the next tag without refilling buffers, but Go's Decode assumes
|
||||
// contiguousness (the src argument is a []byte).
|
||||
CMPQ CX, $16
|
||||
JGT callMemmove
|
||||
CMPQ AX, $16
|
||||
JLT callMemmove
|
||||
CMPQ BX, $16
|
||||
JLT callMemmove
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Implement the copy from src to dst as a 16-byte load and store.
|
||||
// (Decode's documentation says that dst and src must not overlap.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This always copies 16 bytes, instead of only length bytes, but that's
|
||||
// OK. If the input is a valid Snappy encoding then subsequent iterations
|
||||
// will fix up the overrun. Otherwise, Decode returns a nil []byte (and a
|
||||
// non-nil error), so the overrun will be ignored.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that on amd64, it is legal and cheap to issue unaligned 8-byte or
|
||||
// 16-byte loads and stores. This technique probably wouldn't be as
|
||||
// effective on architectures that are fussier about alignment.
|
||||
MOVOU 0(SI), X0
|
||||
MOVOU X0, 0(DI)
|
||||
|
||||
// d += length
|
||||
// s += length
|
||||
ADDQ CX, DI
|
||||
ADDQ CX, SI
|
||||
JMP loop
|
||||
|
||||
callMemmove:
|
||||
// if length > len(dst)-d || length > len(src)-s { etc }
|
||||
CMPQ CX, AX
|
||||
JGT errCorrupt
|
||||
CMPQ CX, BX
|
||||
JGT errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// copy(dst[d:], src[s:s+length])
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This means calling runtime·memmove(&dst[d], &src[s], length), so we push
|
||||
// DI, SI and CX as arguments. Coincidentally, we also need to spill those
|
||||
// three registers to the stack, to save local variables across the CALL.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 0(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ SI, 8(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ CX, 16(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 24(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ SI, 32(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ CX, 40(SP)
|
||||
CALL runtime·memmove(SB)
|
||||
|
||||
// Restore local variables: unspill registers from the stack and
|
||||
// re-calculate R8-R13.
|
||||
MOVQ 24(SP), DI
|
||||
MOVQ 32(SP), SI
|
||||
MOVQ 40(SP), CX
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), R8
|
||||
MOVQ dst_len+8(FP), R9
|
||||
MOVQ R8, R10
|
||||
ADDQ R9, R10
|
||||
MOVQ src_base+24(FP), R11
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+32(FP), R12
|
||||
MOVQ R11, R13
|
||||
ADDQ R12, R13
|
||||
|
||||
// d += length
|
||||
// s += length
|
||||
ADDQ CX, DI
|
||||
ADDQ CX, SI
|
||||
JMP loop
|
||||
|
||||
tagLit60Plus:
|
||||
// !!! This fragment does the
|
||||
//
|
||||
// s += x - 58; if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { etc }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// checks. In the asm version, we code it once instead of once per switch case.
|
||||
ADDQ CX, SI
|
||||
SUBQ $58, SI
|
||||
MOVQ SI, BX
|
||||
SUBQ R11, BX
|
||||
CMPQ BX, R12
|
||||
JA errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// case x == 60:
|
||||
CMPL CX, $61
|
||||
JEQ tagLit61
|
||||
JA tagLit62Plus
|
||||
|
||||
// x = uint32(src[s-1])
|
||||
MOVBLZX -1(SI), CX
|
||||
JMP doLit
|
||||
|
||||
tagLit61:
|
||||
// case x == 61:
|
||||
// x = uint32(src[s-2]) | uint32(src[s-1])<<8
|
||||
MOVWLZX -2(SI), CX
|
||||
JMP doLit
|
||||
|
||||
tagLit62Plus:
|
||||
CMPL CX, $62
|
||||
JA tagLit63
|
||||
|
||||
// case x == 62:
|
||||
// x = uint32(src[s-3]) | uint32(src[s-2])<<8 | uint32(src[s-1])<<16
|
||||
MOVWLZX -3(SI), CX
|
||||
MOVBLZX -1(SI), BX
|
||||
SHLL $16, BX
|
||||
ORL BX, CX
|
||||
JMP doLit
|
||||
|
||||
tagLit63:
|
||||
// case x == 63:
|
||||
// x = uint32(src[s-4]) | uint32(src[s-3])<<8 | uint32(src[s-2])<<16 | uint32(src[s-1])<<24
|
||||
MOVL -4(SI), CX
|
||||
JMP doLit
|
||||
|
||||
// The code above handles literal tags.
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
// The code below handles copy tags.
|
||||
|
||||
tagCopy4:
|
||||
// case tagCopy4:
|
||||
// s += 5
|
||||
ADDQ $5, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ SI, BX
|
||||
SUBQ R11, BX
|
||||
CMPQ BX, R12
|
||||
JA errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// length = 1 + int(src[s-5])>>2
|
||||
SHRQ $2, CX
|
||||
INCQ CX
|
||||
|
||||
// offset = int(uint32(src[s-4]) | uint32(src[s-3])<<8 | uint32(src[s-2])<<16 | uint32(src[s-1])<<24)
|
||||
MOVLQZX -4(SI), DX
|
||||
JMP doCopy
|
||||
|
||||
tagCopy2:
|
||||
// case tagCopy2:
|
||||
// s += 3
|
||||
ADDQ $3, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ SI, BX
|
||||
SUBQ R11, BX
|
||||
CMPQ BX, R12
|
||||
JA errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// length = 1 + int(src[s-3])>>2
|
||||
SHRQ $2, CX
|
||||
INCQ CX
|
||||
|
||||
// offset = int(uint32(src[s-2]) | uint32(src[s-1])<<8)
|
||||
MOVWQZX -2(SI), DX
|
||||
JMP doCopy
|
||||
|
||||
tagCopy:
|
||||
// We have a copy tag. We assume that:
|
||||
// - BX == src[s] & 0x03
|
||||
// - CX == src[s]
|
||||
CMPQ BX, $2
|
||||
JEQ tagCopy2
|
||||
JA tagCopy4
|
||||
|
||||
// case tagCopy1:
|
||||
// s += 2
|
||||
ADDQ $2, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ SI, BX
|
||||
SUBQ R11, BX
|
||||
CMPQ BX, R12
|
||||
JA errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// offset = int(uint32(src[s-2])&0xe0<<3 | uint32(src[s-1]))
|
||||
MOVQ CX, DX
|
||||
ANDQ $0xe0, DX
|
||||
SHLQ $3, DX
|
||||
MOVBQZX -1(SI), BX
|
||||
ORQ BX, DX
|
||||
|
||||
// length = 4 + int(src[s-2])>>2&0x7
|
||||
SHRQ $2, CX
|
||||
ANDQ $7, CX
|
||||
ADDQ $4, CX
|
||||
|
||||
doCopy:
|
||||
// This is the end of the outer "switch", when we have a copy tag.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We assume that:
|
||||
// - CX == length && CX > 0
|
||||
// - DX == offset
|
||||
|
||||
// if offset <= 0 { etc }
|
||||
CMPQ DX, $0
|
||||
JLE errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// if d < offset { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ DI, BX
|
||||
SUBQ R8, BX
|
||||
CMPQ BX, DX
|
||||
JLT errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// if length > len(dst)-d { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ R10, BX
|
||||
SUBQ DI, BX
|
||||
CMPQ CX, BX
|
||||
JGT errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// forwardCopy(dst[d:d+length], dst[d-offset:]); d += length
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Set:
|
||||
// - R14 = len(dst)-d
|
||||
// - R15 = &dst[d-offset]
|
||||
MOVQ R10, R14
|
||||
SUBQ DI, R14
|
||||
MOVQ DI, R15
|
||||
SUBQ DX, R15
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Try a faster technique for short (16 or fewer bytes) forward copies.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// First, try using two 8-byte load/stores, similar to the doLit technique
|
||||
// above. Even if dst[d:d+length] and dst[d-offset:] can overlap, this is
|
||||
// still OK if offset >= 8. Note that this has to be two 8-byte load/stores
|
||||
// and not one 16-byte load/store, and the first store has to be before the
|
||||
// second load, due to the overlap if offset is in the range [8, 16).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if length > 16 || offset < 8 || len(dst)-d < 16 {
|
||||
// goto slowForwardCopy
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// copy 16 bytes
|
||||
// d += length
|
||||
CMPQ CX, $16
|
||||
JGT slowForwardCopy
|
||||
CMPQ DX, $8
|
||||
JLT slowForwardCopy
|
||||
CMPQ R14, $16
|
||||
JLT slowForwardCopy
|
||||
MOVQ 0(R15), AX
|
||||
MOVQ AX, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVQ 8(R15), BX
|
||||
MOVQ BX, 8(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ CX, DI
|
||||
JMP loop
|
||||
|
||||
slowForwardCopy:
|
||||
// !!! If the forward copy is longer than 16 bytes, or if offset < 8, we
|
||||
// can still try 8-byte load stores, provided we can overrun up to 10 extra
|
||||
// bytes. As above, the overrun will be fixed up by subsequent iterations
|
||||
// of the outermost loop.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The C++ snappy code calls this technique IncrementalCopyFastPath. Its
|
||||
// commentary says:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ----
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The main part of this loop is a simple copy of eight bytes at a time
|
||||
// until we've copied (at least) the requested amount of bytes. However,
|
||||
// if d and d-offset are less than eight bytes apart (indicating a
|
||||
// repeating pattern of length < 8), we first need to expand the pattern in
|
||||
// order to get the correct results. For instance, if the buffer looks like
|
||||
// this, with the eight-byte <d-offset> and <d> patterns marked as
|
||||
// intervals:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// abxxxxxxxxxxxx
|
||||
// [------] d-offset
|
||||
// [------] d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// a single eight-byte copy from <d-offset> to <d> will repeat the pattern
|
||||
// once, after which we can move <d> two bytes without moving <d-offset>:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ababxxxxxxxxxx
|
||||
// [------] d-offset
|
||||
// [------] d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// and repeat the exercise until the two no longer overlap.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This allows us to do very well in the special case of one single byte
|
||||
// repeated many times, without taking a big hit for more general cases.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The worst case of extra writing past the end of the match occurs when
|
||||
// offset == 1 and length == 1; the last copy will read from byte positions
|
||||
// [0..7] and write to [4..11], whereas it was only supposed to write to
|
||||
// position 1. Thus, ten excess bytes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ----
|
||||
//
|
||||
// That "10 byte overrun" worst case is confirmed by Go's
|
||||
// TestSlowForwardCopyOverrun, which also tests the fixUpSlowForwardCopy
|
||||
// and finishSlowForwardCopy algorithm.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if length > len(dst)-d-10 {
|
||||
// goto verySlowForwardCopy
|
||||
// }
|
||||
SUBQ $10, R14
|
||||
CMPQ CX, R14
|
||||
JGT verySlowForwardCopy
|
||||
|
||||
makeOffsetAtLeast8:
|
||||
// !!! As above, expand the pattern so that offset >= 8 and we can use
|
||||
// 8-byte load/stores.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// for offset < 8 {
|
||||
// copy 8 bytes from dst[d-offset:] to dst[d:]
|
||||
// length -= offset
|
||||
// d += offset
|
||||
// offset += offset
|
||||
// // The two previous lines together means that d-offset, and therefore
|
||||
// // R15, is unchanged.
|
||||
// }
|
||||
CMPQ DX, $8
|
||||
JGE fixUpSlowForwardCopy
|
||||
MOVQ (R15), BX
|
||||
MOVQ BX, (DI)
|
||||
SUBQ DX, CX
|
||||
ADDQ DX, DI
|
||||
ADDQ DX, DX
|
||||
JMP makeOffsetAtLeast8
|
||||
|
||||
fixUpSlowForwardCopy:
|
||||
// !!! Add length (which might be negative now) to d (implied by DI being
|
||||
// &dst[d]) so that d ends up at the right place when we jump back to the
|
||||
// top of the loop. Before we do that, though, we save DI to AX so that, if
|
||||
// length is positive, copying the remaining length bytes will write to the
|
||||
// right place.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, AX
|
||||
ADDQ CX, DI
|
||||
|
||||
finishSlowForwardCopy:
|
||||
// !!! Repeat 8-byte load/stores until length <= 0. Ending with a negative
|
||||
// length means that we overrun, but as above, that will be fixed up by
|
||||
// subsequent iterations of the outermost loop.
|
||||
CMPQ CX, $0
|
||||
JLE loop
|
||||
MOVQ (R15), BX
|
||||
MOVQ BX, (AX)
|
||||
ADDQ $8, R15
|
||||
ADDQ $8, AX
|
||||
SUBQ $8, CX
|
||||
JMP finishSlowForwardCopy
|
||||
|
||||
verySlowForwardCopy:
|
||||
// verySlowForwardCopy is a simple implementation of forward copy. In C
|
||||
// parlance, this is a do/while loop instead of a while loop, since we know
|
||||
// that length > 0. In Go syntax:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// for {
|
||||
// dst[d] = dst[d - offset]
|
||||
// d++
|
||||
// length--
|
||||
// if length == 0 {
|
||||
// break
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
MOVB (R15), BX
|
||||
MOVB BX, (DI)
|
||||
INCQ R15
|
||||
INCQ DI
|
||||
DECQ CX
|
||||
JNZ verySlowForwardCopy
|
||||
JMP loop
|
||||
|
||||
// The code above handles copy tags.
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
end:
|
||||
// This is the end of the "for s < len(src)".
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if d != len(dst) { etc }
|
||||
CMPQ DI, R10
|
||||
JNE errCorrupt
|
||||
|
||||
// return 0
|
||||
MOVQ $0, ret+48(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
errCorrupt:
|
||||
// return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
MOVQ $1, ret+48(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
101
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
101
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/decode_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !amd64 appengine !gc noasm
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
// decode writes the decoding of src to dst. It assumes that the varint-encoded
|
||||
// length of the decompressed bytes has already been read, and that len(dst)
|
||||
// equals that length.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It returns 0 on success or a decodeErrCodeXxx error code on failure.
|
||||
func decode(dst, src []byte) int {
|
||||
var d, s, offset, length int
|
||||
for s < len(src) {
|
||||
switch src[s] & 0x03 {
|
||||
case tagLiteral:
|
||||
x := uint32(src[s] >> 2)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x < 60:
|
||||
s++
|
||||
case x == 60:
|
||||
s += 2
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = uint32(src[s-1])
|
||||
case x == 61:
|
||||
s += 3
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = uint32(src[s-2]) | uint32(src[s-1])<<8
|
||||
case x == 62:
|
||||
s += 4
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = uint32(src[s-3]) | uint32(src[s-2])<<8 | uint32(src[s-1])<<16
|
||||
case x == 63:
|
||||
s += 5
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = uint32(src[s-4]) | uint32(src[s-3])<<8 | uint32(src[s-2])<<16 | uint32(src[s-1])<<24
|
||||
}
|
||||
length = int(x) + 1
|
||||
if length <= 0 {
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeUnsupportedLiteralLength
|
||||
}
|
||||
if length > len(dst)-d || length > len(src)-s {
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(dst[d:], src[s:s+length])
|
||||
d += length
|
||||
s += length
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
case tagCopy1:
|
||||
s += 2
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
length = 4 + int(src[s-2])>>2&0x7
|
||||
offset = int(uint32(src[s-2])&0xe0<<3 | uint32(src[s-1]))
|
||||
|
||||
case tagCopy2:
|
||||
s += 3
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
length = 1 + int(src[s-3])>>2
|
||||
offset = int(uint32(src[s-2]) | uint32(src[s-1])<<8)
|
||||
|
||||
case tagCopy4:
|
||||
s += 5
|
||||
if uint(s) > uint(len(src)) { // The uint conversions catch overflow from the previous line.
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
length = 1 + int(src[s-5])>>2
|
||||
offset = int(uint32(src[s-4]) | uint32(src[s-3])<<8 | uint32(src[s-2])<<16 | uint32(src[s-1])<<24)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if offset <= 0 || d < offset || length > len(dst)-d {
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Copy from an earlier sub-slice of dst to a later sub-slice. Unlike
|
||||
// the built-in copy function, this byte-by-byte copy always runs
|
||||
// forwards, even if the slices overlap. Conceptually, this is:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// d += forwardCopy(dst[d:d+length], dst[d-offset:])
|
||||
for end := d + length; d != end; d++ {
|
||||
dst[d] = dst[d-offset]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if d != len(dst) {
|
||||
return decodeErrCodeCorrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
285
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
285
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,285 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Encode returns the encoded form of src. The returned slice may be a sub-
|
||||
// slice of dst if dst was large enough to hold the entire encoded block.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a newly allocated slice will be returned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The dst and src must not overlap. It is valid to pass a nil dst.
|
||||
func Encode(dst, src []byte) []byte {
|
||||
if n := MaxEncodedLen(len(src)); n < 0 {
|
||||
panic(ErrTooLarge)
|
||||
} else if len(dst) < n {
|
||||
dst = make([]byte, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The block starts with the varint-encoded length of the decompressed bytes.
|
||||
d := binary.PutUvarint(dst, uint64(len(src)))
|
||||
|
||||
for len(src) > 0 {
|
||||
p := src
|
||||
src = nil
|
||||
if len(p) > maxBlockSize {
|
||||
p, src = p[:maxBlockSize], p[maxBlockSize:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(p) < minNonLiteralBlockSize {
|
||||
d += emitLiteral(dst[d:], p)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
d += encodeBlock(dst[d:], p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dst[:d]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// inputMargin is the minimum number of extra input bytes to keep, inside
|
||||
// encodeBlock's inner loop. On some architectures, this margin lets us
|
||||
// implement a fast path for emitLiteral, where the copy of short (<= 16 byte)
|
||||
// literals can be implemented as a single load to and store from a 16-byte
|
||||
// register. That literal's actual length can be as short as 1 byte, so this
|
||||
// can copy up to 15 bytes too much, but that's OK as subsequent iterations of
|
||||
// the encoding loop will fix up the copy overrun, and this inputMargin ensures
|
||||
// that we don't overrun the dst and src buffers.
|
||||
const inputMargin = 16 - 1
|
||||
|
||||
// minNonLiteralBlockSize is the minimum size of the input to encodeBlock that
|
||||
// could be encoded with a copy tag. This is the minimum with respect to the
|
||||
// algorithm used by encodeBlock, not a minimum enforced by the file format.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The encoded output must start with at least a 1 byte literal, as there are
|
||||
// no previous bytes to copy. A minimal (1 byte) copy after that, generated
|
||||
// from an emitCopy call in encodeBlock's main loop, would require at least
|
||||
// another inputMargin bytes, for the reason above: we want any emitLiteral
|
||||
// calls inside encodeBlock's main loop to use the fast path if possible, which
|
||||
// requires being able to overrun by inputMargin bytes. Thus,
|
||||
// minNonLiteralBlockSize equals 1 + 1 + inputMargin.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The C++ code doesn't use this exact threshold, but it could, as discussed at
|
||||
// https://groups.google.com/d/topic/snappy-compression/oGbhsdIJSJ8/discussion
|
||||
// The difference between Go (2+inputMargin) and C++ (inputMargin) is purely an
|
||||
// optimization. It should not affect the encoded form. This is tested by
|
||||
// TestSameEncodingAsCppShortCopies.
|
||||
const minNonLiteralBlockSize = 1 + 1 + inputMargin
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxEncodedLen returns the maximum length of a snappy block, given its
|
||||
// uncompressed length.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It will return a negative value if srcLen is too large to encode.
|
||||
func MaxEncodedLen(srcLen int) int {
|
||||
n := uint64(srcLen)
|
||||
if n > 0xffffffff {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Compressed data can be defined as:
|
||||
// compressed := item* literal*
|
||||
// item := literal* copy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The trailing literal sequence has a space blowup of at most 62/60
|
||||
// since a literal of length 60 needs one tag byte + one extra byte
|
||||
// for length information.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Item blowup is trickier to measure. Suppose the "copy" op copies
|
||||
// 4 bytes of data. Because of a special check in the encoding code,
|
||||
// we produce a 4-byte copy only if the offset is < 65536. Therefore
|
||||
// the copy op takes 3 bytes to encode, and this type of item leads
|
||||
// to at most the 62/60 blowup for representing literals.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Suppose the "copy" op copies 5 bytes of data. If the offset is big
|
||||
// enough, it will take 5 bytes to encode the copy op. Therefore the
|
||||
// worst case here is a one-byte literal followed by a five-byte copy.
|
||||
// That is, 6 bytes of input turn into 7 bytes of "compressed" data.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This last factor dominates the blowup, so the final estimate is:
|
||||
n = 32 + n + n/6
|
||||
if n > 0xffffffff {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return int(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var errClosed = errors.New("snappy: Writer is closed")
|
||||
|
||||
// NewWriter returns a new Writer that compresses to w.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Writer returned does not buffer writes. There is no need to Flush or
|
||||
// Close such a Writer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: the Writer returned is not suitable for many small writes, only
|
||||
// for few large writes. Use NewBufferedWriter instead, which is efficient
|
||||
// regardless of the frequency and shape of the writes, and remember to Close
|
||||
// that Writer when done.
|
||||
func NewWriter(w io.Writer) *Writer {
|
||||
return &Writer{
|
||||
w: w,
|
||||
obuf: make([]byte, obufLen),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewBufferedWriter returns a new Writer that compresses to w, using the
|
||||
// framing format described at
|
||||
// https://github.com/google/snappy/blob/master/framing_format.txt
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Writer returned buffers writes. Users must call Close to guarantee all
|
||||
// data has been forwarded to the underlying io.Writer. They may also call
|
||||
// Flush zero or more times before calling Close.
|
||||
func NewBufferedWriter(w io.Writer) *Writer {
|
||||
return &Writer{
|
||||
w: w,
|
||||
ibuf: make([]byte, 0, maxBlockSize),
|
||||
obuf: make([]byte, obufLen),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Writer is an io.Writer that can write Snappy-compressed bytes.
|
||||
type Writer struct {
|
||||
w io.Writer
|
||||
err error
|
||||
|
||||
// ibuf is a buffer for the incoming (uncompressed) bytes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Its use is optional. For backwards compatibility, Writers created by the
|
||||
// NewWriter function have ibuf == nil, do not buffer incoming bytes, and
|
||||
// therefore do not need to be Flush'ed or Close'd.
|
||||
ibuf []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// obuf is a buffer for the outgoing (compressed) bytes.
|
||||
obuf []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// wroteStreamHeader is whether we have written the stream header.
|
||||
wroteStreamHeader bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset discards the writer's state and switches the Snappy writer to write to
|
||||
// w. This permits reusing a Writer rather than allocating a new one.
|
||||
func (w *Writer) Reset(writer io.Writer) {
|
||||
w.w = writer
|
||||
w.err = nil
|
||||
if w.ibuf != nil {
|
||||
w.ibuf = w.ibuf[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.wroteStreamHeader = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write satisfies the io.Writer interface.
|
||||
func (w *Writer) Write(p []byte) (nRet int, errRet error) {
|
||||
if w.ibuf == nil {
|
||||
// Do not buffer incoming bytes. This does not perform or compress well
|
||||
// if the caller of Writer.Write writes many small slices. This
|
||||
// behavior is therefore deprecated, but still supported for backwards
|
||||
// compatibility with code that doesn't explicitly Flush or Close.
|
||||
return w.write(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The remainder of this method is based on bufio.Writer.Write from the
|
||||
// standard library.
|
||||
|
||||
for len(p) > (cap(w.ibuf)-len(w.ibuf)) && w.err == nil {
|
||||
var n int
|
||||
if len(w.ibuf) == 0 {
|
||||
// Large write, empty buffer.
|
||||
// Write directly from p to avoid copy.
|
||||
n, _ = w.write(p)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n = copy(w.ibuf[len(w.ibuf):cap(w.ibuf)], p)
|
||||
w.ibuf = w.ibuf[:len(w.ibuf)+n]
|
||||
w.Flush()
|
||||
}
|
||||
nRet += n
|
||||
p = p[n:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if w.err != nil {
|
||||
return nRet, w.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := copy(w.ibuf[len(w.ibuf):cap(w.ibuf)], p)
|
||||
w.ibuf = w.ibuf[:len(w.ibuf)+n]
|
||||
nRet += n
|
||||
return nRet, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *Writer) write(p []byte) (nRet int, errRet error) {
|
||||
if w.err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, w.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for len(p) > 0 {
|
||||
obufStart := len(magicChunk)
|
||||
if !w.wroteStreamHeader {
|
||||
w.wroteStreamHeader = true
|
||||
copy(w.obuf, magicChunk)
|
||||
obufStart = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var uncompressed []byte
|
||||
if len(p) > maxBlockSize {
|
||||
uncompressed, p = p[:maxBlockSize], p[maxBlockSize:]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
uncompressed, p = p, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
checksum := crc(uncompressed)
|
||||
|
||||
// Compress the buffer, discarding the result if the improvement
|
||||
// isn't at least 12.5%.
|
||||
compressed := Encode(w.obuf[obufHeaderLen:], uncompressed)
|
||||
chunkType := uint8(chunkTypeCompressedData)
|
||||
chunkLen := 4 + len(compressed)
|
||||
obufEnd := obufHeaderLen + len(compressed)
|
||||
if len(compressed) >= len(uncompressed)-len(uncompressed)/8 {
|
||||
chunkType = chunkTypeUncompressedData
|
||||
chunkLen = 4 + len(uncompressed)
|
||||
obufEnd = obufHeaderLen
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill in the per-chunk header that comes before the body.
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+0] = chunkType
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+1] = uint8(chunkLen >> 0)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+2] = uint8(chunkLen >> 8)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+3] = uint8(chunkLen >> 16)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+4] = uint8(checksum >> 0)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+5] = uint8(checksum >> 8)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+6] = uint8(checksum >> 16)
|
||||
w.obuf[len(magicChunk)+7] = uint8(checksum >> 24)
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := w.w.Write(w.obuf[obufStart:obufEnd]); err != nil {
|
||||
w.err = err
|
||||
return nRet, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if chunkType == chunkTypeUncompressedData {
|
||||
if _, err := w.w.Write(uncompressed); err != nil {
|
||||
w.err = err
|
||||
return nRet, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
nRet += len(uncompressed)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nRet, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flush flushes the Writer to its underlying io.Writer.
|
||||
func (w *Writer) Flush() error {
|
||||
if w.err != nil {
|
||||
return w.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(w.ibuf) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.write(w.ibuf)
|
||||
w.ibuf = w.ibuf[:0]
|
||||
return w.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Close calls Flush and then closes the Writer.
|
||||
func (w *Writer) Close() error {
|
||||
w.Flush()
|
||||
ret := w.err
|
||||
if w.err == nil {
|
||||
w.err = errClosed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_amd64.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_amd64.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !appengine
|
||||
// +build gc
|
||||
// +build !noasm
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
// emitLiteral has the same semantics as in encode_other.go.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:noescape
|
||||
func emitLiteral(dst, lit []byte) int
|
||||
|
||||
// emitCopy has the same semantics as in encode_other.go.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:noescape
|
||||
func emitCopy(dst []byte, offset, length int) int
|
||||
|
||||
// extendMatch has the same semantics as in encode_other.go.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:noescape
|
||||
func extendMatch(src []byte, i, j int) int
|
||||
|
||||
// encodeBlock has the same semantics as in encode_other.go.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:noescape
|
||||
func encodeBlock(dst, src []byte) (d int)
|
||||
730
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_amd64.s
generated
vendored
Normal file
730
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_amd64.s
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,730 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !appengine
|
||||
// +build gc
|
||||
// +build !noasm
|
||||
|
||||
#include "textflag.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// The XXX lines assemble on Go 1.4, 1.5 and 1.7, but not 1.6, due to a
|
||||
// Go toolchain regression. See https://github.com/golang/go/issues/15426 and
|
||||
// https://github.com/golang/snappy/issues/29
|
||||
//
|
||||
// As a workaround, the package was built with a known good assembler, and
|
||||
// those instructions were disassembled by "objdump -d" to yield the
|
||||
// 4e 0f b7 7c 5c 78 movzwq 0x78(%rsp,%r11,2),%r15
|
||||
// style comments, in AT&T asm syntax. Note that rsp here is a physical
|
||||
// register, not Go/asm's SP pseudo-register (see https://golang.org/doc/asm).
|
||||
// The instructions were then encoded as "BYTE $0x.." sequences, which assemble
|
||||
// fine on Go 1.6.
|
||||
|
||||
// The asm code generally follows the pure Go code in encode_other.go, except
|
||||
// where marked with a "!!!".
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// func emitLiteral(dst, lit []byte) int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All local variables fit into registers. The register allocation:
|
||||
// - AX len(lit)
|
||||
// - BX n
|
||||
// - DX return value
|
||||
// - DI &dst[i]
|
||||
// - R10 &lit[0]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The 24 bytes of stack space is to call runtime·memmove.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The unusual register allocation of local variables, such as R10 for the
|
||||
// source pointer, matches the allocation used at the call site in encodeBlock,
|
||||
// which makes it easier to manually inline this function.
|
||||
TEXT ·emitLiteral(SB), NOSPLIT, $24-56
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), DI
|
||||
MOVQ lit_base+24(FP), R10
|
||||
MOVQ lit_len+32(FP), AX
|
||||
MOVQ AX, DX
|
||||
MOVL AX, BX
|
||||
SUBL $1, BX
|
||||
|
||||
CMPL BX, $60
|
||||
JLT oneByte
|
||||
CMPL BX, $256
|
||||
JLT twoBytes
|
||||
|
||||
threeBytes:
|
||||
MOVB $0xf4, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW BX, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DX
|
||||
JMP memmove
|
||||
|
||||
twoBytes:
|
||||
MOVB $0xf0, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVB BX, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $2, DI
|
||||
ADDQ $2, DX
|
||||
JMP memmove
|
||||
|
||||
oneByte:
|
||||
SHLB $2, BX
|
||||
MOVB BX, 0(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $1, DI
|
||||
ADDQ $1, DX
|
||||
|
||||
memmove:
|
||||
MOVQ DX, ret+48(FP)
|
||||
|
||||
// copy(dst[i:], lit)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This means calling runtime·memmove(&dst[i], &lit[0], len(lit)), so we push
|
||||
// DI, R10 and AX as arguments.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 0(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ R10, 8(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ AX, 16(SP)
|
||||
CALL runtime·memmove(SB)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// func emitCopy(dst []byte, offset, length int) int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All local variables fit into registers. The register allocation:
|
||||
// - AX length
|
||||
// - SI &dst[0]
|
||||
// - DI &dst[i]
|
||||
// - R11 offset
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The unusual register allocation of local variables, such as R11 for the
|
||||
// offset, matches the allocation used at the call site in encodeBlock, which
|
||||
// makes it easier to manually inline this function.
|
||||
TEXT ·emitCopy(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-48
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), DI
|
||||
MOVQ DI, SI
|
||||
MOVQ offset+24(FP), R11
|
||||
MOVQ length+32(FP), AX
|
||||
|
||||
loop0:
|
||||
// for length >= 68 { etc }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $68
|
||||
JLT step1
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit a length 64 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB $0xfe, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
SUBL $64, AX
|
||||
JMP loop0
|
||||
|
||||
step1:
|
||||
// if length > 64 { etc }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $64
|
||||
JLE step2
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit a length 60 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB $0xee, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
SUBL $60, AX
|
||||
|
||||
step2:
|
||||
// if length >= 12 || offset >= 2048 { goto step3 }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $12
|
||||
JGE step3
|
||||
CMPL R11, $2048
|
||||
JGE step3
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 2 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
SHRL $8, R11
|
||||
SHLB $5, R11
|
||||
SUBB $4, AX
|
||||
SHLB $2, AX
|
||||
ORB AX, R11
|
||||
ORB $1, R11
|
||||
MOVB R11, 0(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $2, DI
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the number of bytes written.
|
||||
SUBQ SI, DI
|
||||
MOVQ DI, ret+40(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
step3:
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
SUBL $1, AX
|
||||
SHLB $2, AX
|
||||
ORB $2, AX
|
||||
MOVB AX, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the number of bytes written.
|
||||
SUBQ SI, DI
|
||||
MOVQ DI, ret+40(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// func extendMatch(src []byte, i, j int) int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All local variables fit into registers. The register allocation:
|
||||
// - DX &src[0]
|
||||
// - SI &src[j]
|
||||
// - R13 &src[len(src) - 8]
|
||||
// - R14 &src[len(src)]
|
||||
// - R15 &src[i]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The unusual register allocation of local variables, such as R15 for a source
|
||||
// pointer, matches the allocation used at the call site in encodeBlock, which
|
||||
// makes it easier to manually inline this function.
|
||||
TEXT ·extendMatch(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-48
|
||||
MOVQ src_base+0(FP), DX
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+8(FP), R14
|
||||
MOVQ i+24(FP), R15
|
||||
MOVQ j+32(FP), SI
|
||||
ADDQ DX, R14
|
||||
ADDQ DX, R15
|
||||
ADDQ DX, SI
|
||||
MOVQ R14, R13
|
||||
SUBQ $8, R13
|
||||
|
||||
cmp8:
|
||||
// As long as we are 8 or more bytes before the end of src, we can load and
|
||||
// compare 8 bytes at a time. If those 8 bytes are equal, repeat.
|
||||
CMPQ SI, R13
|
||||
JA cmp1
|
||||
MOVQ (R15), AX
|
||||
MOVQ (SI), BX
|
||||
CMPQ AX, BX
|
||||
JNE bsf
|
||||
ADDQ $8, R15
|
||||
ADDQ $8, SI
|
||||
JMP cmp8
|
||||
|
||||
bsf:
|
||||
// If those 8 bytes were not equal, XOR the two 8 byte values, and return
|
||||
// the index of the first byte that differs. The BSF instruction finds the
|
||||
// least significant 1 bit, the amd64 architecture is little-endian, and
|
||||
// the shift by 3 converts a bit index to a byte index.
|
||||
XORQ AX, BX
|
||||
BSFQ BX, BX
|
||||
SHRQ $3, BX
|
||||
ADDQ BX, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert from &src[ret] to ret.
|
||||
SUBQ DX, SI
|
||||
MOVQ SI, ret+40(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
cmp1:
|
||||
// In src's tail, compare 1 byte at a time.
|
||||
CMPQ SI, R14
|
||||
JAE extendMatchEnd
|
||||
MOVB (R15), AX
|
||||
MOVB (SI), BX
|
||||
CMPB AX, BX
|
||||
JNE extendMatchEnd
|
||||
ADDQ $1, R15
|
||||
ADDQ $1, SI
|
||||
JMP cmp1
|
||||
|
||||
extendMatchEnd:
|
||||
// Convert from &src[ret] to ret.
|
||||
SUBQ DX, SI
|
||||
MOVQ SI, ret+40(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// func encodeBlock(dst, src []byte) (d int)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All local variables fit into registers, other than "var table". The register
|
||||
// allocation:
|
||||
// - AX . .
|
||||
// - BX . .
|
||||
// - CX 56 shift (note that amd64 shifts by non-immediates must use CX).
|
||||
// - DX 64 &src[0], tableSize
|
||||
// - SI 72 &src[s]
|
||||
// - DI 80 &dst[d]
|
||||
// - R9 88 sLimit
|
||||
// - R10 . &src[nextEmit]
|
||||
// - R11 96 prevHash, currHash, nextHash, offset
|
||||
// - R12 104 &src[base], skip
|
||||
// - R13 . &src[nextS], &src[len(src) - 8]
|
||||
// - R14 . len(src), bytesBetweenHashLookups, &src[len(src)], x
|
||||
// - R15 112 candidate
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The second column (56, 64, etc) is the stack offset to spill the registers
|
||||
// when calling other functions. We could pack this slightly tighter, but it's
|
||||
// simpler to have a dedicated spill map independent of the function called.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// "var table [maxTableSize]uint16" takes up 32768 bytes of stack space. An
|
||||
// extra 56 bytes, to call other functions, and an extra 64 bytes, to spill
|
||||
// local variables (registers) during calls gives 32768 + 56 + 64 = 32888.
|
||||
TEXT ·encodeBlock(SB), 0, $32888-56
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), DI
|
||||
MOVQ src_base+24(FP), SI
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+32(FP), R14
|
||||
|
||||
// shift, tableSize := uint32(32-8), 1<<8
|
||||
MOVQ $24, CX
|
||||
MOVQ $256, DX
|
||||
|
||||
calcShift:
|
||||
// for ; tableSize < maxTableSize && tableSize < len(src); tableSize *= 2 {
|
||||
// shift--
|
||||
// }
|
||||
CMPQ DX, $16384
|
||||
JGE varTable
|
||||
CMPQ DX, R14
|
||||
JGE varTable
|
||||
SUBQ $1, CX
|
||||
SHLQ $1, DX
|
||||
JMP calcShift
|
||||
|
||||
varTable:
|
||||
// var table [maxTableSize]uint16
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the asm code, unlike the Go code, we can zero-initialize only the
|
||||
// first tableSize elements. Each uint16 element is 2 bytes and each MOVOU
|
||||
// writes 16 bytes, so we can do only tableSize/8 writes instead of the
|
||||
// 2048 writes that would zero-initialize all of table's 32768 bytes.
|
||||
SHRQ $3, DX
|
||||
LEAQ table-32768(SP), BX
|
||||
PXOR X0, X0
|
||||
|
||||
memclr:
|
||||
MOVOU X0, 0(BX)
|
||||
ADDQ $16, BX
|
||||
SUBQ $1, DX
|
||||
JNZ memclr
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! DX = &src[0]
|
||||
MOVQ SI, DX
|
||||
|
||||
// sLimit := len(src) - inputMargin
|
||||
MOVQ R14, R9
|
||||
SUBQ $15, R9
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Pre-emptively spill CX, DX and R9 to the stack. Their values don't
|
||||
// change for the rest of the function.
|
||||
MOVQ CX, 56(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ DX, 64(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ R9, 88(SP)
|
||||
|
||||
// nextEmit := 0
|
||||
MOVQ DX, R10
|
||||
|
||||
// s := 1
|
||||
ADDQ $1, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// nextHash := hash(load32(src, s), shift)
|
||||
MOVL 0(SI), R11
|
||||
IMULL $0x1e35a7bd, R11
|
||||
SHRL CX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
outer:
|
||||
// for { etc }
|
||||
|
||||
// skip := 32
|
||||
MOVQ $32, R12
|
||||
|
||||
// nextS := s
|
||||
MOVQ SI, R13
|
||||
|
||||
// candidate := 0
|
||||
MOVQ $0, R15
|
||||
|
||||
inner0:
|
||||
// for { etc }
|
||||
|
||||
// s := nextS
|
||||
MOVQ R13, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// bytesBetweenHashLookups := skip >> 5
|
||||
MOVQ R12, R14
|
||||
SHRQ $5, R14
|
||||
|
||||
// nextS = s + bytesBetweenHashLookups
|
||||
ADDQ R14, R13
|
||||
|
||||
// skip += bytesBetweenHashLookups
|
||||
ADDQ R14, R12
|
||||
|
||||
// if nextS > sLimit { goto emitRemainder }
|
||||
MOVQ R13, AX
|
||||
SUBQ DX, AX
|
||||
CMPQ AX, R9
|
||||
JA emitRemainder
|
||||
|
||||
// candidate = int(table[nextHash])
|
||||
// XXX: MOVWQZX table-32768(SP)(R11*2), R15
|
||||
// XXX: 4e 0f b7 7c 5c 78 movzwq 0x78(%rsp,%r11,2),%r15
|
||||
BYTE $0x4e
|
||||
BYTE $0x0f
|
||||
BYTE $0xb7
|
||||
BYTE $0x7c
|
||||
BYTE $0x5c
|
||||
BYTE $0x78
|
||||
|
||||
// table[nextHash] = uint16(s)
|
||||
MOVQ SI, AX
|
||||
SUBQ DX, AX
|
||||
|
||||
// XXX: MOVW AX, table-32768(SP)(R11*2)
|
||||
// XXX: 66 42 89 44 5c 78 mov %ax,0x78(%rsp,%r11,2)
|
||||
BYTE $0x66
|
||||
BYTE $0x42
|
||||
BYTE $0x89
|
||||
BYTE $0x44
|
||||
BYTE $0x5c
|
||||
BYTE $0x78
|
||||
|
||||
// nextHash = hash(load32(src, nextS), shift)
|
||||
MOVL 0(R13), R11
|
||||
IMULL $0x1e35a7bd, R11
|
||||
SHRL CX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
// if load32(src, s) != load32(src, candidate) { continue } break
|
||||
MOVL 0(SI), AX
|
||||
MOVL (DX)(R15*1), BX
|
||||
CMPL AX, BX
|
||||
JNE inner0
|
||||
|
||||
fourByteMatch:
|
||||
// As per the encode_other.go code:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A 4-byte match has been found. We'll later see etc.
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Jump to a fast path for short (<= 16 byte) literals. See the comment
|
||||
// on inputMargin in encode.go.
|
||||
MOVQ SI, AX
|
||||
SUBQ R10, AX
|
||||
CMPQ AX, $16
|
||||
JLE emitLiteralFastPath
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
// Begin inline of the emitLiteral call.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// d += emitLiteral(dst[d:], src[nextEmit:s])
|
||||
|
||||
MOVL AX, BX
|
||||
SUBL $1, BX
|
||||
|
||||
CMPL BX, $60
|
||||
JLT inlineEmitLiteralOneByte
|
||||
CMPL BX, $256
|
||||
JLT inlineEmitLiteralTwoBytes
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitLiteralThreeBytes:
|
||||
MOVB $0xf4, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW BX, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
JMP inlineEmitLiteralMemmove
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitLiteralTwoBytes:
|
||||
MOVB $0xf0, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVB BX, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $2, DI
|
||||
JMP inlineEmitLiteralMemmove
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitLiteralOneByte:
|
||||
SHLB $2, BX
|
||||
MOVB BX, 0(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $1, DI
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitLiteralMemmove:
|
||||
// Spill local variables (registers) onto the stack; call; unspill.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// copy(dst[i:], lit)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This means calling runtime·memmove(&dst[i], &lit[0], len(lit)), so we push
|
||||
// DI, R10 and AX as arguments.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 0(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ R10, 8(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ AX, 16(SP)
|
||||
ADDQ AX, DI // Finish the "d +=" part of "d += emitLiteral(etc)".
|
||||
MOVQ SI, 72(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 80(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ R15, 112(SP)
|
||||
CALL runtime·memmove(SB)
|
||||
MOVQ 56(SP), CX
|
||||
MOVQ 64(SP), DX
|
||||
MOVQ 72(SP), SI
|
||||
MOVQ 80(SP), DI
|
||||
MOVQ 88(SP), R9
|
||||
MOVQ 112(SP), R15
|
||||
JMP inner1
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitLiteralEnd:
|
||||
// End inline of the emitLiteral call.
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
emitLiteralFastPath:
|
||||
// !!! Emit the 1-byte encoding "uint8(len(lit)-1)<<2".
|
||||
MOVB AX, BX
|
||||
SUBB $1, BX
|
||||
SHLB $2, BX
|
||||
MOVB BX, (DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $1, DI
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! Implement the copy from lit to dst as a 16-byte load and store.
|
||||
// (Encode's documentation says that dst and src must not overlap.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This always copies 16 bytes, instead of only len(lit) bytes, but that's
|
||||
// OK. Subsequent iterations will fix up the overrun.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that on amd64, it is legal and cheap to issue unaligned 8-byte or
|
||||
// 16-byte loads and stores. This technique probably wouldn't be as
|
||||
// effective on architectures that are fussier about alignment.
|
||||
MOVOU 0(R10), X0
|
||||
MOVOU X0, 0(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ AX, DI
|
||||
|
||||
inner1:
|
||||
// for { etc }
|
||||
|
||||
// base := s
|
||||
MOVQ SI, R12
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! offset := base - candidate
|
||||
MOVQ R12, R11
|
||||
SUBQ R15, R11
|
||||
SUBQ DX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
// Begin inline of the extendMatch call.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// s = extendMatch(src, candidate+4, s+4)
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! R14 = &src[len(src)]
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+32(FP), R14
|
||||
ADDQ DX, R14
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! R13 = &src[len(src) - 8]
|
||||
MOVQ R14, R13
|
||||
SUBQ $8, R13
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! R15 = &src[candidate + 4]
|
||||
ADDQ $4, R15
|
||||
ADDQ DX, R15
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! s += 4
|
||||
ADDQ $4, SI
|
||||
|
||||
inlineExtendMatchCmp8:
|
||||
// As long as we are 8 or more bytes before the end of src, we can load and
|
||||
// compare 8 bytes at a time. If those 8 bytes are equal, repeat.
|
||||
CMPQ SI, R13
|
||||
JA inlineExtendMatchCmp1
|
||||
MOVQ (R15), AX
|
||||
MOVQ (SI), BX
|
||||
CMPQ AX, BX
|
||||
JNE inlineExtendMatchBSF
|
||||
ADDQ $8, R15
|
||||
ADDQ $8, SI
|
||||
JMP inlineExtendMatchCmp8
|
||||
|
||||
inlineExtendMatchBSF:
|
||||
// If those 8 bytes were not equal, XOR the two 8 byte values, and return
|
||||
// the index of the first byte that differs. The BSF instruction finds the
|
||||
// least significant 1 bit, the amd64 architecture is little-endian, and
|
||||
// the shift by 3 converts a bit index to a byte index.
|
||||
XORQ AX, BX
|
||||
BSFQ BX, BX
|
||||
SHRQ $3, BX
|
||||
ADDQ BX, SI
|
||||
JMP inlineExtendMatchEnd
|
||||
|
||||
inlineExtendMatchCmp1:
|
||||
// In src's tail, compare 1 byte at a time.
|
||||
CMPQ SI, R14
|
||||
JAE inlineExtendMatchEnd
|
||||
MOVB (R15), AX
|
||||
MOVB (SI), BX
|
||||
CMPB AX, BX
|
||||
JNE inlineExtendMatchEnd
|
||||
ADDQ $1, R15
|
||||
ADDQ $1, SI
|
||||
JMP inlineExtendMatchCmp1
|
||||
|
||||
inlineExtendMatchEnd:
|
||||
// End inline of the extendMatch call.
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
// Begin inline of the emitCopy call.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// d += emitCopy(dst[d:], base-candidate, s-base)
|
||||
|
||||
// !!! length := s - base
|
||||
MOVQ SI, AX
|
||||
SUBQ R12, AX
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitCopyLoop0:
|
||||
// for length >= 68 { etc }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $68
|
||||
JLT inlineEmitCopyStep1
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit a length 64 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB $0xfe, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
SUBL $64, AX
|
||||
JMP inlineEmitCopyLoop0
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitCopyStep1:
|
||||
// if length > 64 { etc }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $64
|
||||
JLE inlineEmitCopyStep2
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit a length 60 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB $0xee, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
SUBL $60, AX
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitCopyStep2:
|
||||
// if length >= 12 || offset >= 2048 { goto inlineEmitCopyStep3 }
|
||||
CMPL AX, $12
|
||||
JGE inlineEmitCopyStep3
|
||||
CMPL R11, $2048
|
||||
JGE inlineEmitCopyStep3
|
||||
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 2 bytes.
|
||||
MOVB R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
SHRL $8, R11
|
||||
SHLB $5, R11
|
||||
SUBB $4, AX
|
||||
SHLB $2, AX
|
||||
ORB AX, R11
|
||||
ORB $1, R11
|
||||
MOVB R11, 0(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $2, DI
|
||||
JMP inlineEmitCopyEnd
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitCopyStep3:
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
SUBL $1, AX
|
||||
SHLB $2, AX
|
||||
ORB $2, AX
|
||||
MOVB AX, 0(DI)
|
||||
MOVW R11, 1(DI)
|
||||
ADDQ $3, DI
|
||||
|
||||
inlineEmitCopyEnd:
|
||||
// End inline of the emitCopy call.
|
||||
// ----------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
// nextEmit = s
|
||||
MOVQ SI, R10
|
||||
|
||||
// if s >= sLimit { goto emitRemainder }
|
||||
MOVQ SI, AX
|
||||
SUBQ DX, AX
|
||||
CMPQ AX, R9
|
||||
JAE emitRemainder
|
||||
|
||||
// As per the encode_other.go code:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We could immediately etc.
|
||||
|
||||
// x := load64(src, s-1)
|
||||
MOVQ -1(SI), R14
|
||||
|
||||
// prevHash := hash(uint32(x>>0), shift)
|
||||
MOVL R14, R11
|
||||
IMULL $0x1e35a7bd, R11
|
||||
SHRL CX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
// table[prevHash] = uint16(s-1)
|
||||
MOVQ SI, AX
|
||||
SUBQ DX, AX
|
||||
SUBQ $1, AX
|
||||
|
||||
// XXX: MOVW AX, table-32768(SP)(R11*2)
|
||||
// XXX: 66 42 89 44 5c 78 mov %ax,0x78(%rsp,%r11,2)
|
||||
BYTE $0x66
|
||||
BYTE $0x42
|
||||
BYTE $0x89
|
||||
BYTE $0x44
|
||||
BYTE $0x5c
|
||||
BYTE $0x78
|
||||
|
||||
// currHash := hash(uint32(x>>8), shift)
|
||||
SHRQ $8, R14
|
||||
MOVL R14, R11
|
||||
IMULL $0x1e35a7bd, R11
|
||||
SHRL CX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
// candidate = int(table[currHash])
|
||||
// XXX: MOVWQZX table-32768(SP)(R11*2), R15
|
||||
// XXX: 4e 0f b7 7c 5c 78 movzwq 0x78(%rsp,%r11,2),%r15
|
||||
BYTE $0x4e
|
||||
BYTE $0x0f
|
||||
BYTE $0xb7
|
||||
BYTE $0x7c
|
||||
BYTE $0x5c
|
||||
BYTE $0x78
|
||||
|
||||
// table[currHash] = uint16(s)
|
||||
ADDQ $1, AX
|
||||
|
||||
// XXX: MOVW AX, table-32768(SP)(R11*2)
|
||||
// XXX: 66 42 89 44 5c 78 mov %ax,0x78(%rsp,%r11,2)
|
||||
BYTE $0x66
|
||||
BYTE $0x42
|
||||
BYTE $0x89
|
||||
BYTE $0x44
|
||||
BYTE $0x5c
|
||||
BYTE $0x78
|
||||
|
||||
// if uint32(x>>8) == load32(src, candidate) { continue }
|
||||
MOVL (DX)(R15*1), BX
|
||||
CMPL R14, BX
|
||||
JEQ inner1
|
||||
|
||||
// nextHash = hash(uint32(x>>16), shift)
|
||||
SHRQ $8, R14
|
||||
MOVL R14, R11
|
||||
IMULL $0x1e35a7bd, R11
|
||||
SHRL CX, R11
|
||||
|
||||
// s++
|
||||
ADDQ $1, SI
|
||||
|
||||
// break out of the inner1 for loop, i.e. continue the outer loop.
|
||||
JMP outer
|
||||
|
||||
emitRemainder:
|
||||
// if nextEmit < len(src) { etc }
|
||||
MOVQ src_len+32(FP), AX
|
||||
ADDQ DX, AX
|
||||
CMPQ R10, AX
|
||||
JEQ encodeBlockEnd
|
||||
|
||||
// d += emitLiteral(dst[d:], src[nextEmit:])
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Push args.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 0(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ $0, 8(SP) // Unnecessary, as the callee ignores it, but conservative.
|
||||
MOVQ $0, 16(SP) // Unnecessary, as the callee ignores it, but conservative.
|
||||
MOVQ R10, 24(SP)
|
||||
SUBQ R10, AX
|
||||
MOVQ AX, 32(SP)
|
||||
MOVQ AX, 40(SP) // Unnecessary, as the callee ignores it, but conservative.
|
||||
|
||||
// Spill local variables (registers) onto the stack; call; unspill.
|
||||
MOVQ DI, 80(SP)
|
||||
CALL ·emitLiteral(SB)
|
||||
MOVQ 80(SP), DI
|
||||
|
||||
// Finish the "d +=" part of "d += emitLiteral(etc)".
|
||||
ADDQ 48(SP), DI
|
||||
|
||||
encodeBlockEnd:
|
||||
MOVQ dst_base+0(FP), AX
|
||||
SUBQ AX, DI
|
||||
MOVQ DI, d+48(FP)
|
||||
RET
|
||||
238
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
238
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/encode_other.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,238 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !amd64 appengine !gc noasm
|
||||
|
||||
package snappy
|
||||
|
||||
func load32(b []byte, i int) uint32 {
|
||||
b = b[i : i+4 : len(b)] // Help the compiler eliminate bounds checks on the next line.
|
||||
return uint32(b[0]) | uint32(b[1])<<8 | uint32(b[2])<<16 | uint32(b[3])<<24
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func load64(b []byte, i int) uint64 {
|
||||
b = b[i : i+8 : len(b)] // Help the compiler eliminate bounds checks on the next line.
|
||||
return uint64(b[0]) | uint64(b[1])<<8 | uint64(b[2])<<16 | uint64(b[3])<<24 |
|
||||
uint64(b[4])<<32 | uint64(b[5])<<40 | uint64(b[6])<<48 | uint64(b[7])<<56
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// emitLiteral writes a literal chunk and returns the number of bytes written.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It assumes that:
|
||||
// dst is long enough to hold the encoded bytes
|
||||
// 1 <= len(lit) && len(lit) <= 65536
|
||||
func emitLiteral(dst, lit []byte) int {
|
||||
i, n := 0, uint(len(lit)-1)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case n < 60:
|
||||
dst[0] = uint8(n)<<2 | tagLiteral
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
case n < 1<<8:
|
||||
dst[0] = 60<<2 | tagLiteral
|
||||
dst[1] = uint8(n)
|
||||
i = 2
|
||||
default:
|
||||
dst[0] = 61<<2 | tagLiteral
|
||||
dst[1] = uint8(n)
|
||||
dst[2] = uint8(n >> 8)
|
||||
i = 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i + copy(dst[i:], lit)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// emitCopy writes a copy chunk and returns the number of bytes written.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It assumes that:
|
||||
// dst is long enough to hold the encoded bytes
|
||||
// 1 <= offset && offset <= 65535
|
||||
// 4 <= length && length <= 65535
|
||||
func emitCopy(dst []byte, offset, length int) int {
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
// The maximum length for a single tagCopy1 or tagCopy2 op is 64 bytes. The
|
||||
// threshold for this loop is a little higher (at 68 = 64 + 4), and the
|
||||
// length emitted down below is is a little lower (at 60 = 64 - 4), because
|
||||
// it's shorter to encode a length 67 copy as a length 60 tagCopy2 followed
|
||||
// by a length 7 tagCopy1 (which encodes as 3+2 bytes) than to encode it as
|
||||
// a length 64 tagCopy2 followed by a length 3 tagCopy2 (which encodes as
|
||||
// 3+3 bytes). The magic 4 in the 64±4 is because the minimum length for a
|
||||
// tagCopy1 op is 4 bytes, which is why a length 3 copy has to be an
|
||||
// encodes-as-3-bytes tagCopy2 instead of an encodes-as-2-bytes tagCopy1.
|
||||
for length >= 68 {
|
||||
// Emit a length 64 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
dst[i+0] = 63<<2 | tagCopy2
|
||||
dst[i+1] = uint8(offset)
|
||||
dst[i+2] = uint8(offset >> 8)
|
||||
i += 3
|
||||
length -= 64
|
||||
}
|
||||
if length > 64 {
|
||||
// Emit a length 60 copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
dst[i+0] = 59<<2 | tagCopy2
|
||||
dst[i+1] = uint8(offset)
|
||||
dst[i+2] = uint8(offset >> 8)
|
||||
i += 3
|
||||
length -= 60
|
||||
}
|
||||
if length >= 12 || offset >= 2048 {
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 3 bytes.
|
||||
dst[i+0] = uint8(length-1)<<2 | tagCopy2
|
||||
dst[i+1] = uint8(offset)
|
||||
dst[i+2] = uint8(offset >> 8)
|
||||
return i + 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Emit the remaining copy, encoded as 2 bytes.
|
||||
dst[i+0] = uint8(offset>>8)<<5 | uint8(length-4)<<2 | tagCopy1
|
||||
dst[i+1] = uint8(offset)
|
||||
return i + 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// extendMatch returns the largest k such that k <= len(src) and that
|
||||
// src[i:i+k-j] and src[j:k] have the same contents.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It assumes that:
|
||||
// 0 <= i && i < j && j <= len(src)
|
||||
func extendMatch(src []byte, i, j int) int {
|
||||
for ; j < len(src) && src[i] == src[j]; i, j = i+1, j+1 {
|
||||
}
|
||||
return j
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func hash(u, shift uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
return (u * 0x1e35a7bd) >> shift
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// encodeBlock encodes a non-empty src to a guaranteed-large-enough dst. It
|
||||
// assumes that the varint-encoded length of the decompressed bytes has already
|
||||
// been written.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It also assumes that:
|
||||
// len(dst) >= MaxEncodedLen(len(src)) &&
|
||||
// minNonLiteralBlockSize <= len(src) && len(src) <= maxBlockSize
|
||||
func encodeBlock(dst, src []byte) (d int) {
|
||||
// Initialize the hash table. Its size ranges from 1<<8 to 1<<14 inclusive.
|
||||
// The table element type is uint16, as s < sLimit and sLimit < len(src)
|
||||
// and len(src) <= maxBlockSize and maxBlockSize == 65536.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
maxTableSize = 1 << 14
|
||||
// tableMask is redundant, but helps the compiler eliminate bounds
|
||||
// checks.
|
||||
tableMask = maxTableSize - 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
shift := uint32(32 - 8)
|
||||
for tableSize := 1 << 8; tableSize < maxTableSize && tableSize < len(src); tableSize *= 2 {
|
||||
shift--
|
||||
}
|
||||
// In Go, all array elements are zero-initialized, so there is no advantage
|
||||
// to a smaller tableSize per se. However, it matches the C++ algorithm,
|
||||
// and in the asm versions of this code, we can get away with zeroing only
|
||||
// the first tableSize elements.
|
||||
var table [maxTableSize]uint16
|
||||
|
||||
// sLimit is when to stop looking for offset/length copies. The inputMargin
|
||||
// lets us use a fast path for emitLiteral in the main loop, while we are
|
||||
// looking for copies.
|
||||
sLimit := len(src) - inputMargin
|
||||
|
||||
// nextEmit is where in src the next emitLiteral should start from.
|
||||
nextEmit := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// The encoded form must start with a literal, as there are no previous
|
||||
// bytes to copy, so we start looking for hash matches at s == 1.
|
||||
s := 1
|
||||
nextHash := hash(load32(src, s), shift)
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// Copied from the C++ snappy implementation:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Heuristic match skipping: If 32 bytes are scanned with no matches
|
||||
// found, start looking only at every other byte. If 32 more bytes are
|
||||
// scanned (or skipped), look at every third byte, etc.. When a match
|
||||
// is found, immediately go back to looking at every byte. This is a
|
||||
// small loss (~5% performance, ~0.1% density) for compressible data
|
||||
// due to more bookkeeping, but for non-compressible data (such as
|
||||
// JPEG) it's a huge win since the compressor quickly "realizes" the
|
||||
// data is incompressible and doesn't bother looking for matches
|
||||
// everywhere.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The "skip" variable keeps track of how many bytes there are since
|
||||
// the last match; dividing it by 32 (ie. right-shifting by five) gives
|
||||
// the number of bytes to move ahead for each iteration.
|
||||
skip := 32
|
||||
|
||||
nextS := s
|
||||
candidate := 0
|
||||
for {
|
||||
s = nextS
|
||||
bytesBetweenHashLookups := skip >> 5
|
||||
nextS = s + bytesBetweenHashLookups
|
||||
skip += bytesBetweenHashLookups
|
||||
if nextS > sLimit {
|
||||
goto emitRemainder
|
||||
}
|
||||
candidate = int(table[nextHash&tableMask])
|
||||
table[nextHash&tableMask] = uint16(s)
|
||||
nextHash = hash(load32(src, nextS), shift)
|
||||
if load32(src, s) == load32(src, candidate) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A 4-byte match has been found. We'll later see if more than 4 bytes
|
||||
// match. But, prior to the match, src[nextEmit:s] are unmatched. Emit
|
||||
// them as literal bytes.
|
||||
d += emitLiteral(dst[d:], src[nextEmit:s])
|
||||
|
||||
// Call emitCopy, and then see if another emitCopy could be our next
|
||||
// move. Repeat until we find no match for the input immediately after
|
||||
// what was consumed by the last emitCopy call.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If we exit this loop normally then we need to call emitLiteral next,
|
||||
// though we don't yet know how big the literal will be. We handle that
|
||||
// by proceeding to the next iteration of the main loop. We also can
|
||||
// exit this loop via goto if we get close to exhausting the input.
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// Invariant: we have a 4-byte match at s, and no need to emit any
|
||||
// literal bytes prior to s.
|
||||
base := s
|
||||
|
||||
// Extend the 4-byte match as long as possible.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is an inlined version of:
|
||||
// s = extendMatch(src, candidate+4, s+4)
|
||||
s += 4
|
||||
for i := candidate + 4; s < len(src) && src[i] == src[s]; i, s = i+1, s+1 {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
d += emitCopy(dst[d:], base-candidate, s-base)
|
||||
nextEmit = s
|
||||
if s >= sLimit {
|
||||
goto emitRemainder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We could immediately start working at s now, but to improve
|
||||
// compression we first update the hash table at s-1 and at s. If
|
||||
// another emitCopy is not our next move, also calculate nextHash
|
||||
// at s+1. At least on GOARCH=amd64, these three hash calculations
|
||||
// are faster as one load64 call (with some shifts) instead of
|
||||
// three load32 calls.
|
||||
x := load64(src, s-1)
|
||||
prevHash := hash(uint32(x>>0), shift)
|
||||
table[prevHash&tableMask] = uint16(s - 1)
|
||||
currHash := hash(uint32(x>>8), shift)
|
||||
candidate = int(table[currHash&tableMask])
|
||||
table[currHash&tableMask] = uint16(s)
|
||||
if uint32(x>>8) != load32(src, candidate) {
|
||||
nextHash = hash(uint32(x>>16), shift)
|
||||
s++
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
emitRemainder:
|
||||
if nextEmit < len(src) {
|
||||
d += emitLiteral(dst[d:], src[nextEmit:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d
|
||||
}
|
||||
87
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/snappy.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
87
vendor/github.com/golang/snappy/snappy.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Snappy-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package snappy implements the snappy block-based compression format.
|
||||
// It aims for very high speeds and reasonable compression.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The C++ snappy implementation is at https://github.com/google/snappy
|
||||
package snappy // import "github.com/golang/snappy"
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"hash/crc32"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Each encoded block begins with the varint-encoded length of the decoded data,
|
||||
followed by a sequence of chunks. Chunks begin and end on byte boundaries. The
|
||||
first byte of each chunk is broken into its 2 least and 6 most significant bits
|
||||
called l and m: l ranges in [0, 4) and m ranges in [0, 64). l is the chunk tag.
|
||||
Zero means a literal tag. All other values mean a copy tag.
|
||||
|
||||
For literal tags:
|
||||
- If m < 60, the next 1 + m bytes are literal bytes.
|
||||
- Otherwise, let n be the little-endian unsigned integer denoted by the next
|
||||
m - 59 bytes. The next 1 + n bytes after that are literal bytes.
|
||||
|
||||
For copy tags, length bytes are copied from offset bytes ago, in the style of
|
||||
Lempel-Ziv compression algorithms. In particular:
|
||||
- For l == 1, the offset ranges in [0, 1<<11) and the length in [4, 12).
|
||||
The length is 4 + the low 3 bits of m. The high 3 bits of m form bits 8-10
|
||||
of the offset. The next byte is bits 0-7 of the offset.
|
||||
- For l == 2, the offset ranges in [0, 1<<16) and the length in [1, 65).
|
||||
The length is 1 + m. The offset is the little-endian unsigned integer
|
||||
denoted by the next 2 bytes.
|
||||
- For l == 3, this tag is a legacy format that is no longer issued by most
|
||||
encoders. Nonetheless, the offset ranges in [0, 1<<32) and the length in
|
||||
[1, 65). The length is 1 + m. The offset is the little-endian unsigned
|
||||
integer denoted by the next 4 bytes.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const (
|
||||
tagLiteral = 0x00
|
||||
tagCopy1 = 0x01
|
||||
tagCopy2 = 0x02
|
||||
tagCopy4 = 0x03
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
checksumSize = 4
|
||||
chunkHeaderSize = 4
|
||||
magicChunk = "\xff\x06\x00\x00" + magicBody
|
||||
magicBody = "sNaPpY"
|
||||
|
||||
// maxBlockSize is the maximum size of the input to encodeBlock. It is not
|
||||
// part of the wire format per se, but some parts of the encoder assume
|
||||
// that an offset fits into a uint16.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Also, for the framing format (Writer type instead of Encode function),
|
||||
// https://github.com/google/snappy/blob/master/framing_format.txt says
|
||||
// that "the uncompressed data in a chunk must be no longer than 65536
|
||||
// bytes".
|
||||
maxBlockSize = 65536
|
||||
|
||||
// maxEncodedLenOfMaxBlockSize equals MaxEncodedLen(maxBlockSize), but is
|
||||
// hard coded to be a const instead of a variable, so that obufLen can also
|
||||
// be a const. Their equivalence is confirmed by
|
||||
// TestMaxEncodedLenOfMaxBlockSize.
|
||||
maxEncodedLenOfMaxBlockSize = 76490
|
||||
|
||||
obufHeaderLen = len(magicChunk) + checksumSize + chunkHeaderSize
|
||||
obufLen = obufHeaderLen + maxEncodedLenOfMaxBlockSize
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
chunkTypeCompressedData = 0x00
|
||||
chunkTypeUncompressedData = 0x01
|
||||
chunkTypePadding = 0xfe
|
||||
chunkTypeStreamIdentifier = 0xff
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var crcTable = crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
|
||||
|
||||
// crc implements the checksum specified in section 3 of
|
||||
// https://github.com/google/snappy/blob/master/framing_format.txt
|
||||
func crc(b []byte) uint32 {
|
||||
c := crc32.Update(0, crcTable, b)
|
||||
return uint32(c>>15|c<<17) + 0xa282ead8
|
||||
}
|
||||
42
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
42
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
# Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, contributions are more than welcome. Please read these guidelines for
|
||||
making the process as painless as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Discussion
|
||||
|
||||
Development discussion should take place on the #mage channel of [gopher
|
||||
slack](https://gophers.slack.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
There is a separate #mage-dev channel that has the github app to post github
|
||||
activity to the channel, to make it easy to follow.
|
||||
|
||||
## Issues
|
||||
|
||||
If there's an issue you'd like to work on, please comment on it, so we can
|
||||
discuss approach, etc. and make sure no one else is currently working on that
|
||||
issue.
|
||||
|
||||
Please always create an issue before sending a PR unless it's an obvious typo
|
||||
or other trivial change.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dependency Management
|
||||
|
||||
Currently mage has no dependencies(!) outside the standard libary. Let's keep
|
||||
it that way. Since it's likely that mage will be vendored into a project,
|
||||
adding dependencies to mage adds dependencies to every project that uses mage.
|
||||
|
||||
## Versions
|
||||
|
||||
Please avoid using features of go and the stdlib that prevent mage from being
|
||||
buildable with older versions of Go. The CI tests currently check that mage is
|
||||
buildable with go 1.7 and later. You may build with whatever version you like,
|
||||
but CI has the final say.
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing
|
||||
|
||||
Please write tests for any new features. Tests must use the normal go testing
|
||||
package.
|
||||
|
||||
Tests must pass the race detector (run `go test -race ./...`).
|
||||
|
||||
9
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/Gopkg.lock
generated
vendored
Normal file
9
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/Gopkg.lock
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# This file is autogenerated, do not edit; changes may be undone by the next 'dep ensure'.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[solve-meta]
|
||||
analyzer-name = "dep"
|
||||
analyzer-version = 1
|
||||
inputs-digest = "ab4fef131ee828e96ba67d31a7d690bd5f2f42040c6766b1b12fe856f87e0ff7"
|
||||
solver-name = "gps-cdcl"
|
||||
solver-version = 1
|
||||
22
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/Gopkg.toml
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/Gopkg.toml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Gopkg.toml example
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Refer to https://github.com/golang/dep/blob/master/docs/Gopkg.toml.md
|
||||
# for detailed Gopkg.toml documentation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# required = ["github.com/user/thing/cmd/thing"]
|
||||
# ignored = ["github.com/user/project/pkgX", "bitbucket.org/user/project/pkgA/pkgY"]
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[constraint]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/user/project"
|
||||
# version = "1.0.0"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[constraint]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/user/project2"
|
||||
# branch = "dev"
|
||||
# source = "github.com/myfork/project2"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[override]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/x/y"
|
||||
# version = "2.4.0"
|
||||
|
||||
201
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
201
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
||||
Apache License
|
||||
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
||||
|
||||
1. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
||||
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
||||
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
||||
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
||||
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
||||
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
||||
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
||||
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
||||
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
||||
|
||||
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
||||
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
||||
source, and configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
||||
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
||||
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
||||
and conversions to other media types.
|
||||
|
||||
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
||||
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
||||
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
||||
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
||||
|
||||
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
||||
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
||||
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
||||
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
||||
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
||||
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
||||
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
||||
|
||||
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
||||
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
||||
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
||||
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
||||
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
||||
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
||||
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
||||
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
||||
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
||||
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
||||
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
||||
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
||||
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
||||
|
||||
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
||||
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
||||
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
||||
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
||||
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
||||
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
||||
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
||||
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
||||
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
||||
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
||||
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
||||
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
||||
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
||||
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
||||
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
||||
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
||||
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
||||
meet the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
||||
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
||||
|
||||
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
||||
stating that You changed the files; and
|
||||
|
||||
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
||||
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
||||
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
||||
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
||||
the Derivative Works; and
|
||||
|
||||
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
||||
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
||||
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
||||
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
||||
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
||||
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
||||
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
||||
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
||||
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
||||
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
||||
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
||||
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
||||
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
||||
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
||||
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
||||
as modifying the License.
|
||||
|
||||
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
||||
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
||||
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
||||
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
||||
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
||||
the conditions stated in this License.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
||||
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
||||
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
||||
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
||||
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
||||
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
||||
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
||||
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
||||
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
||||
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
||||
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
||||
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
||||
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
||||
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
||||
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
||||
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
||||
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
||||
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
||||
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
||||
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
||||
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
||||
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
||||
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
||||
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
||||
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
||||
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
||||
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
||||
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
||||
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
||||
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
||||
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
||||
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
||||
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
||||
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
||||
|
||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
||||
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "{}"
|
||||
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
||||
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
||||
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
||||
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
||||
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
||||
identification within third-party archives.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright {yyyy} {name of copyright owner}
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
61
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
61
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/3185864/32058716-5ee9b512-ba38-11e7-978a-287eb2a62743.png"/></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## About [](https://travis-ci.org/magefile/mage)
|
||||
|
||||
Mage is a make/rake-like build tool using Go. You write plain-old go functions,
|
||||
and Mage automatically uses them as Makefile-like runnable targets.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Mage has no dependencies outside the Go standard library, and builds with Go 1.7
|
||||
and above (possibly even lower versions, but they're not regularly tested).
|
||||
|
||||
Install mage by running
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go get -u -d github.com/magefile/mage
|
||||
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/magefile/mage
|
||||
go run bootstrap.go
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will download the code into your GOPATH, and then run the bootstrap script
|
||||
to build mage with version infomation embedded in it. A normal `go get`
|
||||
(without -d) will build the binary correctly, but no version info will be
|
||||
embedded. If you've done this, no worries, just go to
|
||||
$GOPATH/src/github.com/magefile/mage and run `mage install` or `go run
|
||||
bootstrap.go` and a new binary will be created with the correct version
|
||||
information.
|
||||
|
||||
The mage binary will be created in your $GOPATH/bin directory.
|
||||
|
||||
You may also install a binary release from our
|
||||
[releases](https://github.com/magefile/mage/releases) page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Demo
|
||||
|
||||
[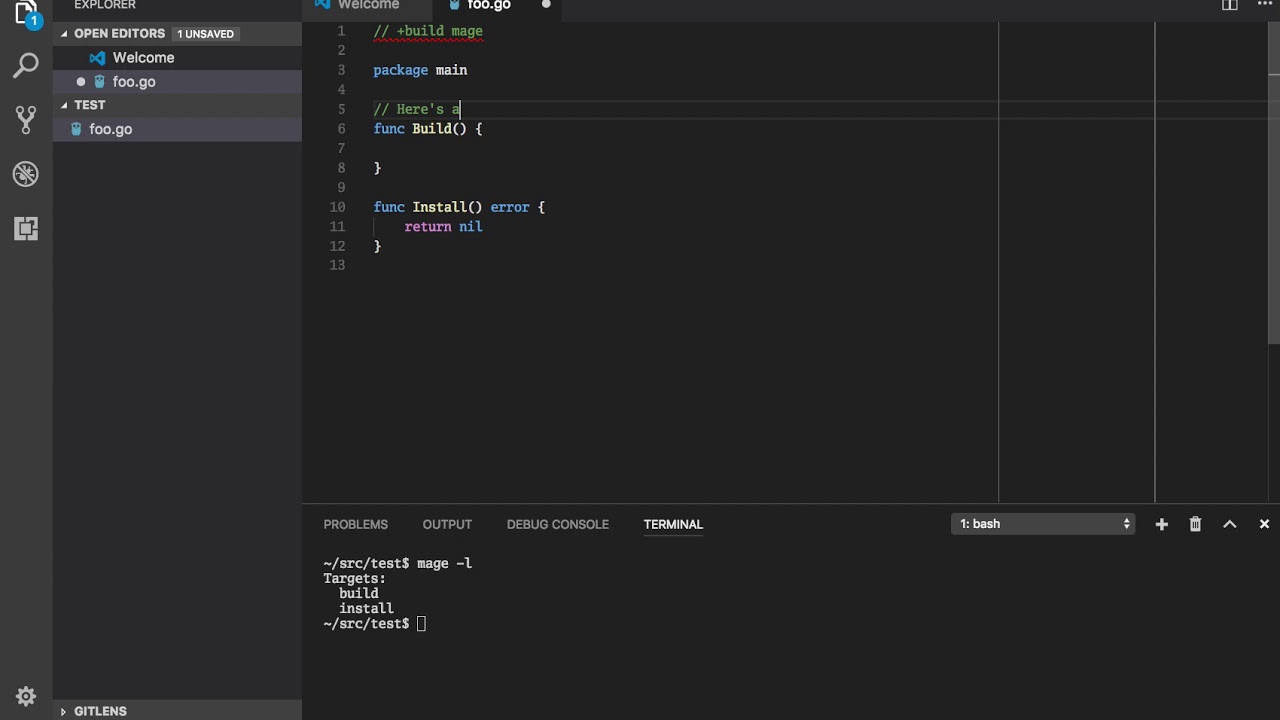](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GOqbD0lF-iA)
|
||||
|
||||
## Discussion
|
||||
|
||||
Join the `#mage` channel on [gophers slack](https://gophers.slack.com/messages/general/) for discussion of usage, development, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
# Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
see [magefile.org](https://magefile.org) for full docs
|
||||
|
||||
see [godoc.org/github.com/magefile/mage/mage](https://godoc.org/github.com/magefile/mage/mage) for how to use mage as a library.
|
||||
|
||||
# Why?
|
||||
|
||||
Makefiles are hard to read and hard to write. Mostly because makefiles are essentially fancy bash scripts with significant white space and additional make-related syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
Mage lets you have multiple magefiles, name your magefiles whatever you
|
||||
want, and they're easy to customize for multiple operating systems. Mage has no
|
||||
dependencies (aside from go) and runs just fine on all major operating systems, whereas make generally uses bash which is not well supported on Windows.
|
||||
Go is superior to bash for any non-trivial task involving branching, looping, anything that's not just straight line execution of commands. And if your project is written in Go, why introduce another
|
||||
language as idiosyncratic as bash? Why not use the language your contributors
|
||||
are already comfortable with?
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO
|
||||
|
||||
* File conversion tasks
|
||||
19
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/bootstrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
19
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/bootstrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
//+build ignore
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/mage"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// This is a bootstrap builder, to build mage when you don't already *have* mage.
|
||||
// Run it like
|
||||
// go run bootstrap.go
|
||||
// and it will install mage with all the right flags created for you.
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
os.Args = []string{os.Args[0], "-v", "install"}
|
||||
os.Exit(mage.Main())
|
||||
}
|
||||
1655
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/build.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
1655
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/build.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
166
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
166
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package build gathers information about Go packages.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Go Path
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Go path is a list of directory trees containing Go source code.
|
||||
// It is consulted to resolve imports that cannot be found in the standard
|
||||
// Go tree. The default path is the value of the GOPATH environment
|
||||
// variable, interpreted as a path list appropriate to the operating system
|
||||
// (on Unix, the variable is a colon-separated string;
|
||||
// on Windows, a semicolon-separated string;
|
||||
// on Plan 9, a list).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Each directory listed in the Go path must have a prescribed structure:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The src/ directory holds source code. The path below 'src' determines
|
||||
// the import path or executable name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The pkg/ directory holds installed package objects.
|
||||
// As in the Go tree, each target operating system and
|
||||
// architecture pair has its own subdirectory of pkg
|
||||
// (pkg/GOOS_GOARCH).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If DIR is a directory listed in the Go path, a package with
|
||||
// source in DIR/src/foo/bar can be imported as "foo/bar" and
|
||||
// has its compiled form installed to "DIR/pkg/GOOS_GOARCH/foo/bar.a"
|
||||
// (or, for gccgo, "DIR/pkg/gccgo/foo/libbar.a").
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The bin/ directory holds compiled commands.
|
||||
// Each command is named for its source directory, but only
|
||||
// using the final element, not the entire path. That is, the
|
||||
// command with source in DIR/src/foo/quux is installed into
|
||||
// DIR/bin/quux, not DIR/bin/foo/quux. The foo/ is stripped
|
||||
// so that you can add DIR/bin to your PATH to get at the
|
||||
// installed commands.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Here's an example directory layout:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// GOPATH=/home/user/gocode
|
||||
//
|
||||
// /home/user/gocode/
|
||||
// src/
|
||||
// foo/
|
||||
// bar/ (go code in package bar)
|
||||
// x.go
|
||||
// quux/ (go code in package main)
|
||||
// y.go
|
||||
// bin/
|
||||
// quux (installed command)
|
||||
// pkg/
|
||||
// linux_amd64/
|
||||
// foo/
|
||||
// bar.a (installed package object)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Build Constraints
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A build constraint, also known as a build tag, is a line comment that begins
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build
|
||||
//
|
||||
// that lists the conditions under which a file should be included in the package.
|
||||
// Constraints may appear in any kind of source file (not just Go), but
|
||||
// they must appear near the top of the file, preceded
|
||||
// only by blank lines and other line comments. These rules mean that in Go
|
||||
// files a build constraint must appear before the package clause.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To distinguish build constraints from package documentation, a series of
|
||||
// build constraints must be followed by a blank line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A build constraint is evaluated as the OR of space-separated options;
|
||||
// each option evaluates as the AND of its comma-separated terms;
|
||||
// and each term is an alphanumeric word or, preceded by !, its negation.
|
||||
// That is, the build constraint:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build linux,386 darwin,!cgo
|
||||
//
|
||||
// corresponds to the boolean formula:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (linux AND 386) OR (darwin AND (NOT cgo))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A file may have multiple build constraints. The overall constraint is the AND
|
||||
// of the individual constraints. That is, the build constraints:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build linux darwin
|
||||
// // +build 386
|
||||
//
|
||||
// corresponds to the boolean formula:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (linux OR darwin) AND 386
|
||||
//
|
||||
// During a particular build, the following words are satisfied:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - the target operating system, as spelled by runtime.GOOS
|
||||
// - the target architecture, as spelled by runtime.GOARCH
|
||||
// - the compiler being used, either "gc" or "gccgo"
|
||||
// - "cgo", if ctxt.CgoEnabled is true
|
||||
// - "go1.1", from Go version 1.1 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.2", from Go version 1.2 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.3", from Go version 1.3 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.4", from Go version 1.4 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.5", from Go version 1.5 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.6", from Go version 1.6 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.7", from Go version 1.7 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.8", from Go version 1.8 onward
|
||||
// - "go1.9", from Go version 1.9 onward
|
||||
// - any additional words listed in ctxt.BuildTags
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If a file's name, after stripping the extension and a possible _test suffix,
|
||||
// matches any of the following patterns:
|
||||
// *_GOOS
|
||||
// *_GOARCH
|
||||
// *_GOOS_GOARCH
|
||||
// (example: source_windows_amd64.go) where GOOS and GOARCH represent
|
||||
// any known operating system and architecture values respectively, then
|
||||
// the file is considered to have an implicit build constraint requiring
|
||||
// those terms (in addition to any explicit constraints in the file).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To keep a file from being considered for the build:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build ignore
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (any other unsatisfied word will work as well, but ``ignore'' is conventional.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To build a file only when using cgo, and only on Linux and OS X:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build linux,cgo darwin,cgo
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Such a file is usually paired with another file implementing the
|
||||
// default functionality for other systems, which in this case would
|
||||
// carry the constraint:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // +build !linux,!darwin !cgo
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Naming a file dns_windows.go will cause it to be included only when
|
||||
// building the package for Windows; similarly, math_386.s will be included
|
||||
// only when building the package for 32-bit x86.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Using GOOS=android matches build tags and files as for GOOS=linux
|
||||
// in addition to android tags and files.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Binary-Only Packages
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It is possible to distribute packages in binary form without including the
|
||||
// source code used for compiling the package. To do this, the package must
|
||||
// be distributed with a source file not excluded by build constraints and
|
||||
// containing a "//go:binary-only-package" comment.
|
||||
// Like a build constraint, this comment must appear near the top of the file,
|
||||
// preceded only by blank lines and other line comments and with a blank line
|
||||
// following the comment, to separate it from the package documentation.
|
||||
// Unlike build constraints, this comment is only recognized in non-test
|
||||
// Go source files.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The minimal source code for a binary-only package is therefore:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// //go:binary-only-package
|
||||
//
|
||||
// package mypkg
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The source code may include additional Go code. That code is never compiled
|
||||
// but will be processed by tools like godoc and might be useful as end-user
|
||||
// documentation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
package build
|
||||
247
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/read.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
247
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/read.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,247 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package build
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type importReader struct {
|
||||
b *bufio.Reader
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
peek byte
|
||||
err error
|
||||
eof bool
|
||||
nerr int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isIdent(c byte) bool {
|
||||
return 'A' <= c && c <= 'Z' || 'a' <= c && c <= 'z' || '0' <= c && c <= '9' || c == '_' || c >= utf8.RuneSelf
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errSyntax = errors.New("syntax error")
|
||||
errNUL = errors.New("unexpected NUL in input")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// syntaxError records a syntax error, but only if an I/O error has not already been recorded.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) syntaxError() {
|
||||
if r.err == nil {
|
||||
r.err = errSyntax
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readByte reads the next byte from the input, saves it in buf, and returns it.
|
||||
// If an error occurs, readByte records the error in r.err and returns 0.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) readByte() byte {
|
||||
c, err := r.b.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
r.buf = append(r.buf, c)
|
||||
if c == 0 {
|
||||
err = errNUL
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
r.eof = true
|
||||
} else if r.err == nil {
|
||||
r.err = err
|
||||
}
|
||||
c = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// peekByte returns the next byte from the input reader but does not advance beyond it.
|
||||
// If skipSpace is set, peekByte skips leading spaces and comments.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) peekByte(skipSpace bool) byte {
|
||||
if r.err != nil {
|
||||
if r.nerr++; r.nerr > 10000 {
|
||||
panic("go/build: import reader looping")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Use r.peek as first input byte.
|
||||
// Don't just return r.peek here: it might have been left by peekByte(false)
|
||||
// and this might be peekByte(true).
|
||||
c := r.peek
|
||||
if c == 0 {
|
||||
c = r.readByte()
|
||||
}
|
||||
for r.err == nil && !r.eof {
|
||||
if skipSpace {
|
||||
// For the purposes of this reader, semicolons are never necessary to
|
||||
// understand the input and are treated as spaces.
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case ' ', '\f', '\t', '\r', '\n', ';':
|
||||
c = r.readByte()
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
case '/':
|
||||
c = r.readByte()
|
||||
if c == '/' {
|
||||
for c != '\n' && r.err == nil && !r.eof {
|
||||
c = r.readByte()
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if c == '*' {
|
||||
var c1 byte
|
||||
for (c != '*' || c1 != '/') && r.err == nil {
|
||||
if r.eof {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
c, c1 = c1, r.readByte()
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
c = r.readByte()
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.peek = c
|
||||
return r.peek
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// nextByte is like peekByte but advances beyond the returned byte.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) nextByte(skipSpace bool) byte {
|
||||
c := r.peekByte(skipSpace)
|
||||
r.peek = 0
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readKeyword reads the given keyword from the input.
|
||||
// If the keyword is not present, readKeyword records a syntax error.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) readKeyword(kw string) {
|
||||
r.peekByte(true)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(kw); i++ {
|
||||
if r.nextByte(false) != kw[i] {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if isIdent(r.peekByte(false)) {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readIdent reads an identifier from the input.
|
||||
// If an identifier is not present, readIdent records a syntax error.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) readIdent() {
|
||||
c := r.peekByte(true)
|
||||
if !isIdent(c) {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for isIdent(r.peekByte(false)) {
|
||||
r.peek = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readString reads a quoted string literal from the input.
|
||||
// If an identifier is not present, readString records a syntax error.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) readString(save *[]string) {
|
||||
switch r.nextByte(true) {
|
||||
case '`':
|
||||
start := len(r.buf) - 1
|
||||
for r.err == nil {
|
||||
if r.nextByte(false) == '`' {
|
||||
if save != nil {
|
||||
*save = append(*save, string(r.buf[start:]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.eof {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case '"':
|
||||
start := len(r.buf) - 1
|
||||
for r.err == nil {
|
||||
c := r.nextByte(false)
|
||||
if c == '"' {
|
||||
if save != nil {
|
||||
*save = append(*save, string(r.buf[start:]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.eof || c == '\n' {
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c == '\\' {
|
||||
r.nextByte(false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
r.syntaxError()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readImport reads an import clause - optional identifier followed by quoted string -
|
||||
// from the input.
|
||||
func (r *importReader) readImport(imports *[]string) {
|
||||
c := r.peekByte(true)
|
||||
if c == '.' {
|
||||
r.peek = 0
|
||||
} else if isIdent(c) {
|
||||
r.readIdent()
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.readString(imports)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readComments is like ioutil.ReadAll, except that it only reads the leading
|
||||
// block of comments in the file.
|
||||
func readComments(f io.Reader) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
r := &importReader{b: bufio.NewReader(f)}
|
||||
r.peekByte(true)
|
||||
if r.err == nil && !r.eof {
|
||||
// Didn't reach EOF, so must have found a non-space byte. Remove it.
|
||||
r.buf = r.buf[:len(r.buf)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r.buf, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readImports is like ioutil.ReadAll, except that it expects a Go file as input
|
||||
// and stops reading the input once the imports have completed.
|
||||
func readImports(f io.Reader, reportSyntaxError bool, imports *[]string) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
r := &importReader{b: bufio.NewReader(f)}
|
||||
|
||||
r.readKeyword("package")
|
||||
r.readIdent()
|
||||
for r.peekByte(true) == 'i' {
|
||||
r.readKeyword("import")
|
||||
if r.peekByte(true) == '(' {
|
||||
r.nextByte(false)
|
||||
for r.peekByte(true) != ')' && r.err == nil {
|
||||
r.readImport(imports)
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.nextByte(false)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.readImport(imports)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we stopped successfully before EOF, we read a byte that told us we were done.
|
||||
// Return all but that last byte, which would cause a syntax error if we let it through.
|
||||
if r.err == nil && !r.eof {
|
||||
return r.buf[:len(r.buf)-1], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we stopped for a syntax error, consume the whole file so that
|
||||
// we are sure we don't change the errors that go/parser returns.
|
||||
if r.err == errSyntax && !reportSyntaxError {
|
||||
r.err = nil
|
||||
for r.err == nil && !r.eof {
|
||||
r.readByte()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r.buf, r.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
8
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/syslist.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
8
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/syslist.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package build
|
||||
|
||||
const goosList = "android darwin dragonfly freebsd linux nacl netbsd openbsd plan9 solaris windows zos "
|
||||
const goarchList = "386 amd64 amd64p32 arm armbe arm64 arm64be ppc64 ppc64le mips mipsle mips64 mips64le mips64p32 mips64p32le ppc s390 s390x sparc sparc64 "
|
||||
37
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/zcgo.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
37
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/build/zcgo.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
// auto generated by go tool dist
|
||||
|
||||
package build
|
||||
|
||||
const defaultCGO_ENABLED = ""
|
||||
|
||||
var cgoEnabled = map[string]bool{
|
||||
"android/386": true,
|
||||
"android/amd64": true,
|
||||
"android/arm": true,
|
||||
"android/arm64": true,
|
||||
"darwin/386": true,
|
||||
"darwin/amd64": true,
|
||||
"darwin/arm": true,
|
||||
"darwin/arm64": true,
|
||||
"dragonfly/amd64": true,
|
||||
"freebsd/386": true,
|
||||
"freebsd/amd64": true,
|
||||
"linux/386": true,
|
||||
"linux/amd64": true,
|
||||
"linux/arm": true,
|
||||
"linux/arm64": true,
|
||||
"linux/mips": true,
|
||||
"linux/mips64": true,
|
||||
"linux/mips64le": true,
|
||||
"linux/mipsle": true,
|
||||
"linux/ppc64le": true,
|
||||
"linux/s390x": true,
|
||||
"netbsd/386": true,
|
||||
"netbsd/amd64": true,
|
||||
"netbsd/arm": true,
|
||||
"openbsd/386": true,
|
||||
"openbsd/amd64": true,
|
||||
"solaris/amd64": true,
|
||||
"windows/386": true,
|
||||
"windows/amd64": true,
|
||||
}
|
||||
16
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/command_string.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
16
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/command_string.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// Code generated by "stringer -type=Command"; DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package mage
|
||||
|
||||
import "fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
const _Command_name = "NoneVersionInitClean"
|
||||
|
||||
var _Command_index = [...]uint8{0, 4, 11, 15, 20}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i Command) String() string {
|
||||
if i < 0 || i >= Command(len(_Command_index)-1) {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("Command(%d)", i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return _Command_name[_Command_index[i]:_Command_index[i+1]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/magefile_tmpl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
46
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/magefile_tmpl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
package mage
|
||||
|
||||
var mageTpl = `// +build mage
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/mg" // mg contains helpful utility functions, like Deps
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Default target to run when none is specified
|
||||
// If not set, running mage will list available targets
|
||||
// var Default = Build
|
||||
|
||||
// A build step that requires additional params, or platform specific steps for example
|
||||
func Build() error {
|
||||
mg.Deps(InstallDeps)
|
||||
fmt.Println("Building...")
|
||||
cmd := exec.Command("go", "build", "-o", "MyApp", ".")
|
||||
return cmd.Run()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A custom install step if you need your bin someplace other than go/bin
|
||||
func Install() error {
|
||||
mg.Deps(Build)
|
||||
fmt.Println("Installing...")
|
||||
return os.Rename("./MyApp", "/usr/bin/MyApp")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Manage your deps, or running package managers.
|
||||
func InstallDeps() error {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Installing Deps...")
|
||||
cmd := exec.Command("go", "get", "github.com/stretchr/piglatin")
|
||||
return cmd.Run()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clean up after yourself
|
||||
func Clean() {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Cleaning...")
|
||||
os.RemoveAll("MyApp")
|
||||
}
|
||||
`
|
||||
459
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/main.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
459
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/main.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,459 @@
|
||||
package mage
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"crypto/sha1"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"flag"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"text/template"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/build"
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/mg"
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/parse"
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/sh"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// magicRebuildKey is used when hashing the output binary to ensure that we get
|
||||
// a new binary even if nothing in the input files or generated mainfile has
|
||||
// changed. This can be used when we change how we parse files, or otherwise
|
||||
// change the inputs to the compiling process.
|
||||
const magicRebuildKey = "v0.3"
|
||||
|
||||
var output = template.Must(template.New("").Funcs(map[string]interface{}{
|
||||
"lower": strings.ToLower,
|
||||
"lowerfirst": func(s string) string {
|
||||
r := []rune(s)
|
||||
return string(unicode.ToLower(r[0])) + string(r[1:])
|
||||
},
|
||||
}).Parse(tpl))
|
||||
var initOutput = template.Must(template.New("").Parse(mageTpl))
|
||||
|
||||
const mainfile = "mage_output_file.go"
|
||||
const initFile = "magefile.go"
|
||||
|
||||
// set by ldflags when you "mage build"
|
||||
var (
|
||||
commitHash string
|
||||
timestamp string
|
||||
gitTag = "v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
//go:generate stringer -type=Command
|
||||
|
||||
// Command tracks invocations of mage that run without targets or other flags.
|
||||
type Command int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
None Command = iota
|
||||
Version // report the current version of mage
|
||||
Init // create a starting template for mage
|
||||
Clean // clean out old compiled mage binaries from the cache
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Main is the entrypoint for running mage. It exists external to mage's main
|
||||
// function to allow it to be used from other programs, specifically so you can
|
||||
// go run a simple file that run's mage's Main.
|
||||
func Main() int {
|
||||
return ParseAndRun(".", os.Stdout, os.Stderr, os.Stdin, os.Args[1:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Invocation contains the args for invoking a run of Mage.
|
||||
type Invocation struct {
|
||||
Dir string // directory to read magefiles from
|
||||
Force bool // forces recreation of the compiled binary
|
||||
Verbose bool // tells the magefile to print out log statements
|
||||
List bool // tells the magefile to print out a list of targets
|
||||
Help bool // tells the magefile to print out help for a specific target
|
||||
Keep bool // tells mage to keep the generated main file after compiling
|
||||
Timeout time.Duration // tells mage to set a timeout to running the targets
|
||||
Stdout io.Writer // writer to write stdout messages to
|
||||
Stderr io.Writer // writer to write stderr messages to
|
||||
Stdin io.Reader // reader to read stdin from
|
||||
Args []string // args to pass to the compiled binary
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseAndRun parses the command line, and then compiles and runs the mage
|
||||
// files in the given directory with the given args (do not include the command
|
||||
// name in the args).
|
||||
func ParseAndRun(dir string, stdout, stderr io.Writer, stdin io.Reader, args []string) int {
|
||||
log := log.New(stderr, "", 0)
|
||||
inv, cmd, err := Parse(stdout, args)
|
||||
inv.Dir = dir
|
||||
inv.Stderr = stderr
|
||||
inv.Stdin = stdin
|
||||
if err == flag.ErrHelp {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch cmd {
|
||||
case Version:
|
||||
if timestamp == "" {
|
||||
timestamp = "<not set>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
if commitHash == "" {
|
||||
commitHash = "<not set>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.Println("Mage Build Tool", gitTag)
|
||||
log.Println("Build Date:", timestamp)
|
||||
log.Println("Commit:", commitHash)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
case Init:
|
||||
if err := generateInit(dir); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.Println(initFile, "created")
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
case Clean:
|
||||
dir := mg.CacheDir()
|
||||
if err := removeContents(dir); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.Println(dir, "cleaned")
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
case None:
|
||||
return Invoke(inv)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("Unknown command type: %v", cmd))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses the given args and returns structured data. If parse returns
|
||||
// flag.ErrHelp, the calling process should exit with code 0.
|
||||
func Parse(stdout io.Writer, args []string) (inv Invocation, cmd Command, err error) {
|
||||
inv.Stdout = stdout
|
||||
fs := flag.FlagSet{}
|
||||
fs.SetOutput(stdout)
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&inv.Force, "f", false, "force recreation of compiled magefile")
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&inv.Verbose, "v", false, "show verbose output when running mage targets")
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&inv.List, "l", false, "list mage targets in this directory")
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&inv.Help, "h", false, "show this help")
|
||||
fs.DurationVar(&inv.Timeout, "t", 0, "timeout in duration parsable format (e.g. 5m30s)")
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&inv.Keep, "keep", false, "keep intermediate mage files around after running")
|
||||
var showVersion bool
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&showVersion, "version", false, "show version info for the mage binary")
|
||||
var mageInit bool
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&mageInit, "init", false, "create a starting template if no mage files exist")
|
||||
var clean bool
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(&clean, "clean", false, "clean out old generated binaries from CACHE_DIR")
|
||||
|
||||
fs.Usage = func() {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(stdout, "mage [options] [target]")
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(stdout, "Options:")
|
||||
fs.PrintDefaults()
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = fs.Parse(args)
|
||||
if err == flag.ErrHelp {
|
||||
// parse will have already called fs.Usage()
|
||||
return inv, cmd, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err == nil && inv.Help && len(fs.Args()) == 0 {
|
||||
fs.Usage()
|
||||
// tell upstream, to just exit
|
||||
return inv, cmd, flag.ErrHelp
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
numFlags := 0
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case mageInit:
|
||||
numFlags++
|
||||
cmd = Init
|
||||
case showVersion:
|
||||
numFlags++
|
||||
cmd = Version
|
||||
case clean:
|
||||
numFlags++
|
||||
cmd = Clean
|
||||
if fs.NArg() > 0 || fs.NFlag() > 1 {
|
||||
// Temporary dupe of below check until we refactor the other commands to use this check
|
||||
return inv, cmd, errors.New("-h, -init, -clean, and -version cannot be used simultaneously")
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if inv.Help {
|
||||
numFlags++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If verbose is still false, we're going to peek at the environment variable to see if
|
||||
// MAGE_VERBOSE has been set. If so, we're going to use it for the value of MAGE_VERBOSE.
|
||||
if inv.Verbose == false {
|
||||
envVerbose, err := strconv.ParseBool(os.Getenv("MAGE_VERBOSE"))
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
inv.Verbose = envVerbose
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if numFlags > 1 {
|
||||
return inv, cmd, errors.New("-h, -init, -clean, and -version cannot be used simultaneously")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inv.Args = fs.Args()
|
||||
if inv.Help && len(inv.Args) > 1 {
|
||||
return inv, cmd, errors.New("-h can only show help for a single target")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return inv, cmd, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Invoke runs Mage with the given arguments.
|
||||
func Invoke(inv Invocation) int {
|
||||
log := log.New(inv.Stderr, "", 0)
|
||||
|
||||
files, err := Magefiles(inv.Dir)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(files) == 0 {
|
||||
log.Println("No .go files marked with the mage build tag in this directory.")
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
exePath, err := ExeName(files)
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !inv.Force {
|
||||
if _, err := os.Stat(exePath); err == nil {
|
||||
return RunCompiled(inv, exePath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parse wants dir + filenames... arg
|
||||
fnames := make([]string, 0, len(files))
|
||||
for i := range files {
|
||||
fnames = append(fnames, filepath.Base(files[i]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
info, err := parse.Package(inv.Dir, fnames)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
hasDupes, names := CheckDupes(info)
|
||||
if hasDupes {
|
||||
log.Println("Build targets must be case insensitive, thus the follow targets conflict:")
|
||||
for _, v := range names {
|
||||
if len(v) > 1 {
|
||||
log.Println(" " + strings.Join(v, ", "))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
main := filepath.Join(inv.Dir, mainfile)
|
||||
if err := GenerateMainfile(main, info); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !inv.Keep {
|
||||
defer os.Remove(main)
|
||||
}
|
||||
files = append(files, main)
|
||||
if err := Compile(exePath, inv.Stdout, inv.Stderr, files); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !inv.Keep {
|
||||
// remove this file before we run the compiled version, in case the
|
||||
// compiled file screws things up. Yes this doubles up with the above
|
||||
// defer, that's ok.
|
||||
os.Remove(main)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return RunCompiled(inv, exePath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CheckDupes checks a package for duplicate target names.
|
||||
func CheckDupes(info *parse.PkgInfo) (hasDupes bool, names map[string][]string) {
|
||||
names = map[string][]string{}
|
||||
lowers := map[string]bool{}
|
||||
for _, f := range info.Funcs {
|
||||
low := strings.ToLower(f.Name)
|
||||
if lowers[low] {
|
||||
hasDupes = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
lowers[low] = true
|
||||
names[low] = append(names[low], f.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return hasDupes, names
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type data struct {
|
||||
Funcs []parse.Function
|
||||
DefaultError bool
|
||||
Default string
|
||||
DefaultFunc parse.Function
|
||||
Aliases map[string]string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Magefiles returns the list of magefiles in dir.
|
||||
func Magefiles(dir string) ([]string, error) {
|
||||
ctx := build.Default
|
||||
ctx.RequiredTags = []string{"mage"}
|
||||
ctx.BuildTags = []string{"mage"}
|
||||
p, err := ctx.ImportDir(dir, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if _, ok := err.(*build.NoGoError); ok {
|
||||
return []string{}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range p.GoFiles {
|
||||
p.GoFiles[i] = filepath.Join(dir, p.GoFiles[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p.GoFiles, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compile uses the go tool to compile the files into an executable at path.
|
||||
func Compile(path string, stdout, stderr io.Writer, gofiles []string) error {
|
||||
c := exec.Command("go", append([]string{"build", "-o", path}, gofiles...)...)
|
||||
c.Env = os.Environ()
|
||||
c.Stderr = stderr
|
||||
c.Stdout = stdout
|
||||
err := c.Run()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.New("error compiling magefiles")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, err := os.Stat(path); err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.New("failed to find compiled magefile")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GenerateMainfile creates the mainfile at path with the info from
|
||||
func GenerateMainfile(path string, info *parse.PkgInfo) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Create(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can't create mainfile: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
data := data{
|
||||
Funcs: info.Funcs,
|
||||
Default: info.DefaultName,
|
||||
DefaultFunc: info.DefaultFunc,
|
||||
Aliases: info.Aliases,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
data.DefaultError = info.DefaultIsError
|
||||
|
||||
if err := output.Execute(f, data); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can't execute mainfile template: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExeName reports the executable filename that this version of Mage would
|
||||
// create for the given magefiles.
|
||||
func ExeName(files []string) (string, error) {
|
||||
var hashes []string
|
||||
for _, s := range files {
|
||||
h, err := hashFile(s)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
hashes = append(hashes, h)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// hash the mainfile template to ensure if it gets updated, we make a new
|
||||
// binary.
|
||||
hashes = append(hashes, fmt.Sprintf("%x", sha1.Sum([]byte(tpl))))
|
||||
sort.Strings(hashes)
|
||||
hash := sha1.Sum([]byte(strings.Join(hashes, "") + magicRebuildKey))
|
||||
filename := fmt.Sprintf("%x", hash)
|
||||
|
||||
out := filepath.Join(mg.CacheDir(), filename)
|
||||
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
|
||||
out += ".exe"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func hashFile(fn string) (string, error) {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(fn)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", fmt.Errorf("can't open input file: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
h := sha1.New()
|
||||
if _, err := io.Copy(h, f); err != nil {
|
||||
return "", fmt.Errorf("can't write data to hash: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%x", h.Sum(nil)), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func generateInit(dir string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Create(filepath.Join(dir, initFile))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not create mage template: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
if err := initOutput.Execute(f, nil); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can't execute magefile template: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RunCompiled runs an already-compiled mage command with the given args,
|
||||
func RunCompiled(inv Invocation, exePath string) int {
|
||||
c := exec.Command(exePath, inv.Args...)
|
||||
c.Stderr = inv.Stderr
|
||||
c.Stdout = inv.Stdout
|
||||
c.Stdin = inv.Stdin
|
||||
c.Env = os.Environ()
|
||||
if inv.Verbose {
|
||||
c.Env = append(c.Env, "MAGEFILE_VERBOSE=1")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if inv.List {
|
||||
c.Env = append(c.Env, "MAGEFILE_LIST=1")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if inv.Help {
|
||||
c.Env = append(c.Env, "MAGEFILE_HELP=1")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if inv.Timeout > 0 {
|
||||
c.Env = append(c.Env, fmt.Sprintf("MAGEFILE_TIMEOUT=%s", inv.Timeout.String()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sh.ExitStatus(c.Run())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func removeContents(dir string) error {
|
||||
files, err := ioutil.ReadDir(dir)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, f := range files {
|
||||
if f.IsDir() {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = os.Remove(filepath.Join(dir, f.Name()))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
202
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/template.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
202
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mage/template.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
|
||||
package mage
|
||||
|
||||
// var only for tests
|
||||
var tpl = `// +build ignore
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"text/tabwriter"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
// These functions are local variables to avoid name conflicts with
|
||||
// magefiles.
|
||||
list := func() error {
|
||||
{{- $default := .Default}}
|
||||
w := tabwriter.NewWriter(os.Stdout, 0, 4, 4, ' ', 0)
|
||||
fmt.Println("Targets:")
|
||||
{{- range .Funcs}}
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(w, " {{lowerfirst .Name}}{{if eq .Name $default}}*{{end}}\t" + {{printf "%q" .Synopsis}})
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
err := w.Flush()
|
||||
{{- if .Default}}
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("\n* default target")
|
||||
}
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var ctx context.Context
|
||||
var ctxCancel func()
|
||||
|
||||
getContext := func() (context.Context, func()) {
|
||||
if ctx != nil {
|
||||
return ctx, ctxCancel
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_TIMEOUT") != "" {
|
||||
timeout, err := time.ParseDuration(os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_TIMEOUT"))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("timeout error: %v\n", err)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx, ctxCancel = context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), timeout)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ctx = context.Background()
|
||||
ctxCancel = func() {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ctx, ctxCancel
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
runTarget := func(fn func(context.Context) error) interface{} {
|
||||
var err interface{}
|
||||
ctx, cancel := getContext()
|
||||
d := make(chan interface{})
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
err := recover()
|
||||
d <- err
|
||||
}()
|
||||
err := fn(ctx)
|
||||
d <- err
|
||||
}()
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-ctx.Done():
|
||||
cancel()
|
||||
e := ctx.Err()
|
||||
fmt.Printf("ctx err: %v\n", e)
|
||||
return e
|
||||
case err = <-d:
|
||||
cancel()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// This is necessary in case there aren't any targets, to avoid an unused
|
||||
// variable error.
|
||||
_ = runTarget
|
||||
|
||||
handleError := func(logger *log.Logger, err interface{}) {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
logger.Printf("Error: %v\n", err)
|
||||
type code interface {
|
||||
ExitStatus() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c, ok := err.(code); ok {
|
||||
os.Exit(c.ExitStatus())
|
||||
}
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
_ = handleError
|
||||
|
||||
log.SetFlags(0)
|
||||
if os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_VERBOSE") == "" {
|
||||
log.SetOutput(ioutil.Discard)
|
||||
}
|
||||
logger := log.New(os.Stderr, "", 0)
|
||||
if os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_LIST") != "" {
|
||||
if err := list(); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Println(err)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
targets := map[string]bool {
|
||||
{{range $alias, $funci := .Aliases}}"{{lower $alias}}": true,
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
{{range .Funcs}}"{{lower .Name}}": true,
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var unknown []string
|
||||
for _, arg := range os.Args[1:] {
|
||||
if !targets[strings.ToLower(arg)] {
|
||||
unknown = append(unknown, arg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(unknown) == 1 {
|
||||
logger.Println("Unknown target specified:", unknown[0])
|
||||
os.Exit(2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(unknown) > 1 {
|
||||
logger.Println("Unknown targets specified:", strings.Join(unknown, ", "))
|
||||
os.Exit(2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_HELP") != "" {
|
||||
if len(os.Args) < 2 {
|
||||
logger.Println("no target specified")
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch strings.ToLower(os.Args[1]) {
|
||||
{{range .Funcs}}case "{{lower .Name}}":
|
||||
fmt.Print("mage {{lower .Name}}:\n\n")
|
||||
{{if ne .Comment ""}}fmt.Println({{printf "%q" .Comment}}){{end}}
|
||||
var aliases []string
|
||||
{{- $name := .Name -}}
|
||||
{{range $alias, $func := $.Aliases}}
|
||||
{{if eq $name $func}}aliases = append(aliases, "{{$alias}}"){{end -}}
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
if len(aliases) > 0 {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("Aliases: %s\n\n", strings.Join(aliases, ", "))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
logger.Printf("Unknown target: %q\n", os.Args[1])
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(os.Args) < 2 {
|
||||
{{- if .Default}}
|
||||
{{.DefaultFunc.TemplateString}}
|
||||
handleError(logger, err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
{{- else}}
|
||||
if err := list(); err != nil {
|
||||
logger.Println("Error:", err)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, target := range os.Args[1:] {
|
||||
switch strings.ToLower(target) {
|
||||
{{range $alias, $func := .Aliases}}
|
||||
case "{{lower $alias}}":
|
||||
target = "{{$func}}"
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch strings.ToLower(target) {
|
||||
{{range .Funcs }}
|
||||
case "{{lower .Name}}":
|
||||
if os.Getenv("MAGEFILE_VERBOSE") != "" {
|
||||
logger.Println("Running target:", "{{.Name}}")
|
||||
}
|
||||
{{.TemplateString}}
|
||||
handleError(logger, err)
|
||||
{{- end}}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// should be impossible since we check this above.
|
||||
logger.Printf("Unknown target: %q\n", os.Args[1])
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`
|
||||
94
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/magefile.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
94
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/magefile.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
//+build mage
|
||||
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/sh"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Runs "go install" for mage. This generates the version info the binary.
|
||||
func Install() error {
|
||||
ldf, err := flags()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
name := "mage"
|
||||
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
|
||||
name += ".exe"
|
||||
}
|
||||
gopath, err := sh.Output("go", "env", "GOPATH")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can't determine GOPATH: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
paths := strings.Split(gopath, string([]rune{os.PathListSeparator}))
|
||||
bin := filepath.Join(paths[0], "bin")
|
||||
// specifically don't mkdirall, if you have an invalid gopath in the first
|
||||
// place, that's not on us to fix.
|
||||
if err := os.Mkdir(bin, 0700); err != nil && !os.IsExist(err) {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("failed to create %q: %v", bin, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
path := filepath.Join(bin, name)
|
||||
|
||||
// we use go build here because if someone built with go get, then `go
|
||||
// install` turns into a no-op, and `go install -a` fails on people's
|
||||
// machines that have go installed in a non-writeable directory (such as
|
||||
// normal OS installs in /usr/bin)
|
||||
return sh.RunV("go", "build", "-o", path, "-ldflags="+ldf, "github.com/magefile/mage")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Generates a new release. Expects the TAG environment variable to be set,
|
||||
// which will create a new tag with that name.
|
||||
func Release() (err error) {
|
||||
if os.Getenv("TAG") == "" {
|
||||
return errors.New("MSG and TAG environment variables are required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := sh.RunV("git", "tag", "-a", "$TAG"); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := sh.RunV("git", "push", "origin", "$TAG"); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
sh.RunV("git", "tag", "--delete", "$TAG")
|
||||
sh.RunV("git", "push", "--delete", "origin", "$TAG")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
return sh.RunV("goreleaser")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Remove the temporarily generated files from Release.
|
||||
func Clean() error {
|
||||
return sh.Rm("dist")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func flags() (string, error) {
|
||||
timestamp := time.Now().Format(time.RFC3339)
|
||||
hash := hash()
|
||||
tag := tag()
|
||||
if tag == "" {
|
||||
tag = "dev"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(`-X "github.com/magefile/mage/mage.timestamp=%s" -X "github.com/magefile/mage/mage.commitHash=%s" -X "github.com/magefile/mage/mage.gitTag=%s"`, timestamp, hash, tag), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tag returns the git tag for the current branch or "" if none.
|
||||
func tag() string {
|
||||
s, _ := sh.Output("git", "describe", "--tags")
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hash returns the git hash for the current repo or "" if none.
|
||||
func hash() string {
|
||||
hash, _ := sh.Output("git", "rev-parse", "--short", "HEAD")
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
11
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/main.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/main.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/mage"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
os.Exit(mage.Main())
|
||||
}
|
||||
166
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/deps.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
166
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/deps.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
package mg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type onceMap struct {
|
||||
mu *sync.Mutex
|
||||
m map[string]*onceFun
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *onceMap) LoadOrStore(s string, one *onceFun) *onceFun {
|
||||
defer o.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
o.mu.Lock()
|
||||
|
||||
existing, ok := o.m[s]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
return existing
|
||||
}
|
||||
o.m[s] = one
|
||||
return one
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var onces = &onceMap{
|
||||
mu: &sync.Mutex{},
|
||||
m: map[string]*onceFun{},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SerialDeps is like Deps except it runs each dependency serially, instead of
|
||||
// in parallel. This can be useful for resource intensive dependencies that
|
||||
// shouldn't be run at the same time.
|
||||
func SerialDeps(fns ...interface{}) {
|
||||
checkFns(fns)
|
||||
ctx := context.Background()
|
||||
for _, f := range fns {
|
||||
runDeps(ctx, f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SerialCtxDeps is like CtxDeps except it runs each dependency serially,
|
||||
// instead of in parallel. This can be useful for resource intensive
|
||||
// dependencies that shouldn't be run at the same time.
|
||||
func SerialCtxDeps(ctx context.Context, fns ...interface{}) {
|
||||
checkFns(fns)
|
||||
for _, f := range fns {
|
||||
runDeps(ctx, f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CtxDeps runs the given functions as dependencies of the calling function.
|
||||
// Dependencies must only be of type: github.com/magefile/mage/types.FuncType.
|
||||
// The function calling Deps is guaranteed that all dependent functions will be
|
||||
// run exactly once when Deps returns. Dependent functions may in turn declare
|
||||
// their own dependencies using Deps. Each dependency is run in their own
|
||||
// goroutines. Each function is given the context provided if the function
|
||||
// prototype allows for it.
|
||||
func CtxDeps(ctx context.Context, fns ...interface{}) {
|
||||
checkFns(fns)
|
||||
runDeps(ctx, fns...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// runDeps assumes you've already called checkFns.
|
||||
func runDeps(ctx context.Context, fns ...interface{}) {
|
||||
mu := &sync.Mutex{}
|
||||
var errs []string
|
||||
var exit int
|
||||
wg := &sync.WaitGroup{}
|
||||
for _, f := range fns {
|
||||
fn := addDep(ctx, f)
|
||||
wg.Add(1)
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if v := recover(); v != nil {
|
||||
mu.Lock()
|
||||
if err, ok := v.(error); ok {
|
||||
exit = changeExit(exit, ExitStatus(err))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
exit = changeExit(exit, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
errs = append(errs, fmt.Sprint(v))
|
||||
mu.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
wg.Done()
|
||||
}()
|
||||
if err := fn.run(); err != nil {
|
||||
mu.Lock()
|
||||
errs = append(errs, fmt.Sprint(err))
|
||||
exit = changeExit(exit, ExitStatus(err))
|
||||
mu.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
wg.Wait()
|
||||
if len(errs) > 0 {
|
||||
panic(Fatal(exit, strings.Join(errs, "\n")))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkFns(fns []interface{}) {
|
||||
for _, f := range fns {
|
||||
if err := types.FuncCheck(f); err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Deps runs the given functions with the default runtime context
|
||||
func Deps(fns ...interface{}) {
|
||||
CtxDeps(context.Background(), fns...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func changeExit(old, new int) int {
|
||||
if new == 0 {
|
||||
return old
|
||||
}
|
||||
if old == 0 {
|
||||
return new
|
||||
}
|
||||
if old == new {
|
||||
return old
|
||||
}
|
||||
// both different and both non-zero, just set
|
||||
// exit to 1. Nothing more we can do.
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func addDep(ctx context.Context, f interface{}) *onceFun {
|
||||
var fn func(context.Context) error
|
||||
if fn = types.FuncTypeWrap(f); fn == nil {
|
||||
// should be impossible, since we already checked this
|
||||
panic("attempted to add a dep that did not match required type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n := name(f)
|
||||
of := onces.LoadOrStore(n, &onceFun{
|
||||
fn: fn,
|
||||
ctx: ctx,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return of
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func name(i interface{}) string {
|
||||
return runtime.FuncForPC(reflect.ValueOf(i).Pointer()).Name()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type onceFun struct {
|
||||
once sync.Once
|
||||
fn func(context.Context) error
|
||||
ctx context.Context
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *onceFun) run() error {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
o.once.Do(func() {
|
||||
err = o.fn(o.ctx)
|
||||
})
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
51
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
51
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
package mg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type fatalErr struct {
|
||||
code int
|
||||
error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f fatalErr) ExitStatus() int {
|
||||
return f.code
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type exitStatus interface {
|
||||
ExitStatus() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatal returns an error that will cause mage to print out the
|
||||
// given args and exit with the given exit code.
|
||||
func Fatal(code int, args ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
return fatalErr{
|
||||
code: code,
|
||||
error: errors.New(fmt.Sprint(args...)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatalf returns an error that will cause mage to print out the
|
||||
// given message and exit with an exit code of 1.
|
||||
func Fatalf(code int, format string, args ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
return fatalErr{
|
||||
code: code,
|
||||
error: fmt.Errorf(format, args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitStatus queries the error for an exit status. If the error is nil, it
|
||||
// returns 0. If the error does not implement ExitStatus() int, it returns 1.
|
||||
// Otherwise it retiurns the value from ExitStatus().
|
||||
func ExitStatus(err error) int {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
exit, ok := err.(exitStatus)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return exit.ExitStatus()
|
||||
}
|
||||
36
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/runtime.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
36
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/mg/runtime.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
package mg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CacheEnv is the environment variable that users may set to change the
|
||||
// location where mage stores its compiled binaries.
|
||||
const CacheEnv = "MAGEFILE_CACHE"
|
||||
|
||||
// verboseEnv is the environment variable that indicates the user requested
|
||||
// verbose mode when running a magefile.
|
||||
const verboseEnv = "MAGEFILE_VERBOSE"
|
||||
|
||||
// Verbose reports whether a magefile was run with the verbose flag.
|
||||
func Verbose() bool {
|
||||
return os.Getenv(verboseEnv) != ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CacheDir returns the directory where mage caches compiled binaries. It
|
||||
// defaults to $HOME/.magefile, but may be overridden by the MAGEFILE_CACHE
|
||||
// environment variable.
|
||||
func CacheDir() string {
|
||||
d := os.Getenv(CacheEnv)
|
||||
if d != "" {
|
||||
return d
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch runtime.GOOS {
|
||||
case "windows":
|
||||
return filepath.Join(os.Getenv("HOMEDRIVE"), os.Getenv("HOMEPATH"), "magefile")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return filepath.Join(os.Getenv("HOME"), ".magefile")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/import_go1.9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
13
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/import_go1.9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
// +build go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/importer"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func getImporter(*token.FileSet) types.Importer {
|
||||
return importer.For("source", nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/import_not_go1.9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/import_not_go1.9.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
// +build !go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/build"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/parse/srcimporter"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func getImporter(fset *token.FileSet) types.Importer {
|
||||
return srcimporter.New(&build.Default, fset, make(map[string]*types.Package))
|
||||
}
|
||||
341
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/parse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
341
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/parse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,341 @@
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/build"
|
||||
"go/doc"
|
||||
"go/parser"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
mgTypes "github.com/magefile/mage/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type PkgInfo struct {
|
||||
Funcs []Function
|
||||
DefaultIsError bool
|
||||
DefaultIsContext bool
|
||||
DefaultName string
|
||||
DefaultFunc Function
|
||||
Aliases map[string]string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Function represented a job function from a mage file
|
||||
type Function struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
IsError bool
|
||||
IsContext bool
|
||||
Synopsis string
|
||||
Comment string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TemplateString returns code for the template switch to run the target.
|
||||
// It wraps each target call to match the func(context.Context) error that
|
||||
// runTarget requires.
|
||||
func (f Function) TemplateString() string {
|
||||
if f.IsContext && f.IsError {
|
||||
out := `wrapFn := func(ctx context.Context) error {
|
||||
return %s(ctx)
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := runTarget(wrapFn)`
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(out, f.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f.IsContext && !f.IsError {
|
||||
out := `wrapFn := func(ctx context.Context) error {
|
||||
%s(ctx)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := runTarget(wrapFn)`
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(out, f.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !f.IsContext && f.IsError {
|
||||
out := `wrapFn := func(ctx context.Context) error {
|
||||
return %s()
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := runTarget(wrapFn)`
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(out, f.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !f.IsContext && !f.IsError {
|
||||
out := `wrapFn := func(ctx context.Context) error {
|
||||
%s()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := runTarget(wrapFn)`
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(out, f.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return `fmt.Printf("Error formatting job code\n")
|
||||
os.Exit(1)`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Package parses a package
|
||||
func Package(path string, files []string) (*PkgInfo, error) {
|
||||
fset := token.NewFileSet()
|
||||
|
||||
pkg, err := getPackage(path, files, fset)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
info, err := makeInfo(path, fset, pkg.Files)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pi := &PkgInfo{}
|
||||
|
||||
p := doc.New(pkg, "./", 0)
|
||||
for _, f := range p.Funcs {
|
||||
if f.Recv != "" {
|
||||
// skip methods
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !ast.IsExported(f.Name) {
|
||||
// skip non-exported functions
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typ := voidOrError(f.Decl.Type, info); typ != mgTypes.InvalidType {
|
||||
pi.Funcs = append(pi.Funcs, Function{
|
||||
Name: f.Name,
|
||||
Comment: f.Doc,
|
||||
Synopsis: sanitizeSynopsis(f),
|
||||
IsError: typ == mgTypes.ErrorType || typ == mgTypes.ContextErrorType,
|
||||
IsContext: typ == mgTypes.ContextVoidType || typ == mgTypes.ContextErrorType,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
setDefault(p, pi, info)
|
||||
setAliases(p, pi, info)
|
||||
|
||||
return pi, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sanitizeSynopsis sanitizes function Doc to create a summary.
|
||||
func sanitizeSynopsis(f *doc.Func) string {
|
||||
synopsis := doc.Synopsis(f.Doc)
|
||||
|
||||
// If the synopsis begins with the function name, remove it. This is done to
|
||||
// not repeat the text.
|
||||
// From:
|
||||
// clean Clean removes the temporarily generated files
|
||||
// To:
|
||||
// clean removes the temporarily generated files
|
||||
if syns := strings.Split(synopsis, " "); strings.EqualFold(f.Name, syns[0]) {
|
||||
return strings.Join(syns[1:], " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return synopsis
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func setDefault(p *doc.Package, pi *PkgInfo, info types.Info) {
|
||||
for _, v := range p.Vars {
|
||||
for x, name := range v.Names {
|
||||
if name != "Default" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
spec := v.Decl.Specs[x].(*ast.ValueSpec)
|
||||
if len(spec.Values) != 1 {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: default declaration has multiple values")
|
||||
}
|
||||
id, ok := spec.Values[0].(*ast.Ident)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: default declaration is not a function name")
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, f := range pi.Funcs {
|
||||
if f.Name == id.Name {
|
||||
pi.DefaultName = f.Name
|
||||
pi.DefaultIsError = f.IsError
|
||||
pi.DefaultIsContext = f.IsContext
|
||||
pi.DefaultFunc = f
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.Println("warning: default declaration does not reference a mage target")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func setAliases(p *doc.Package, pi *PkgInfo, info types.Info) {
|
||||
for _, v := range p.Vars {
|
||||
for x, name := range v.Names {
|
||||
if name != "Aliases" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
spec, ok := v.Decl.Specs[x].(*ast.ValueSpec)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: aliases declaration is not a value")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(spec.Values) != 1 {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: aliases declaration has multiple values")
|
||||
}
|
||||
comp, ok := spec.Values[0].(*ast.CompositeLit)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: aliases declaration is not a map")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
pi.Aliases = make(map[string]string)
|
||||
for _, elem := range comp.Elts {
|
||||
kv, ok := elem.(*ast.KeyValueExpr)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: alias declaration is not a map element")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
k, ok := kv.Key.(*ast.BasicLit)
|
||||
if !ok || k.Kind != token.STRING {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: alias is not a string")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
v, ok := kv.Value.(*ast.Ident)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
log.Println("warning: alias target is not a function")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
alias := strings.Trim(k.Value, "\"")
|
||||
valid := false
|
||||
for _, f := range pi.Funcs {
|
||||
valid = valid || f.Name == v.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !valid {
|
||||
log.Printf("warning: alias declaration (%s) does not reference a mage target", alias)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pi.Aliases[alias] = v.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getPackage returns the non-test package at the given path.
|
||||
func getPackage(path string, files []string, fset *token.FileSet) (*ast.Package, error) {
|
||||
fm := make(map[string]bool, len(files))
|
||||
for _, f := range files {
|
||||
fm[f] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
filter := func(f os.FileInfo) bool {
|
||||
return fm[f.Name()]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pkgs, err := parser.ParseDir(fset, path, filter, parser.ParseComments)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse directory: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for name, pkg := range pkgs {
|
||||
if !strings.HasSuffix(name, "_test") {
|
||||
return pkg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no non-test packages found in %s", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func makeInfo(dir string, fset *token.FileSet, files map[string]*ast.File) (types.Info, error) {
|
||||
goroot := os.Getenv("GOROOT")
|
||||
if goroot == "" {
|
||||
c := exec.Command("go", "env", "GOROOT")
|
||||
b, err := c.Output()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return types.Info{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to get GOROOT from 'go env': %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
goroot = strings.TrimSpace(string(b))
|
||||
if goroot == "" {
|
||||
return types.Info{}, fmt.Errorf("could not determine GOROOT")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
build.Default.GOROOT = goroot
|
||||
|
||||
cfg := types.Config{
|
||||
Importer: getImporter(fset),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
info := types.Info{
|
||||
Types: make(map[ast.Expr]types.TypeAndValue),
|
||||
Defs: make(map[*ast.Ident]types.Object),
|
||||
Uses: make(map[*ast.Ident]types.Object),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fs := make([]*ast.File, 0, len(files))
|
||||
for _, v := range files {
|
||||
fs = append(fs, v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, err := cfg.Check(dir, fset, fs, &info)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return info, fmt.Errorf("failed to check types in directory: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return info, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errorOrVoid filters the list of functions to only those that return only an
|
||||
// error or have no return value, and have no parameters.
|
||||
func errorOrVoid(fns []*ast.FuncDecl, info types.Info) []*ast.FuncDecl {
|
||||
fds := []*ast.FuncDecl{}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, fn := range fns {
|
||||
if voidOrError(fn.Type, info) != mgTypes.InvalidType {
|
||||
fds = append(fds, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fds
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func hasContextParam(ft *ast.FuncType, info types.Info) bool {
|
||||
if ft.Params.NumFields() == 1 {
|
||||
ret := ft.Params.List[0]
|
||||
t := info.TypeOf(ret.Type)
|
||||
if t != nil && t.String() == "context.Context" {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func hasVoidReturn(ft *ast.FuncType, info types.Info) bool {
|
||||
res := ft.Results
|
||||
if res.NumFields() == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func hasErrorReturn(ft *ast.FuncType, info types.Info) bool {
|
||||
res := ft.Results
|
||||
if res.NumFields() == 1 {
|
||||
ret := res.List[0]
|
||||
if len(ret.Names) > 1 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
t := info.TypeOf(ret.Type)
|
||||
if t != nil && t.String() == "error" {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func voidOrError(ft *ast.FuncType, info types.Info) mgTypes.FuncType {
|
||||
if hasContextParam(ft, info) {
|
||||
if hasVoidReturn(ft, info) {
|
||||
return mgTypes.ContextVoidType
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasErrorReturn(ft, info) {
|
||||
return mgTypes.ContextErrorType
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ft.Params.NumFields() == 0 {
|
||||
if hasVoidReturn(ft, info) {
|
||||
return mgTypes.VoidType
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasErrorReturn(ft, info) {
|
||||
return mgTypes.ErrorType
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return mgTypes.InvalidType
|
||||
}
|
||||
40
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/srcimporter/sizes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
40
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/srcimporter/sizes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
// +build !go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package srcimporter
|
||||
|
||||
import "go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
// common architecture word sizes and alignments
|
||||
var gcArchSizes = map[string]*types.StdSizes{
|
||||
"386": {4, 4},
|
||||
"arm": {4, 4},
|
||||
"arm64": {8, 8},
|
||||
"amd64": {8, 8},
|
||||
"amd64p32": {4, 8},
|
||||
"mips": {4, 4},
|
||||
"mipsle": {4, 4},
|
||||
"mips64": {8, 8},
|
||||
"mips64le": {8, 8},
|
||||
"ppc64": {8, 8},
|
||||
"ppc64le": {8, 8},
|
||||
"s390x": {8, 8},
|
||||
// When adding more architectures here,
|
||||
// update the doc string of SizesFor below.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SizesFor returns the Sizes used by a compiler for an architecture.
|
||||
// The result is nil if a compiler/architecture pair is not known.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Supported architectures for compiler "gc":
|
||||
// "386", "arm", "arm64", "amd64", "amd64p32", "mips", "mipsle",
|
||||
// "mips64", "mips64le", "ppc64", "ppc64le", "s390x".
|
||||
func SizesFor(compiler, arch string) types.Sizes {
|
||||
if compiler != "gc" {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
s, ok := gcArchSizes[arch]
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
213
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/srcimporter/srcimporter.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
213
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/parse/srcimporter/srcimporter.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,213 @@
|
||||
// +build !go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
// Copyright 2017 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package srcimporter implements importing directly
|
||||
// from source files rather than installed packages.
|
||||
package srcimporter
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/build"
|
||||
"go/parser"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// An Importer provides the context for importing packages from source code.
|
||||
type Importer struct {
|
||||
ctxt *build.Context
|
||||
fset *token.FileSet
|
||||
sizes types.Sizes
|
||||
packages map[string]*types.Package
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewImporter returns a new Importer for the given context, file set, and map
|
||||
// of packages. The context is used to resolve import paths to package paths,
|
||||
// and identifying the files belonging to the package. If the context provides
|
||||
// non-nil file system functions, they are used instead of the regular package
|
||||
// os functions. The file set is used to track position information of package
|
||||
// files; and imported packages are added to the packages map.
|
||||
func New(ctxt *build.Context, fset *token.FileSet, packages map[string]*types.Package) *Importer {
|
||||
return &Importer{
|
||||
ctxt: ctxt,
|
||||
fset: fset,
|
||||
sizes: SizesFor(ctxt.Compiler, ctxt.GOARCH), // uses go/types default if GOARCH not found
|
||||
packages: packages,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Importing is a sentinel taking the place in Importer.packages
|
||||
// for a package that is in the process of being imported.
|
||||
var importing types.Package
|
||||
|
||||
// Import(path) is a shortcut for ImportFrom(path, "", 0).
|
||||
func (p *Importer) Import(path string) (*types.Package, error) {
|
||||
return p.ImportFrom(path, "", 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ImportFrom imports the package with the given import path resolved from the given srcDir,
|
||||
// adds the new package to the set of packages maintained by the importer, and returns the
|
||||
// package. Package path resolution and file system operations are controlled by the context
|
||||
// maintained with the importer. The import mode must be zero but is otherwise ignored.
|
||||
// Packages that are not comprised entirely of pure Go files may fail to import because the
|
||||
// type checker may not be able to determine all exported entities (e.g. due to cgo dependencies).
|
||||
func (p *Importer) ImportFrom(path, srcDir string, mode types.ImportMode) (*types.Package, error) {
|
||||
if mode != 0 {
|
||||
panic("non-zero import mode")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// determine package path (do vendor resolution)
|
||||
var bp *build.Package
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if abs, err := p.absPath(srcDir); err == nil { // see issue #14282
|
||||
srcDir = abs
|
||||
}
|
||||
bp, err = p.ctxt.Import(path, srcDir, build.FindOnly)
|
||||
|
||||
case build.IsLocalImport(path):
|
||||
// "./x" -> "srcDir/x"
|
||||
bp, err = p.ctxt.ImportDir(filepath.Join(srcDir, path), build.FindOnly)
|
||||
|
||||
case p.isAbsPath(path):
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid absolute import path %q", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err // err may be *build.NoGoError - return as is
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// package unsafe is known to the type checker
|
||||
if bp.ImportPath == "unsafe" {
|
||||
return types.Unsafe, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// no need to re-import if the package was imported completely before
|
||||
pkg := p.packages[bp.ImportPath]
|
||||
if pkg != nil {
|
||||
if pkg == &importing {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("import cycle through package %q", bp.ImportPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !pkg.Complete() {
|
||||
// Package exists but is not complete - we cannot handle this
|
||||
// at the moment since the source importer replaces the package
|
||||
// wholesale rather than augmenting it (see #19337 for details).
|
||||
// Return incomplete package with error (see #16088).
|
||||
return pkg, fmt.Errorf("reimported partially imported package %q", bp.ImportPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pkg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.packages[bp.ImportPath] = &importing
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
// clean up in case of error
|
||||
// TODO(gri) Eventually we may want to leave a (possibly empty)
|
||||
// package in the map in all cases (and use that package to
|
||||
// identify cycles). See also issue 16088.
|
||||
if p.packages[bp.ImportPath] == &importing {
|
||||
p.packages[bp.ImportPath] = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// collect package files
|
||||
bp, err = p.ctxt.ImportDir(bp.Dir, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err // err may be *build.NoGoError - return as is
|
||||
}
|
||||
var filenames []string
|
||||
filenames = append(filenames, bp.GoFiles...)
|
||||
filenames = append(filenames, bp.CgoFiles...)
|
||||
|
||||
files, err := p.parseFiles(bp.Dir, filenames)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// type-check package files
|
||||
conf := types.Config{
|
||||
IgnoreFuncBodies: true,
|
||||
FakeImportC: true,
|
||||
Importer: p,
|
||||
Sizes: p.sizes,
|
||||
}
|
||||
pkg, err = conf.Check(bp.ImportPath, p.fset, files, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
// Type-checking stops after the first error (types.Config.Error is not set),
|
||||
// so the returned package is very likely incomplete. Don't return it since
|
||||
// we don't know its condition: It's very likely unsafe to use and it's also
|
||||
// not added to p.packages which may cause further problems (issue #20837).
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("type-checking package %q failed (%v)", bp.ImportPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.packages[bp.ImportPath] = pkg
|
||||
return pkg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Importer) parseFiles(dir string, filenames []string) ([]*ast.File, error) {
|
||||
open := p.ctxt.OpenFile // possibly nil
|
||||
|
||||
files := make([]*ast.File, len(filenames))
|
||||
errors := make([]error, len(filenames))
|
||||
|
||||
var wg sync.WaitGroup
|
||||
wg.Add(len(filenames))
|
||||
for i, filename := range filenames {
|
||||
go func(i int, filepath string) {
|
||||
defer wg.Done()
|
||||
if open != nil {
|
||||
src, err := open(filepath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
errors[i] = fmt.Errorf("opening package file %s failed (%v)", filepath, err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
files[i], errors[i] = parser.ParseFile(p.fset, filepath, src, 0)
|
||||
src.Close() // ignore Close error - parsing may have succeeded which is all we need
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Special-case when ctxt doesn't provide a custom OpenFile and use the
|
||||
// parser's file reading mechanism directly. This appears to be quite a
|
||||
// bit faster than opening the file and providing an io.ReaderCloser in
|
||||
// both cases.
|
||||
// TODO(gri) investigate performance difference (issue #19281)
|
||||
files[i], errors[i] = parser.ParseFile(p.fset, filepath, nil, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}(i, p.joinPath(dir, filename))
|
||||
}
|
||||
wg.Wait()
|
||||
|
||||
// if there are errors, return the first one for deterministic results
|
||||
for _, err := range errors {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return files, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// context-controlled file system operations
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Importer) absPath(path string) (string, error) {
|
||||
// TODO(gri) This should be using p.ctxt.AbsPath which doesn't
|
||||
// exist but probably should. See also issue #14282.
|
||||
return filepath.Abs(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Importer) isAbsPath(path string) bool {
|
||||
if f := p.ctxt.IsAbsPath; f != nil {
|
||||
return f(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return filepath.IsAbs(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Importer) joinPath(elem ...string) string {
|
||||
if f := p.ctxt.JoinPath; f != nil {
|
||||
return f(elem...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return filepath.Join(elem...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
165
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/sh/cmd.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
165
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/sh/cmd.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
|
||||
package sh
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"os/exec"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/magefile/mage/mg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RunCmd returns a function that will call Run with the given command. This is
|
||||
// useful for creating command aliases to make your scripts easier to read, like
|
||||
// this:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // in a helper file somewhere
|
||||
// var g0 = sh.RunCmd("go") // go is a keyword :(
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // somewhere in your main code
|
||||
// if err := g0("install", "github.com/gohugo/hugo"); err != nil {
|
||||
// return err
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Args passed to command get baked in as args to the command when you run it.
|
||||
// Any args passed in when you run the returned function will be appended to the
|
||||
// original args. For example, this is equivalent to the above:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var goInstall = sh.RunCmd("go", "install") goInstall("github.com/gohugo/hugo")
|
||||
//
|
||||
// RunCmd uses Exec underneath, so see those docs for more details.
|
||||
func RunCmd(cmd string, args ...string) func(args ...string) error {
|
||||
return func(args2 ...string) error {
|
||||
return Run(cmd, append(args, args2...)...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OutCmd is like RunCmd except the command returns the output of the
|
||||
// command.
|
||||
func OutCmd(cmd string, args ...string) func(args ...string) (string, error) {
|
||||
return func(args2 ...string) (string, error) {
|
||||
return Output(cmd, append(args, args2...)...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run is like RunWith, but doesn't specify any environment variables.
|
||||
func Run(cmd string, args ...string) error {
|
||||
return RunWith(nil, cmd, args...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RunV is like Run, but always sends the command's stdout to os.Stdout.
|
||||
func RunV(cmd string, args ...string) error {
|
||||
_, err := Exec(nil, os.Stdout, os.Stderr, cmd, args...)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RunWith runs the given command, directing stderr to this program's stderr and
|
||||
// printing stdout to stdout if mage was run with -v. It adds adds env to the
|
||||
// environment variables for the command being run. Environment variables should
|
||||
// be in the format name=value.
|
||||
func RunWith(env map[string]string, cmd string, args ...string) error {
|
||||
var output io.Writer
|
||||
if mg.Verbose() {
|
||||
output = os.Stdout
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, err := Exec(env, output, os.Stderr, cmd, args...)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Output runs the command and returns the text from stdout.
|
||||
func Output(cmd string, args ...string) (string, error) {
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
_, err := Exec(nil, buf, os.Stderr, cmd, args...)
|
||||
return strings.TrimSuffix(buf.String(), "\n"), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OutputWith is like RunWith, ubt returns what is written to stdout.
|
||||
func OutputWith(env map[string]string, cmd string, args ...string) (string, error) {
|
||||
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
_, err := Exec(env, buf, os.Stderr, cmd, args...)
|
||||
return strings.TrimSuffix(buf.String(), "\n"), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Exec executes the command, piping its stderr to mage's stderr and
|
||||
// piping its stdout to the given writer. If the command fails, it will return
|
||||
// an error that, if returned from a target or mg.Deps call, will cause mage to
|
||||
// exit with the same code as the command failed with. Env is a list of
|
||||
// environment variables to set when running the command, these override the
|
||||
// current environment variables set (which are also passed to the command). cmd
|
||||
// and args may include references to environment variables in $FOO format, in
|
||||
// which case these will be expanded before the command is run.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Ran reports if the command ran (rather than was not found or not executable).
|
||||
// Code reports the exit code the command returned if it ran. If err == nil, ran
|
||||
// is always true and code is always 0.
|
||||
func Exec(env map[string]string, stdout, stderr io.Writer, cmd string, args ...string) (ran bool, err error) {
|
||||
expand := func(s string) string {
|
||||
s2, ok := env[s]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
return s2
|
||||
}
|
||||
return os.Getenv(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
cmd = os.Expand(cmd, expand)
|
||||
for i := range args {
|
||||
args[i] = os.Expand(args[i], expand)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ran, code, err := run(env, stdout, stderr, cmd, args...)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ran {
|
||||
return ran, mg.Fatalf(code, `running "%s %s" failed with exit code %d`, cmd, strings.Join(args, " "), code)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ran, fmt.Errorf(`failed to run "%s %s: %v"`, cmd, strings.Join(args, " "), err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func run(env map[string]string, stdout, stderr io.Writer, cmd string, args ...string) (ran bool, code int, err error) {
|
||||
c := exec.Command(cmd, args...)
|
||||
c.Env = os.Environ()
|
||||
for k, v := range env {
|
||||
c.Env = append(c.Env, k+"="+v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.Stderr = stderr
|
||||
c.Stdout = stdout
|
||||
c.Stdin = os.Stdin
|
||||
log.Println("exec:", cmd, strings.Join(args, " "))
|
||||
err = c.Run()
|
||||
return cmdRan(err), ExitStatus(err), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func cmdRan(err error) bool {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
ee, ok := err.(*exec.ExitError)
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
return ee.Exited()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type exitStatus interface {
|
||||
ExitStatus() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitStatus returns the exit status of the error if it is an exec.ExitError
|
||||
// or if it implements ExitStatus() int.
|
||||
// 0 if it is nil or 1 if it is a different error.
|
||||
func ExitStatus(err error) int {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if e, ok := err.(exitStatus); ok {
|
||||
return e.ExitStatus()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if e, ok := err.(*exec.ExitError); ok {
|
||||
if ex, ok := e.Sys().(exitStatus); ok {
|
||||
return ex.ExitStatus()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
16
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/sh/helpers.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
16
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/sh/helpers.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
package sh
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Rm removes the given file or directory even if non-empty. It will not return
|
||||
// an error if the target doesn't exist, only if the target cannot be removed.
|
||||
func Rm(path string) error {
|
||||
err := os.RemoveAll(path)
|
||||
if err == nil || os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf(`failed to remove %s: %v`, path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
122
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/target/target.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
122
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/target/target.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
package target
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Path reports if any of the sources have been modified more recently
|
||||
// than the destination. Path does not descend into directories, it literally
|
||||
// just checks the modtime of each thing you pass to it.
|
||||
func Path(dst string, sources ...string) (bool, error) {
|
||||
stat, err := os.Stat(dst)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
srcTime := stat.ModTime()
|
||||
dt, err := loadTargets(sources)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
t := dt.modTime()
|
||||
if t.After(srcTime) {
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Dir reports whether any of the sources have been modified
|
||||
// more recently than the destination. If a source or destination is
|
||||
// a directory, modtimes of files under those directories are compared
|
||||
// instead.
|
||||
func Dir(dst string, sources ...string) (bool, error) {
|
||||
stat, err := os.Stat(dst)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
srcTime := stat.ModTime()
|
||||
if stat.IsDir() {
|
||||
srcTime, err = calDirModTimeRecursive(stat)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dt, err := loadTargets(sources)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
t, err := dt.modTimeDir()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.After(srcTime) {
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func calDirModTimeRecursive(dir os.FileInfo) (time.Time, error) {
|
||||
t := dir.ModTime()
|
||||
ferr := filepath.Walk(dir.Name(), func(path string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if info.ModTime().After(t) {
|
||||
t = info.ModTime()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
})
|
||||
if ferr != nil {
|
||||
return time.Time{}, ferr
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type depTargets struct {
|
||||
src []os.FileInfo
|
||||
hasdir bool
|
||||
latest time.Time
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func loadTargets(targets []string) (*depTargets, error) {
|
||||
d := &depTargets{}
|
||||
for _, v := range targets {
|
||||
stat, err := os.Stat(v)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if stat.IsDir() {
|
||||
d.hasdir = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.src = append(d.src, stat)
|
||||
if stat.ModTime().After(d.latest) {
|
||||
d.latest = stat.ModTime()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *depTargets) modTime() time.Time {
|
||||
return d.latest
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *depTargets) modTimeDir() (time.Time, error) {
|
||||
if !d.hasdir {
|
||||
return d.latest, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
for _, i := range d.src {
|
||||
t := i.ModTime()
|
||||
if i.IsDir() {
|
||||
t, err = calDirModTimeRecursive(i)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return time.Time{}, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.After(d.latest) {
|
||||
d.latest = t
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d.latest, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
58
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/types/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
58
vendor/github.com/magefile/mage/types/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
package types
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FuncType indicates a prototype of build job function
|
||||
type FuncType int
|
||||
|
||||
// FuncTypes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
InvalidType FuncType = iota
|
||||
VoidType
|
||||
ErrorType
|
||||
ContextVoidType
|
||||
ContextErrorType
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FuncCheck tests if a function is one of FuncType
|
||||
func FuncCheck(fn interface{}) error {
|
||||
switch fn.(type) {
|
||||
case func():
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case func() error:
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case func(context.Context):
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case func(context.Context) error:
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("Invalid type for dependent function: %T. Dependencies must be func(), func() error, func(context.Context) or func(context.Context) error", fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FuncTypeWrap wraps a valid FuncType to FuncContextError
|
||||
func FuncTypeWrap(fn interface{}) func(context.Context) error {
|
||||
if FuncCheck(fn) == nil {
|
||||
switch f := fn.(type) {
|
||||
case func():
|
||||
return func(context.Context) error {
|
||||
f()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
case func() error:
|
||||
return func(context.Context) error {
|
||||
return f()
|
||||
}
|
||||
case func(context.Context):
|
||||
return func(ctx context.Context) error {
|
||||
f(ctx)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
case func(context.Context) error:
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2016 Matthew Holt
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
archiver [](https://godoc.org/github.com/mholt/archiver) [](https://travis-ci.org/mholt/archiver) [](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/mholt/archiver)
|
||||
========
|
||||
|
||||
Package archiver makes it trivially easy to make and extract common archive formats such as .zip, and .tar.gz. Simply name the input and output file(s).
|
||||
|
||||
Files are put into the root of the archive; directories are recursively added, preserving structure.
|
||||
|
||||
The `archiver` command runs the same cross-platform and has no external dependencies (not even libc); powered by the Go standard library, [dsnet/compress](https://github.com/dsnet/compress), [nwaples/rardecode](https://github.com/nwaples/rardecode), and [ulikunitz/xz](https://github.com/ulikunitz/xz). Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
Supported formats/extensions:
|
||||
|
||||
- .zip
|
||||
- .tar
|
||||
- .tar.gz & .tgz
|
||||
- .tar.bz2 & .tbz2
|
||||
- .tar.xz & .txz
|
||||
- .tar.lz4 & .tlz4
|
||||
- .tar.sz & .tsz
|
||||
- .rar (open only)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Install
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
go get github.com/mholt/archiver/cmd/archiver
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or download binaries from the [releases](https://github.com/mholt/archiver/releases) page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Command Use
|
||||
|
||||
Make a new archive:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ archiver make [archive name] [input files...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(At least one input file is required.)
|
||||
|
||||
To extract an archive:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ archiver open [archive name] [destination]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(The destination path is optional; default is current directory.)
|
||||
|
||||
The archive name must end with a supported file extension—this is how it knows what kind of archive to make. Run `archiver -h` for more help.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Library Use
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/mholt/archiver"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a .zip file:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
err := archiver.Zip.Make("output.zip", []string{"file.txt", "folder"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Extract a .zip file:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
err := archiver.Zip.Open("input.zip", "output_folder")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Working with other file formats is exactly the same, but with [their own Archiver implementations](https://godoc.org/github.com/mholt/archiver#Archiver).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Can I list a file in one folder to go into a different folder in the archive?
|
||||
|
||||
No. This works just like your OS would make an archive in the file explorer: organize your input files to mirror the structure you want in the archive.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Can it add files to an existing archive?
|
||||
|
||||
Nope. This is a simple tool; it just makes new archives or extracts existing ones.
|
||||
32
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
32
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
version: "{build}"
|
||||
|
||||
os: Windows Server 2012 R2
|
||||
|
||||
clone_folder: c:\gopath\src\github.com\mholt\archiver
|
||||
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
GOPATH: c:\gopath
|
||||
CGO_ENABLED: 0
|
||||
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- rmdir c:\go /s /q
|
||||
- appveyor DownloadFile https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip
|
||||
- 7z x go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip -y -oC:\ > NUL
|
||||
- go version
|
||||
- go env
|
||||
- go get -t ./...
|
||||
- go get github.com/golang/lint/golint
|
||||
- go get github.com/gordonklaus/ineffassign
|
||||
- set PATH=%GOPATH%\bin;%PATH%
|
||||
|
||||
build: off
|
||||
|
||||
test_script:
|
||||
- go vet ./...
|
||||
- go test ./...
|
||||
- ineffassign .
|
||||
|
||||
after_test:
|
||||
- golint ./...
|
||||
|
||||
deploy: off
|
||||
107
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/archiver.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
107
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/archiver.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Archiver represent a archive format
|
||||
type Archiver interface {
|
||||
// Match checks supported files
|
||||
Match(filename string) bool
|
||||
// Make makes an archive file on disk.
|
||||
Make(destination string, sources []string) error
|
||||
// Open extracts an archive file on disk.
|
||||
Open(source, destination string) error
|
||||
// Write writes an archive to a Writer.
|
||||
Write(output io.Writer, sources []string) error
|
||||
// Read reads an archive from a Reader.
|
||||
Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SupportedFormats contains all supported archive formats
|
||||
var SupportedFormats = map[string]Archiver{}
|
||||
|
||||
// RegisterFormat adds a supported archive format
|
||||
func RegisterFormat(name string, format Archiver) {
|
||||
if _, ok := SupportedFormats[name]; ok {
|
||||
log.Printf("Format %s already exists, skip!\n", name)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
SupportedFormats[name] = format
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MatchingFormat returns the first archive format that matches
|
||||
// the given file, or nil if there is no match
|
||||
func MatchingFormat(fpath string) Archiver {
|
||||
for _, fmt := range SupportedFormats {
|
||||
if fmt.Match(fpath) {
|
||||
return fmt
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeNewFile(fpath string, in io.Reader, fm os.FileMode) error {
|
||||
err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(fpath), 0755)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making directory for file: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(fpath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: creating new file: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
err = out.Chmod(fm)
|
||||
if err != nil && runtime.GOOS != "windows" {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: changing file mode: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = io.Copy(out, in)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: writing file: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeNewSymbolicLink(fpath string, target string) error {
|
||||
err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(fpath), 0755)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making directory for file: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = os.Symlink(target, fpath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making symbolic link for: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeNewHardLink(fpath string, target string) error {
|
||||
err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(fpath), 0755)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making directory for file: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = os.Link(target, fpath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making hard link for: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func mkdir(dirPath string) error {
|
||||
err := os.MkdirAll(dirPath, 0755)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making directory: %v", dirPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/build.bash
generated
vendored
Executable file
21
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/build.bash
generated
vendored
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
set -ex
|
||||
|
||||
# This script builds archiver for most common platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
export CGO_ENABLED=0
|
||||
|
||||
cd cmd/archiver
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=386 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_linux_386
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_linux_amd64
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=arm go build -o ../../builds/archiver_linux_arm7
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=arm64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_linux_arm64
|
||||
GOOS=darwin GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_mac_amd64
|
||||
GOOS=windows GOARCH=386 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_windows_386.exe
|
||||
GOOS=windows GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_windows_amd64.exe
|
||||
GOOS=freebsd GOARCH=386 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_freebsd_386
|
||||
GOOS=freebsd GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_freebsd_amd64
|
||||
GOOS=freebsd GOARCH=arm go build -o ../../builds/archiver_freebsd_arm7
|
||||
GOOS=openbsd GOARCH=386 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_openbsd_386
|
||||
GOOS=openbsd GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ../../builds/archiver_openbsd_amd64
|
||||
cd ../..
|
||||
109
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/rar.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
109
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/rar.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/nwaples/rardecode"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Rar is for RAR archive format
|
||||
var Rar rarFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("Rar", Rar)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type rarFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (rarFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".rar") || isRar(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isRar checks the file has the RAR 1.5 or 5.0 format signature by reading its
|
||||
// beginning bytes and matching it
|
||||
func isRar(rarPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(rarPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, 8)
|
||||
if n, err := f.Read(buf); err != nil || n < 8 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return bytes.Equal(buf[:7], []byte("Rar!\x1a\x07\x00")) || // ver 1.5
|
||||
bytes.Equal(buf, []byte("Rar!\x1a\x07\x01\x00")) // ver 5.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .rar archive, but this is not implemented because
|
||||
// RAR is a proprietary format. It is here only for symmetry with
|
||||
// the other archive formats in this package.
|
||||
func (rarFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("write: RAR not implemented (proprietary format)")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make makes a .rar archive, but this is not implemented because
|
||||
// RAR is a proprietary format. It is here only for symmetry with
|
||||
// the other archive formats in this package.
|
||||
func (rarFormat) Make(rarPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("make %s: RAR not implemented (proprietary format)", rarPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read extracts the RAR file read from input and puts the contents
|
||||
// into destination.
|
||||
func (rarFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
rr, err := rardecode.NewReader(input, "")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("read: failed to create reader: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
header, err := rr.Next()
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
break
|
||||
} else if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if header.IsDir {
|
||||
err = mkdir(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// if files come before their containing folders, then we must
|
||||
// create their folders before writing the file
|
||||
err = mkdir(filepath.Dir(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name)))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = writeNewFile(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name), rr, header.Mode())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open extracts the RAR file at source and puts the contents
|
||||
// into destination.
|
||||
func (rarFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
rf, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open file: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer rf.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return Rar.Read(rf, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
234
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tar.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
234
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tar.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,234 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"archive/tar"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Tar is for Tar format
|
||||
var Tar tarFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("Tar", Tar)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tarFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (tarFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar") || isTar(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const tarBlockSize int = 512
|
||||
|
||||
// isTar checks the file has the Tar format header by reading its beginning
|
||||
// block.
|
||||
func isTar(tarPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(tarPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
if _, err = io.ReadFull(f, buf); err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hasTarHeader checks passed bytes has a valid tar header or not. buf must
|
||||
// contain at least 512 bytes and if not, it always returns false.
|
||||
func hasTarHeader(buf []byte) bool {
|
||||
if len(buf) < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := buf[148:156]
|
||||
b = bytes.Trim(b, " \x00") // clean up all spaces and null bytes
|
||||
if len(b) == 0 {
|
||||
return false // unknown format
|
||||
}
|
||||
hdrSum, err := strconv.ParseUint(string(b), 8, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// According to the go official archive/tar, Sun tar uses signed byte
|
||||
// values so this calcs both signed and unsigned
|
||||
var usum uint64
|
||||
var sum int64
|
||||
for i, c := range buf {
|
||||
if 148 <= i && i < 156 {
|
||||
c = ' ' // checksum field itself is counted as branks
|
||||
}
|
||||
usum += uint64(uint8(c))
|
||||
sum += int64(int8(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if hdrSum != usum && int64(hdrSum) != sum {
|
||||
return false // invalid checksum
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar file to a Writer containing the
|
||||
// contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths can
|
||||
// be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar file at tarPath containing the
|
||||
// contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths can
|
||||
// be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarFormat) Make(tarPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(tarPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", tarPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, out, tarPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTar(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
tarWriter := tar.NewWriter(output)
|
||||
defer tarWriter.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return tarball(filePaths, tarWriter, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tarball writes all files listed in filePaths into tarWriter, which is
|
||||
// writing into a file located at dest.
|
||||
func tarball(filePaths []string, tarWriter *tar.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
for _, fpath := range filePaths {
|
||||
err := tarFile(tarWriter, fpath, dest)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tarFile writes the file at source into tarWriter. It does so
|
||||
// recursively for directories.
|
||||
func tarFile(tarWriter *tar.Writer, source, dest string) error {
|
||||
sourceInfo, err := os.Stat(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: stat: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var baseDir string
|
||||
if sourceInfo.IsDir() {
|
||||
baseDir = filepath.Base(source)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return filepath.Walk(source, func(path string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error walking to %s: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
header, err := tar.FileInfoHeader(info, path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making header: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if baseDir != "" {
|
||||
header.Name = filepath.Join(baseDir, strings.TrimPrefix(path, source))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if header.Name == dest {
|
||||
// our new tar file is inside the directory being archived; skip it
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if info.IsDir() {
|
||||
header.Name += "/"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = tarWriter.WriteHeader(header)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: writing header: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if info.IsDir() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if header.Typeflag == tar.TypeReg {
|
||||
file, err := os.Open(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: open: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = io.CopyN(tarWriter, file, info.Size())
|
||||
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: copying contents: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar file read from a Reader and puts
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
return untar(tar.NewReader(input), destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and puts the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// untar un-tarballs the contents of tr into destination.
|
||||
func untar(tr *tar.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
header, err := tr.Next()
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
break
|
||||
} else if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := untarFile(tr, header, destination); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// untarFile untars a single file from tr with header header into destination.
|
||||
func untarFile(tr *tar.Reader, header *tar.Header, destination string) error {
|
||||
switch header.Typeflag {
|
||||
case tar.TypeDir:
|
||||
return mkdir(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name))
|
||||
case tar.TypeReg, tar.TypeRegA, tar.TypeChar, tar.TypeBlock, tar.TypeFifo:
|
||||
return writeNewFile(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name), tr, header.FileInfo().Mode())
|
||||
case tar.TypeSymlink:
|
||||
return writeNewSymbolicLink(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name), header.Linkname)
|
||||
case tar.TypeLink:
|
||||
return writeNewHardLink(filepath.Join(destination, header.Name), filepath.Join(destination, header.Linkname))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: unknown type flag: %c", header.Name, header.Typeflag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
106
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarbz2.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
106
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarbz2.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/dsnet/compress/bzip2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TarBz2 is for TarBz2 format
|
||||
var TarBz2 tarBz2Format
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("TarBz2", TarBz2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tarBz2Format struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (tarBz2Format) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar.bz2") ||
|
||||
strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tbz2") ||
|
||||
isTarBz2(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTarBz2 checks the file has the bzip2 compressed Tar format header by
|
||||
// reading its beginning block.
|
||||
func isTarBz2(tarbz2Path string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(tarbz2Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
bz2r, err := bzip2.NewReader(f, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer bz2r.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
n, err := bz2r.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil || n < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar.bz2 file to a Writer containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarBz2Format) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTarBz2(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar.bz2 file at tarbz2Path containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarBz2Format) Make(tarbz2Path string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(tarbz2Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", tarbz2Path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTarBz2(filePaths, out, tarbz2Path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTarBz2(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
bz2w, err := bzip2.NewWriter(output, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error compressing bzip2: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer bz2w.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, bz2w, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar.bz2 file read from a Reader and decompresses
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarBz2Format) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
bz2r, err := bzip2.NewReader(input, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error decompressing bzip2: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer bz2r.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(bz2r, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and decompresses the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarBz2Format) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return TarBz2.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
98
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/targz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
98
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/targz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"compress/gzip"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TarGz is for TarGz format
|
||||
var TarGz tarGzFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("TarGz", TarGz)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tarGzFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (tarGzFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar.gz") ||
|
||||
strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tgz") ||
|
||||
isTarGz(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTarGz checks the file has the gzip compressed Tar format header by reading
|
||||
// its beginning block.
|
||||
func isTarGz(targzPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(targzPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
gzr, err := gzip.NewReader(f)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer gzr.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
n, err := gzr.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil || n < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar.gz file to a Writer containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. It works
|
||||
// the same way Tar does, but with gzip compression.
|
||||
func (tarGzFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTarGz(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar.gz file at targzPath containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. It works
|
||||
// the same way Tar does, but with gzip compression.
|
||||
func (tarGzFormat) Make(targzPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(targzPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", targzPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTarGz(filePaths, out, targzPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTarGz(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
gzw := gzip.NewWriter(output)
|
||||
defer gzw.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, gzw, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar.gz file read from a Reader and decompresses
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarGzFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
gzr, err := gzip.NewReader(input)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error decompressing: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer gzr.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(gzr, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and decompresses the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarGzFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return TarGz.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
92
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarlz4.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
92
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarlz4.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/pierrec/lz4"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TarLz4 is for TarLz4 format
|
||||
var TarLz4 tarLz4Format
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("TarLz4", TarLz4)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tarLz4Format struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (tarLz4Format) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar.lz4") || strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tlz4") || isTarLz4(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTarLz4 checks the file has the lz4 compressed Tar format header by
|
||||
// reading its beginning block.
|
||||
func isTarLz4(tarlz4Path string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(tarlz4Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
lz4r := lz4.NewReader(f)
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
n, err := lz4r.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil || n < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar.lz4 file to a Writer containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarLz4Format) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTarLz4(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar.lz4 file at tarlz4Path containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarLz4Format) Make(tarlz4Path string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(tarlz4Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", tarlz4Path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTarLz4(filePaths, out, tarlz4Path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTarLz4(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
lz4w := lz4.NewWriter(output)
|
||||
defer lz4w.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, lz4w, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar.xz file read from a Reader and decompresses
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarLz4Format) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
lz4r := lz4.NewReader(input)
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(lz4r, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and decompresses the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarLz4Format) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return TarLz4.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
92
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarsz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
92
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarsz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/snappy"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TarSz is for TarSz format
|
||||
var TarSz tarSzFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("TarSz", TarSz)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tarSzFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (tarSzFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar.sz") || strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tsz") || isTarSz(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTarSz checks the file has the sz compressed Tar format header by
|
||||
// reading its beginning block.
|
||||
func isTarSz(tarszPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(tarszPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
szr := snappy.NewReader(f)
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
n, err := szr.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil || n < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar.sz file to a Writer containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarSzFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTarSz(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar.sz file at tarszPath containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (tarSzFormat) Make(tarszPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(tarszPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", tarszPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTarSz(filePaths, out, tarszPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTarSz(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
szw := snappy.NewBufferedWriter(output)
|
||||
defer szw.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, szw, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar.sz file read from a Reader and decompresses
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarSzFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
szr := snappy.NewReader(input)
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(szr, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and decompresses the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (tarSzFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return TarSz.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
105
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarxz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
105
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/tarxz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/ulikunitz/xz"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TarXZ is for TarXZ format
|
||||
var TarXZ xzFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("TarXZ", TarXZ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type xzFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Match returns whether filename matches this format.
|
||||
func (xzFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".tar.xz") ||
|
||||
strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".txz") ||
|
||||
isTarXz(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTarXz checks the file has the xz compressed Tar format header by reading
|
||||
// its beginning block.
|
||||
func isTarXz(tarxzPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(tarxzPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
xzr, err := xz.NewReader(f)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, tarBlockSize)
|
||||
n, err := xzr.Read(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil || n < tarBlockSize {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hasTarHeader(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .tar.xz file to a Writer containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (xzFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
return writeTarXZ(filePaths, output, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .tar.xz file at xzPath containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File
|
||||
// paths can be those of regular files or directories.
|
||||
// Regular files are stored at the 'root' of the
|
||||
// archive, and directories are recursively added.
|
||||
func (xzFormat) Make(xzPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(xzPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", xzPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTarXZ(filePaths, out, xzPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeTarXZ(filePaths []string, output io.Writer, dest string) error {
|
||||
xzw, err := xz.NewWriter(output)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error compressing xz: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer xzw.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeTar(filePaths, xzw, dest)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read untars a .tar.xz file read from a Reader and decompresses
|
||||
// the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (xzFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
xzr, err := xz.NewReader(input)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error decompressing xz: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return Tar.Read(xzr, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open untars source and decompresses the contents into destination.
|
||||
func (xzFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: failed to open archive: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return TarXZ.Read(f, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
233
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/zip.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
233
vendor/github.com/mholt/archiver/zip.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
|
||||
// Package archiver makes it super easy to create and open .zip,
|
||||
// .tar.gz, and .tar.bz2 files.
|
||||
package archiver
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"archive/zip"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Zip is for Zip format
|
||||
var Zip zipFormat
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
RegisterFormat("Zip", Zip)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type zipFormat struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (zipFormat) Match(filename string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.HasSuffix(strings.ToLower(filename), ".zip") || isZip(filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isZip checks the file has the Zip format signature by reading its beginning
|
||||
// bytes and matching it against "PK\x03\x04"
|
||||
func isZip(zipPath string) bool {
|
||||
f, err := os.Open(zipPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, 4)
|
||||
if n, err := f.Read(buf); err != nil || n < 4 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return bytes.Equal(buf, []byte("PK\x03\x04"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write outputs a .zip file to the given writer with
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Files with an extension for formats that are already
|
||||
// compressed will be stored only, not compressed.
|
||||
func (zipFormat) Write(output io.Writer, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
w := zip.NewWriter(output)
|
||||
for _, fpath := range filePaths {
|
||||
if err := zipFile(w, fpath); err != nil {
|
||||
w.Close()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return w.Close()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make creates a .zip file in the location zipPath containing
|
||||
// the contents of files listed in filePaths. File paths
|
||||
// can be those of regular files or directories. Regular
|
||||
// files are stored at the 'root' of the archive, and
|
||||
// directories are recursively added.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Files with an extension for formats that are already
|
||||
// compressed will be stored only, not compressed.
|
||||
func (zipFormat) Make(zipPath string, filePaths []string) error {
|
||||
out, err := os.Create(zipPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error creating %s: %v", zipPath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer out.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return Zip.Write(out, filePaths)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func zipFile(w *zip.Writer, source string) error {
|
||||
sourceInfo, err := os.Stat(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: stat: %v", source, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var baseDir string
|
||||
if sourceInfo.IsDir() {
|
||||
baseDir = filepath.Base(source)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return filepath.Walk(source, func(fpath string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("walking to %s: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
header, err := zip.FileInfoHeader(info)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: getting header: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if baseDir != "" {
|
||||
name, err := filepath.Rel(source, fpath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
header.Name = path.Join(baseDir, filepath.ToSlash(name))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if info.IsDir() {
|
||||
header.Name += "/"
|
||||
header.Method = zip.Store
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ext := strings.ToLower(path.Ext(header.Name))
|
||||
if _, ok := compressedFormats[ext]; ok {
|
||||
header.Method = zip.Store
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
header.Method = zip.Deflate
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
writer, err := w.CreateHeader(header)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: making header: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if info.IsDir() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if header.Mode().IsRegular() {
|
||||
file, err := os.Open(fpath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: opening: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = io.CopyN(writer, file, info.Size())
|
||||
if err != nil && err != io.EOF {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: copying contents: %v", fpath, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read unzips the .zip file read from the input Reader into destination.
|
||||
func (zipFormat) Read(input io.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
buf, err := ioutil.ReadAll(input)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
rdr := bytes.NewReader(buf)
|
||||
r, err := zip.NewReader(rdr, rdr.Size())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return unzipAll(r, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open unzips the .zip file at source into destination.
|
||||
func (zipFormat) Open(source, destination string) error {
|
||||
r, err := zip.OpenReader(source)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer r.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return unzipAll(&r.Reader, destination)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func unzipAll(r *zip.Reader, destination string) error {
|
||||
for _, zf := range r.File {
|
||||
if err := unzipFile(zf, destination); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func unzipFile(zf *zip.File, destination string) error {
|
||||
if strings.HasSuffix(zf.Name, "/") {
|
||||
return mkdir(filepath.Join(destination, zf.Name))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
rc, err := zf.Open()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s: open compressed file: %v", zf.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer rc.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
return writeNewFile(filepath.Join(destination, zf.Name), rc, zf.FileInfo().Mode())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// compressedFormats is a (non-exhaustive) set of lowercased
|
||||
// file extensions for formats that are typically already
|
||||
// compressed. Compressing already-compressed files often
|
||||
// results in a larger file, so when possible, we check this
|
||||
// set to avoid that.
|
||||
var compressedFormats = map[string]struct{}{
|
||||
".7z": {},
|
||||
".avi": {},
|
||||
".bz2": {},
|
||||
".cab": {},
|
||||
".gif": {},
|
||||
".gz": {},
|
||||
".jar": {},
|
||||
".jpeg": {},
|
||||
".jpg": {},
|
||||
".lz": {},
|
||||
".lzma": {},
|
||||
".mov": {},
|
||||
".mp3": {},
|
||||
".mp4": {},
|
||||
".mpeg": {},
|
||||
".mpg": {},
|
||||
".png": {},
|
||||
".rar": {},
|
||||
".tbz2": {},
|
||||
".tgz": {},
|
||||
".txz": {},
|
||||
".xz": {},
|
||||
".zip": {},
|
||||
".zipx": {},
|
||||
}
|
||||
23
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
23
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2015, Nicholas Waples
|
||||
All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
|
||||
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
|
||||
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
|
||||
AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
|
||||
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
|
||||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
|
||||
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
|
||||
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
|
||||
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
|
||||
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
4
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
4
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# rardecode
|
||||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/nwaples/rardecode)
|
||||
|
||||
A go package for reading RAR archives.
|
||||
306
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
306
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,306 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
maxSfxSize = 0x100000 // maximum number of bytes to read when searching for RAR signature
|
||||
sigPrefix = "Rar!\x1A\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
fileFmt15 = iota + 1 // Version 1.5 archive file format
|
||||
fileFmt50 // Version 5.0 archive file format
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errNoSig = errors.New("rardecode: RAR signature not found")
|
||||
errVerMismatch = errors.New("rardecode: volume version mistmatch")
|
||||
errCorruptHeader = errors.New("rardecode: corrupt block header")
|
||||
errCorruptFileHeader = errors.New("rardecode: corrupt file header")
|
||||
errBadHeaderCrc = errors.New("rardecode: bad header crc")
|
||||
errUnknownArc = errors.New("rardecode: unknown archive version")
|
||||
errUnknownDecoder = errors.New("rardecode: unknown decoder version")
|
||||
errUnsupportedDecoder = errors.New("rardecode: unsupported decoder version")
|
||||
errArchiveContinues = errors.New("rardecode: archive continues in next volume")
|
||||
errArchiveEnd = errors.New("rardecode: archive end reached")
|
||||
errDecoderOutOfData = errors.New("rardecode: decoder expected more data than is in packed file")
|
||||
|
||||
reDigits = regexp.MustCompile(`\d+`)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type readBuf []byte
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *readBuf) byte() byte {
|
||||
v := (*b)[0]
|
||||
*b = (*b)[1:]
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *readBuf) uint16() uint16 {
|
||||
v := uint16((*b)[0]) | uint16((*b)[1])<<8
|
||||
*b = (*b)[2:]
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *readBuf) uint32() uint32 {
|
||||
v := uint32((*b)[0]) | uint32((*b)[1])<<8 | uint32((*b)[2])<<16 | uint32((*b)[3])<<24
|
||||
*b = (*b)[4:]
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *readBuf) bytes(n int) []byte {
|
||||
v := (*b)[:n]
|
||||
*b = (*b)[n:]
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *readBuf) uvarint() uint64 {
|
||||
var x uint64
|
||||
var s uint
|
||||
for i, n := range *b {
|
||||
if n < 0x80 {
|
||||
*b = (*b)[i+1:]
|
||||
return x | uint64(n)<<s
|
||||
}
|
||||
x |= uint64(n&0x7f) << s
|
||||
s += 7
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
// if we run out of bytes, just return 0
|
||||
*b = (*b)[len(*b):]
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readFull wraps io.ReadFull to return io.ErrUnexpectedEOF instead
|
||||
// of io.EOF when 0 bytes are read.
|
||||
func readFull(r io.Reader, buf []byte) error {
|
||||
_, err := io.ReadFull(r, buf)
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
return io.ErrUnexpectedEOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findSig searches for the RAR signature and version at the beginning of a file.
|
||||
// It searches no more than maxSfxSize bytes.
|
||||
func findSig(br *bufio.Reader) (int, error) {
|
||||
for n := 0; n <= maxSfxSize; {
|
||||
b, err := br.ReadSlice(sigPrefix[0])
|
||||
n += len(b)
|
||||
if err == bufio.ErrBufferFull {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = errNoSig
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b, err = br.Peek(len(sigPrefix[1:]) + 2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = errNoSig
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !bytes.HasPrefix(b, []byte(sigPrefix[1:])) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
b = b[len(sigPrefix)-1:]
|
||||
|
||||
var ver int
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case b[0] == 0:
|
||||
ver = fileFmt15
|
||||
case b[0] == 1 && b[1] == 0:
|
||||
ver = fileFmt50
|
||||
default:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, _ = br.ReadSlice('\x00')
|
||||
|
||||
return ver, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, errNoSig
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// volume extends a fileBlockReader to be used across multiple
|
||||
// files in a multi-volume archive
|
||||
type volume struct {
|
||||
fileBlockReader
|
||||
f *os.File // current file handle
|
||||
br *bufio.Reader // buffered reader for current volume file
|
||||
dir string // volume directory
|
||||
file string // current volume file
|
||||
num int // volume number
|
||||
old bool // uses old naming scheme
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// nextVolName updates name to the next filename in the archive.
|
||||
func (v *volume) nextVolName() {
|
||||
if v.num == 0 {
|
||||
// check file extensions
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(v.file, ".")
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
// no file extension, add one
|
||||
i = len(v.file)
|
||||
v.file += ".rar"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ext := strings.ToLower(v.file[i+1:])
|
||||
// replace with .rar for empty extensions & self extracting archives
|
||||
if ext == "" || ext == "exe" || ext == "sfx" {
|
||||
v.file = v.file[:i+1] + "rar"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if a, ok := v.fileBlockReader.(*archive15); ok {
|
||||
v.old = a.old
|
||||
}
|
||||
// new naming scheme must have volume number in filename
|
||||
if !v.old && reDigits.FindStringIndex(v.file) == nil {
|
||||
v.old = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// For old style naming if 2nd and 3rd character of file extension is not a digit replace
|
||||
// with "00" and ignore any trailing characters.
|
||||
if v.old && (len(v.file) < i+4 || v.file[i+2] < '0' || v.file[i+2] > '9' || v.file[i+3] < '0' || v.file[i+3] > '9') {
|
||||
v.file = v.file[:i+2] + "00"
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// new style volume naming
|
||||
if !v.old {
|
||||
// find all numbers in volume name
|
||||
m := reDigits.FindAllStringIndex(v.file, -1)
|
||||
if l := len(m); l > 1 {
|
||||
// More than 1 match so assume name.part###of###.rar style.
|
||||
// Take the last 2 matches where the first is the volume number.
|
||||
m = m[l-2 : l]
|
||||
if strings.Contains(v.file[m[0][1]:m[1][0]], ".") || !strings.Contains(v.file[:m[0][0]], ".") {
|
||||
// Didn't match above style as volume had '.' between the two numbers or didnt have a '.'
|
||||
// before the first match. Use the second number as volume number.
|
||||
m = m[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// extract and increment volume number
|
||||
lo, hi := m[0][0], m[0][1]
|
||||
n, err := strconv.Atoi(v.file[lo:hi])
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n++
|
||||
}
|
||||
// volume number must use at least the same number of characters as previous volume
|
||||
vol := fmt.Sprintf("%0"+fmt.Sprint(hi-lo)+"d", n)
|
||||
v.file = v.file[:lo] + vol + v.file[hi:]
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// old style volume naming
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(v.file, ".")
|
||||
// get file extension
|
||||
b := []byte(v.file[i+1:])
|
||||
// start incrementing volume number digits from rightmost
|
||||
for j := 2; j >= 0; j-- {
|
||||
if b[j] != '9' {
|
||||
b[j]++
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
// digit overflow
|
||||
if j == 0 {
|
||||
// last character before '.'
|
||||
b[j] = 'A'
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// set to '0' and loop to next character
|
||||
b[j] = '0'
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
v.file = v.file[:i+1] + string(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *volume) next() (*fileBlockHeader, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
var atEOF bool
|
||||
|
||||
h, err := v.fileBlockReader.next()
|
||||
switch err {
|
||||
case errArchiveContinues:
|
||||
case io.EOF:
|
||||
// Read all of volume without finding an end block. The only way
|
||||
// to tell if the archive continues is to try to open the next volume.
|
||||
atEOF = true
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return h, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
v.f.Close()
|
||||
v.nextVolName()
|
||||
v.f, err = os.Open(v.dir + v.file) // Open next volume file
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if atEOF && os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
// volume not found so assume that the archive has ended
|
||||
return nil, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
v.num++
|
||||
v.br.Reset(v.f)
|
||||
ver, err := findSig(v.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.version() != ver {
|
||||
return nil, errVerMismatch
|
||||
}
|
||||
v.reset() // reset encryption
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *volume) Close() error {
|
||||
// may be nil if os.Open fails in next()
|
||||
if v.f == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.f.Close()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func openVolume(name, password string) (*volume, error) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
v := new(volume)
|
||||
v.dir, v.file = filepath.Split(name)
|
||||
v.f, err = os.Open(name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
v.br = bufio.NewReader(v.f)
|
||||
v.fileBlockReader, err = newFileBlockReader(v.br, password)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
v.f.Close()
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newFileBlockReader(br *bufio.Reader, pass string) (fileBlockReader, error) {
|
||||
runes := []rune(pass)
|
||||
if len(runes) > maxPassword {
|
||||
pass = string(runes[:maxPassword])
|
||||
}
|
||||
ver, err := findSig(br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch ver {
|
||||
case fileFmt15:
|
||||
return newArchive15(br, pass), nil
|
||||
case fileFmt50:
|
||||
return newArchive50(br, pass), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, errUnknownArc
|
||||
}
|
||||
468
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive15.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
468
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive15.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"crypto/sha1"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"hash"
|
||||
"hash/crc32"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
"unicode/utf16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// block types
|
||||
blockArc = 0x73
|
||||
blockFile = 0x74
|
||||
blockService = 0x7a
|
||||
blockEnd = 0x7b
|
||||
|
||||
// block flags
|
||||
blockHasData = 0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
// archive block flags
|
||||
arcVolume = 0x0001
|
||||
arcSolid = 0x0008
|
||||
arcNewNaming = 0x0010
|
||||
arcEncrypted = 0x0080
|
||||
|
||||
// file block flags
|
||||
fileSplitBefore = 0x0001
|
||||
fileSplitAfter = 0x0002
|
||||
fileEncrypted = 0x0004
|
||||
fileSolid = 0x0010
|
||||
fileWindowMask = 0x00e0
|
||||
fileLargeData = 0x0100
|
||||
fileUnicode = 0x0200
|
||||
fileSalt = 0x0400
|
||||
fileVersion = 0x0800
|
||||
fileExtTime = 0x1000
|
||||
|
||||
// end block flags
|
||||
endArcNotLast = 0x0001
|
||||
|
||||
saltSize = 8 // size of salt for calculating AES keys
|
||||
cacheSize30 = 4 // number of AES keys to cache
|
||||
hashRounds = 0x40000
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errMultipleDecoders = errors.New("rardecode: multiple decoders in a single archive not supported")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type blockHeader15 struct {
|
||||
htype byte // block header type
|
||||
flags uint16
|
||||
data readBuf // header data
|
||||
dataSize int64 // size of extra block data
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fileHash32 implements fileChecksum for 32-bit hashes
|
||||
type fileHash32 struct {
|
||||
hash.Hash32 // hash to write file contents to
|
||||
sum uint32 // 32bit checksum for file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *fileHash32) valid() bool {
|
||||
return h.sum == h.Sum32()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// archive15 implements fileBlockReader for RAR 1.5 file format archives
|
||||
type archive15 struct {
|
||||
byteReader // reader for current block data
|
||||
v *bufio.Reader // reader for current archive volume
|
||||
dec decoder // current decoder
|
||||
decVer byte // current decoder version
|
||||
multi bool // archive is multi-volume
|
||||
old bool // archive uses old naming scheme
|
||||
solid bool // archive is a solid archive
|
||||
encrypted bool
|
||||
pass []uint16 // password in UTF-16
|
||||
checksum fileHash32 // file checksum
|
||||
buf readBuf // temporary buffer
|
||||
keyCache [cacheSize30]struct { // cache of previously calculated decryption keys
|
||||
salt []byte
|
||||
key []byte
|
||||
iv []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculates the key and iv for AES decryption given a password and salt.
|
||||
func calcAes30Params(pass []uint16, salt []byte) (key, iv []byte) {
|
||||
p := make([]byte, 0, len(pass)*2+len(salt))
|
||||
for _, v := range pass {
|
||||
p = append(p, byte(v), byte(v>>8))
|
||||
}
|
||||
p = append(p, salt...)
|
||||
|
||||
hash := sha1.New()
|
||||
iv = make([]byte, 16)
|
||||
s := make([]byte, 0, hash.Size())
|
||||
for i := 0; i < hashRounds; i++ {
|
||||
hash.Write(p)
|
||||
hash.Write([]byte{byte(i), byte(i >> 8), byte(i >> 16)})
|
||||
if i%(hashRounds/16) == 0 {
|
||||
s = hash.Sum(s[:0])
|
||||
iv[i/(hashRounds/16)] = s[4*4+3]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
key = hash.Sum(s[:0])
|
||||
key = key[:16]
|
||||
|
||||
for k := key; len(k) >= 4; k = k[4:] {
|
||||
k[0], k[1], k[2], k[3] = k[3], k[2], k[1], k[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return key, iv
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseDosTime converts a 32bit DOS time value to time.Time
|
||||
func parseDosTime(t uint32) time.Time {
|
||||
n := int(t)
|
||||
sec := n & 0x1f << 1
|
||||
min := n >> 5 & 0x3f
|
||||
hr := n >> 11 & 0x1f
|
||||
day := n >> 16 & 0x1f
|
||||
mon := time.Month(n >> 21 & 0x0f)
|
||||
yr := n>>25&0x7f + 1980
|
||||
return time.Date(yr, mon, day, hr, min, sec, 0, time.Local)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// decodeName decodes a non-unicode filename from a file header.
|
||||
func decodeName(buf []byte) string {
|
||||
i := bytes.IndexByte(buf, 0)
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
return string(buf) // filename is UTF-8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
name := buf[:i]
|
||||
encName := readBuf(buf[i+1:])
|
||||
if len(encName) < 2 {
|
||||
return "" // invalid encoding
|
||||
}
|
||||
highByte := uint16(encName.byte()) << 8
|
||||
flags := encName.byte()
|
||||
flagBits := 8
|
||||
var wchars []uint16 // decoded characters are UTF-16
|
||||
for len(wchars) < len(name) && len(encName) > 0 {
|
||||
if flagBits == 0 {
|
||||
flags = encName.byte()
|
||||
flagBits = 8
|
||||
if len(encName) == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch flags >> 6 {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
wchars = append(wchars, uint16(encName.byte()))
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
wchars = append(wchars, uint16(encName.byte())|highByte)
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
if len(encName) < 2 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
wchars = append(wchars, encName.uint16())
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
n := encName.byte()
|
||||
b := name[len(wchars):]
|
||||
if l := int(n&0x7f) + 2; l < len(b) {
|
||||
b = b[:l]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n&0x80 > 0 {
|
||||
if len(encName) < 1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
ec := encName.byte()
|
||||
for _, c := range b {
|
||||
wchars = append(wchars, uint16(c+ec)|highByte)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for _, c := range b {
|
||||
wchars = append(wchars, uint16(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
flags <<= 2
|
||||
flagBits -= 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(utf16.Decode(wchars))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readExtTimes reads and parses the optional extra time field from the file header.
|
||||
func readExtTimes(f *fileBlockHeader, b *readBuf) {
|
||||
if len(*b) < 2 {
|
||||
return // invalid, not enough data
|
||||
}
|
||||
flags := b.uint16()
|
||||
|
||||
ts := []*time.Time{&f.ModificationTime, &f.CreationTime, &f.AccessTime}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, t := range ts {
|
||||
n := flags >> uint((3-i)*4)
|
||||
if n&0x8 == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i != 0 { // ModificationTime already read so skip
|
||||
if len(*b) < 4 {
|
||||
return // invalid, not enough data
|
||||
}
|
||||
*t = parseDosTime(b.uint32())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n&0x4 > 0 {
|
||||
*t = t.Add(time.Second)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n &= 0x3
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(*b) < int(n) {
|
||||
return // invalid, not enough data
|
||||
}
|
||||
// add extra time data in 100's of nanoseconds
|
||||
d := time.Duration(0)
|
||||
for j := 3 - n; j < n; j++ {
|
||||
d |= time.Duration(b.byte()) << (j * 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
d *= 100
|
||||
*t = t.Add(d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive15) getKeys(salt []byte) (key, iv []byte) {
|
||||
// check cache of keys
|
||||
for _, v := range a.keyCache {
|
||||
if bytes.Equal(v.salt[:], salt) {
|
||||
return v.key, v.iv
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
key, iv = calcAes30Params(a.pass, salt)
|
||||
|
||||
// save a copy in the cache
|
||||
copy(a.keyCache[1:], a.keyCache[:])
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].salt = append([]byte(nil), salt...) // copy so byte slice can be reused
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].key = key
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].iv = iv
|
||||
|
||||
return key, iv
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive15) parseFileHeader(h *blockHeader15) (*fileBlockHeader, error) {
|
||||
f := new(fileBlockHeader)
|
||||
|
||||
f.first = h.flags&fileSplitBefore == 0
|
||||
f.last = h.flags&fileSplitAfter == 0
|
||||
|
||||
f.solid = h.flags&fileSolid > 0
|
||||
f.IsDir = h.flags&fileWindowMask == fileWindowMask
|
||||
if !f.IsDir {
|
||||
f.winSize = uint(h.flags&fileWindowMask)>>5 + 16
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := h.data
|
||||
if len(b) < 21 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.PackedSize = h.dataSize
|
||||
f.UnPackedSize = int64(b.uint32())
|
||||
f.HostOS = b.byte() + 1
|
||||
if f.HostOS > HostOSBeOS {
|
||||
f.HostOS = HostOSUnknown
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.checksum.sum = b.uint32()
|
||||
|
||||
f.ModificationTime = parseDosTime(b.uint32())
|
||||
unpackver := b.byte() // decoder version
|
||||
method := b.byte() - 0x30 // decryption method
|
||||
namesize := int(b.uint16())
|
||||
f.Attributes = int64(b.uint32())
|
||||
if h.flags&fileLargeData > 0 {
|
||||
if len(b) < 8 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
_ = b.uint32() // already read large PackedSize in readBlockHeader
|
||||
f.UnPackedSize |= int64(b.uint32()) << 32
|
||||
f.UnKnownSize = f.UnPackedSize == -1
|
||||
} else if int32(f.UnPackedSize) == -1 {
|
||||
f.UnKnownSize = true
|
||||
f.UnPackedSize = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(b) < namesize {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
name := b.bytes(namesize)
|
||||
if h.flags&fileUnicode == 0 {
|
||||
f.Name = string(name)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
f.Name = decodeName(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Rar 4.x uses '\' as file separator
|
||||
f.Name = strings.Replace(f.Name, "\\", "/", -1)
|
||||
|
||||
if h.flags&fileVersion > 0 {
|
||||
// file version is stored as ';n' appended to file name
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(f.Name, ";")
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
j, err := strconv.Atoi(f.Name[i+1:])
|
||||
if err == nil && j >= 0 {
|
||||
f.Version = j
|
||||
f.Name = f.Name[:i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var salt []byte
|
||||
if h.flags&fileSalt > 0 {
|
||||
if len(b) < saltSize {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
salt = b.bytes(saltSize)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if h.flags&fileExtTime > 0 {
|
||||
readExtTimes(f, &b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !f.first {
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// fields only needed for first block in a file
|
||||
if h.flags&fileEncrypted > 0 && len(salt) == saltSize {
|
||||
f.key, f.iv = a.getKeys(salt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.checksum.Reset()
|
||||
f.cksum = &a.checksum
|
||||
if method == 0 {
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if a.dec == nil {
|
||||
switch unpackver {
|
||||
case 15, 20, 26:
|
||||
return nil, errUnsupportedDecoder
|
||||
case 29:
|
||||
a.dec = new(decoder29)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, errUnknownDecoder
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.decVer = unpackver
|
||||
} else if a.decVer != unpackver {
|
||||
return nil, errMultipleDecoders
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.decoder = a.dec
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readBlockHeader returns the next block header in the archive.
|
||||
// It will return io.EOF if there were no bytes read.
|
||||
func (a *archive15) readBlockHeader() (*blockHeader15, error) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
b := a.buf[:7]
|
||||
r := io.Reader(a.v)
|
||||
if a.encrypted {
|
||||
salt := a.buf[:saltSize]
|
||||
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, salt)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
key, iv := a.getKeys(salt)
|
||||
r = newAesDecryptReader(r, key, iv)
|
||||
err = readFull(r, b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
crc := b.uint16()
|
||||
hash := crc32.NewIEEE()
|
||||
hash.Write(b)
|
||||
h := new(blockHeader15)
|
||||
h.htype = b.byte()
|
||||
h.flags = b.uint16()
|
||||
size := b.uint16()
|
||||
if size < 7 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
size -= 7
|
||||
if int(size) > cap(a.buf) {
|
||||
a.buf = readBuf(make([]byte, size))
|
||||
}
|
||||
h.data = a.buf[:size]
|
||||
if err := readFull(r, h.data); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
hash.Write(h.data)
|
||||
if crc != uint16(hash.Sum32()) {
|
||||
return nil, errBadHeaderCrc
|
||||
}
|
||||
if h.flags&blockHasData > 0 {
|
||||
if len(h.data) < 4 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
h.dataSize = int64(h.data.uint32())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (h.htype == blockService || h.htype == blockFile) && h.flags&fileLargeData > 0 {
|
||||
if len(h.data) < 25 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
b := h.data[21:25]
|
||||
h.dataSize |= int64(b.uint32()) << 32
|
||||
}
|
||||
return h, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// next advances to the next file block in the archive
|
||||
func (a *archive15) next() (*fileBlockHeader, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// could return an io.EOF here as 1.5 archives may not have an end block.
|
||||
h, err := a.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.byteReader = limitByteReader(a.v, h.dataSize) // reader for block data
|
||||
|
||||
switch h.htype {
|
||||
case blockFile:
|
||||
return a.parseFileHeader(h)
|
||||
case blockArc:
|
||||
a.encrypted = h.flags&arcEncrypted > 0
|
||||
a.multi = h.flags&arcVolume > 0
|
||||
a.old = h.flags&arcNewNaming == 0
|
||||
a.solid = h.flags&arcSolid > 0
|
||||
case blockEnd:
|
||||
if h.flags&endArcNotLast == 0 || !a.multi {
|
||||
return nil, errArchiveEnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, errArchiveContinues
|
||||
default:
|
||||
_, err = io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, a.byteReader)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive15) version() int { return fileFmt15 }
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive15) reset() {
|
||||
a.encrypted = false // reset encryption when opening new volume file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive15) isSolid() bool {
|
||||
return a.solid
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newArchive15 creates a new fileBlockReader for a Version 1.5 archive
|
||||
func newArchive15(r *bufio.Reader, password string) fileBlockReader {
|
||||
a := new(archive15)
|
||||
a.v = r
|
||||
a.pass = utf16.Encode([]rune(password)) // convert to UTF-16
|
||||
a.checksum.Hash32 = crc32.NewIEEE()
|
||||
a.buf = readBuf(make([]byte, 100))
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
475
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive50.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
475
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/archive50.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,475 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bufio"
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"crypto/hmac"
|
||||
"crypto/sha256"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"hash"
|
||||
"hash/crc32"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// block types
|
||||
block5Arc = 1
|
||||
block5File = 2
|
||||
block5Service = 3
|
||||
block5Encrypt = 4
|
||||
block5End = 5
|
||||
|
||||
// block flags
|
||||
block5HasExtra = 0x0001
|
||||
block5HasData = 0x0002
|
||||
block5DataNotFirst = 0x0008
|
||||
block5DataNotLast = 0x0010
|
||||
|
||||
// end block flags
|
||||
endArc5NotLast = 0x0001
|
||||
|
||||
// archive encryption block flags
|
||||
enc5CheckPresent = 0x0001 // password check data is present
|
||||
|
||||
// main archive block flags
|
||||
arc5MultiVol = 0x0001
|
||||
arc5Solid = 0x0004
|
||||
|
||||
// file block flags
|
||||
file5IsDir = 0x0001
|
||||
file5HasUnixMtime = 0x0002
|
||||
file5HasCRC32 = 0x0004
|
||||
file5UnpSizeUnknown = 0x0008
|
||||
|
||||
// file encryption record flags
|
||||
file5EncCheckPresent = 0x0001 // password check data is present
|
||||
file5EncUseMac = 0x0002 // use MAC instead of plain checksum
|
||||
|
||||
cacheSize50 = 4
|
||||
maxPbkdf2Salt = 64
|
||||
pwCheckSize = 8
|
||||
maxKdfCount = 24
|
||||
|
||||
minHeaderSize = 7
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errBadPassword = errors.New("rardecode: incorrect password")
|
||||
errCorruptEncrypt = errors.New("rardecode: corrupt encryption data")
|
||||
errUnknownEncMethod = errors.New("rardecode: unknown encryption method")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type extra struct {
|
||||
ftype uint64 // field type
|
||||
data readBuf // field data
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type blockHeader50 struct {
|
||||
htype uint64 // block type
|
||||
flags uint64
|
||||
data readBuf // block header data
|
||||
extra []extra // extra fields
|
||||
dataSize int64 // size of block data
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// leHash32 wraps a hash.Hash32 to return the result of Sum in little
|
||||
// endian format.
|
||||
type leHash32 struct {
|
||||
hash.Hash32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h leHash32) Sum(b []byte) []byte {
|
||||
s := h.Sum32()
|
||||
return append(b, byte(s), byte(s>>8), byte(s>>16), byte(s>>24))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newLittleEndianCRC32() hash.Hash32 {
|
||||
return leHash32{crc32.NewIEEE()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hash50 implements fileChecksum for RAR 5 archives
|
||||
type hash50 struct {
|
||||
hash.Hash // hash file data is written to
|
||||
sum []byte // file checksum
|
||||
key []byte // if present used with hmac in calculating checksum from hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *hash50) valid() bool {
|
||||
sum := h.Sum(nil)
|
||||
if len(h.key) > 0 {
|
||||
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, h.key)
|
||||
mac.Write(sum)
|
||||
sum = mac.Sum(sum[:0])
|
||||
if len(h.sum) == 4 {
|
||||
// CRC32
|
||||
for i, v := range sum[4:] {
|
||||
sum[i&3] ^= v
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum = sum[:4]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bytes.Equal(sum, h.sum)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// archive50 implements fileBlockReader for RAR 5 file format archives
|
||||
type archive50 struct {
|
||||
byteReader // reader for current block data
|
||||
v *bufio.Reader // reader for current archive volume
|
||||
pass []byte
|
||||
blockKey []byte // key used to encrypt blocks
|
||||
multi bool // archive is multi-volume
|
||||
solid bool // is a solid archive
|
||||
checksum hash50 // file checksum
|
||||
dec decoder // optional decoder used to unpack file
|
||||
buf readBuf // temporary buffer
|
||||
keyCache [cacheSize50]struct { // encryption key cache
|
||||
kdfCount int
|
||||
salt []byte
|
||||
keys [][]byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// calcKeys50 calculates the keys used in RAR 5 archive processing.
|
||||
// The returned slice of byte slices contains 3 keys.
|
||||
// Key 0 is used for block or file decryption.
|
||||
// Key 1 is optionally used for file checksum calculation.
|
||||
// Key 2 is optionally used for password checking.
|
||||
func calcKeys50(pass, salt []byte, kdfCount int) [][]byte {
|
||||
if len(salt) > maxPbkdf2Salt {
|
||||
salt = salt[:maxPbkdf2Salt]
|
||||
}
|
||||
keys := make([][]byte, 3)
|
||||
if len(keys) == 0 {
|
||||
return keys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
prf := hmac.New(sha256.New, pass)
|
||||
prf.Write(salt)
|
||||
prf.Write([]byte{0, 0, 0, 1})
|
||||
|
||||
t := prf.Sum(nil)
|
||||
u := append([]byte(nil), t...)
|
||||
|
||||
kdfCount--
|
||||
|
||||
for i, iter := range []int{kdfCount, 16, 16} {
|
||||
for iter > 0 {
|
||||
prf.Reset()
|
||||
prf.Write(u)
|
||||
u = prf.Sum(u[:0])
|
||||
for j := range u {
|
||||
t[j] ^= u[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
iter--
|
||||
}
|
||||
keys[i] = append([]byte(nil), t...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pwcheck := keys[2]
|
||||
for i, v := range pwcheck[pwCheckSize:] {
|
||||
pwcheck[i&(pwCheckSize-1)] ^= v
|
||||
}
|
||||
keys[2] = pwcheck[:pwCheckSize]
|
||||
|
||||
return keys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getKeys reads kdfcount and salt from b and returns the corresponding encryption keys.
|
||||
func (a *archive50) getKeys(b *readBuf) (keys [][]byte, err error) {
|
||||
if len(*b) < 17 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptEncrypt
|
||||
}
|
||||
// read kdf count and salt
|
||||
kdfCount := int(b.byte())
|
||||
if kdfCount > maxKdfCount {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptEncrypt
|
||||
}
|
||||
kdfCount = 1 << uint(kdfCount)
|
||||
salt := b.bytes(16)
|
||||
|
||||
// check cache of keys for match
|
||||
for _, v := range a.keyCache {
|
||||
if kdfCount == v.kdfCount && bytes.Equal(salt, v.salt) {
|
||||
return v.keys, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// not found, calculate keys
|
||||
keys = calcKeys50(a.pass, salt, kdfCount)
|
||||
|
||||
// store in cache
|
||||
copy(a.keyCache[1:], a.keyCache[:])
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].kdfCount = kdfCount
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].salt = append([]byte(nil), salt...)
|
||||
a.keyCache[0].keys = keys
|
||||
|
||||
return keys, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkPassword calculates if a password is correct given password check data and keys.
|
||||
func checkPassword(b *readBuf, keys [][]byte) error {
|
||||
if len(*b) < 12 {
|
||||
return nil // not enough bytes, ignore for the moment
|
||||
}
|
||||
pwcheck := b.bytes(8)
|
||||
sum := b.bytes(4)
|
||||
csum := sha256.Sum256(pwcheck)
|
||||
if bytes.Equal(sum, csum[:len(sum)]) && !bytes.Equal(pwcheck, keys[2]) {
|
||||
return errBadPassword
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseFileEncryptionRecord processes the optional file encryption record from a file header.
|
||||
func (a *archive50) parseFileEncryptionRecord(b readBuf, f *fileBlockHeader) error {
|
||||
if ver := b.uvarint(); ver != 0 {
|
||||
return errUnknownEncMethod
|
||||
}
|
||||
flags := b.uvarint()
|
||||
|
||||
keys, err := a.getKeys(&b)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.key = keys[0]
|
||||
if len(b) < 16 {
|
||||
return errCorruptEncrypt
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.iv = b.bytes(16)
|
||||
|
||||
if flags&file5EncCheckPresent > 0 {
|
||||
if err := checkPassword(&b, keys); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&file5EncUseMac > 0 {
|
||||
a.checksum.key = keys[1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive50) parseFileHeader(h *blockHeader50) (*fileBlockHeader, error) {
|
||||
a.checksum.sum = nil
|
||||
a.checksum.key = nil
|
||||
|
||||
f := new(fileBlockHeader)
|
||||
|
||||
f.first = h.flags&block5DataNotFirst == 0
|
||||
f.last = h.flags&block5DataNotLast == 0
|
||||
|
||||
flags := h.data.uvarint() // file flags
|
||||
f.IsDir = flags&file5IsDir > 0
|
||||
f.UnKnownSize = flags&file5UnpSizeUnknown > 0
|
||||
f.UnPackedSize = int64(h.data.uvarint())
|
||||
f.PackedSize = h.dataSize
|
||||
f.Attributes = int64(h.data.uvarint())
|
||||
if flags&file5HasUnixMtime > 0 {
|
||||
if len(h.data) < 4 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.ModificationTime = time.Unix(int64(h.data.uint32()), 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&file5HasCRC32 > 0 {
|
||||
if len(h.data) < 4 {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.checksum.sum = append([]byte(nil), h.data.bytes(4)...)
|
||||
if f.first {
|
||||
a.checksum.Hash = newLittleEndianCRC32()
|
||||
f.cksum = &a.checksum
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
flags = h.data.uvarint() // compression flags
|
||||
f.solid = flags&0x0040 > 0
|
||||
f.winSize = uint(flags&0x3C00)>>10 + 17
|
||||
method := (flags >> 7) & 7 // compression method (0 == none)
|
||||
if f.first && method != 0 {
|
||||
unpackver := flags & 0x003f
|
||||
if unpackver != 0 {
|
||||
return nil, errUnknownDecoder
|
||||
}
|
||||
if a.dec == nil {
|
||||
a.dec = new(decoder50)
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.decoder = a.dec
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch h.data.uvarint() {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
f.HostOS = HostOSWindows
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
f.HostOS = HostOSUnix
|
||||
default:
|
||||
f.HostOS = HostOSUnknown
|
||||
}
|
||||
nlen := int(h.data.uvarint())
|
||||
if len(h.data) < nlen {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptFileHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Name = string(h.data.bytes(nlen))
|
||||
|
||||
// parse optional extra records
|
||||
for _, e := range h.extra {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
switch e.ftype {
|
||||
case 1: // encryption
|
||||
err = a.parseFileEncryptionRecord(e.data, f)
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
// TODO: hash
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
// TODO: time
|
||||
case 4: // version
|
||||
_ = e.data.uvarint() // ignore flags field
|
||||
f.Version = int(e.data.uvarint())
|
||||
case 5:
|
||||
// TODO: redirection
|
||||
case 6:
|
||||
// TODO: owner
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseEncryptionBlock calculates the key for block encryption.
|
||||
func (a *archive50) parseEncryptionBlock(b readBuf) error {
|
||||
if ver := b.uvarint(); ver != 0 {
|
||||
return errUnknownEncMethod
|
||||
}
|
||||
flags := b.uvarint()
|
||||
keys, err := a.getKeys(&b)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&enc5CheckPresent > 0 {
|
||||
if err := checkPassword(&b, keys); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.blockKey = keys[0]
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive50) readBlockHeader() (*blockHeader50, error) {
|
||||
r := io.Reader(a.v)
|
||||
if a.blockKey != nil {
|
||||
// block is encrypted
|
||||
iv := a.buf[:16]
|
||||
if err := readFull(r, iv); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
r = newAesDecryptReader(r, a.blockKey, iv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := a.buf[:minHeaderSize]
|
||||
if err := readFull(r, b); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
crc := b.uint32()
|
||||
|
||||
hash := crc32.NewIEEE()
|
||||
hash.Write(b)
|
||||
|
||||
size := int(b.uvarint()) // header size
|
||||
if size > cap(a.buf) {
|
||||
a.buf = readBuf(make([]byte, size))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
a.buf = a.buf[:size]
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := copy(a.buf, b) // copy left over bytes
|
||||
if err := readFull(r, a.buf[n:]); err != nil { // read rest of header
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check header crc
|
||||
hash.Write(a.buf[n:])
|
||||
if crc != hash.Sum32() {
|
||||
return nil, errBadHeaderCrc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b = a.buf
|
||||
h := new(blockHeader50)
|
||||
h.htype = b.uvarint()
|
||||
h.flags = b.uvarint()
|
||||
|
||||
var extraSize int
|
||||
if h.flags&block5HasExtra > 0 {
|
||||
extraSize = int(b.uvarint())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if h.flags&block5HasData > 0 {
|
||||
h.dataSize = int64(b.uvarint())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(b) < extraSize {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
h.data = b.bytes(len(b) - extraSize)
|
||||
|
||||
// read header extra records
|
||||
for len(b) > 0 {
|
||||
size = int(b.uvarint())
|
||||
if len(b) < size {
|
||||
return nil, errCorruptHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
data := readBuf(b.bytes(size))
|
||||
ftype := data.uvarint()
|
||||
h.extra = append(h.extra, extra{ftype, data})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return h, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// next advances to the next file block in the archive
|
||||
func (a *archive50) next() (*fileBlockHeader, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
h, err := a.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.byteReader = limitByteReader(a.v, h.dataSize)
|
||||
switch h.htype {
|
||||
case block5File:
|
||||
return a.parseFileHeader(h)
|
||||
case block5Arc:
|
||||
flags := h.data.uvarint()
|
||||
a.multi = flags&arc5MultiVol > 0
|
||||
a.solid = flags&arc5Solid > 0
|
||||
case block5Encrypt:
|
||||
err = a.parseEncryptionBlock(h.data)
|
||||
case block5End:
|
||||
flags := h.data.uvarint()
|
||||
if flags&endArc5NotLast == 0 || !a.multi {
|
||||
return nil, errArchiveEnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, errArchiveContinues
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// discard block data
|
||||
_, err = io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, a.byteReader)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive50) version() int { return fileFmt50 }
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive50) reset() {
|
||||
a.blockKey = nil // reset encryption when opening new volume file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *archive50) isSolid() bool {
|
||||
return a.solid
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newArchive50 creates a new fileBlockReader for a Version 5 archive.
|
||||
func newArchive50(r *bufio.Reader, password string) fileBlockReader {
|
||||
a := new(archive50)
|
||||
a.v = r
|
||||
a.pass = []byte(password)
|
||||
a.buf = make([]byte, 100)
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
119
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/bit_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
119
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/bit_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import "io"
|
||||
|
||||
type bitReader interface {
|
||||
readBits(n uint) (int, error) // read n bits of data
|
||||
unreadBits(n uint) // revert the reading of the last n bits read
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type limitedBitReader struct {
|
||||
br bitReader
|
||||
n int
|
||||
err error // error to return if br returns EOF before all n bits have been read
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// limitBitReader returns a bitReader that reads from br and stops with io.EOF after n bits.
|
||||
// If br returns an io.EOF before reading n bits, err is returned.
|
||||
func limitBitReader(br bitReader, n int, err error) bitReader {
|
||||
return &limitedBitReader{br, n, err}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *limitedBitReader) readBits(n uint) (int, error) {
|
||||
if int(n) > l.n {
|
||||
return 0, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
v, err := l.br.readBits(n)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
l.n -= int(n)
|
||||
} else if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = l.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *limitedBitReader) unreadBits(n uint) {
|
||||
l.n += int(n)
|
||||
l.br.unreadBits(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rarBitReader wraps an io.ByteReader to perform various bit and byte
|
||||
// reading utility functions used in RAR file processing.
|
||||
type rarBitReader struct {
|
||||
r io.ByteReader
|
||||
v int
|
||||
n uint
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) reset(br io.ByteReader) {
|
||||
r.r = br
|
||||
r.n = 0
|
||||
r.v = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) readBits(n uint) (int, error) {
|
||||
for n > r.n {
|
||||
c, err := r.r.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.v = r.v<<8 | int(c)
|
||||
r.n += 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.n -= n
|
||||
return (r.v >> r.n) & ((1 << n) - 1), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) unreadBits(n uint) {
|
||||
r.n += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alignByte aligns the current bit reading input to the next byte boundary.
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) alignByte() {
|
||||
r.n -= r.n % 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readUint32 reads a RAR V3 encoded uint32
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) readUint32() (uint32, error) {
|
||||
n, err := r.readBits(2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n != 1 {
|
||||
n, err = r.readBits(4 << uint(n))
|
||||
return uint32(n), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err = r.readBits(4)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
n, err = r.readBits(8)
|
||||
n |= -1 << 8
|
||||
return uint32(n), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
nlow, err := r.readBits(4)
|
||||
n = n<<4 | nlow
|
||||
return uint32(n), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) ReadByte() (byte, error) {
|
||||
n, err := r.readBits(8)
|
||||
return byte(n), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readFull reads len(p) bytes into p. If fewer bytes are read an error is returned.
|
||||
func (r *rarBitReader) readFull(p []byte) error {
|
||||
for i := range p {
|
||||
c, err := r.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
p[i] = c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newRarBitReader(r io.ByteReader) *rarBitReader {
|
||||
return &rarBitReader{r: r}
|
||||
}
|
||||
264
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
264
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,264 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
maxCodeSize = 0x10000
|
||||
maxUniqueFilters = 1024
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// Errors marking the end of the decoding block and/or file
|
||||
endOfFile = errors.New("rardecode: end of file")
|
||||
endOfBlock = errors.New("rardecode: end of block")
|
||||
endOfBlockAndFile = errors.New("rardecode: end of block and file")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// decoder29 implements the decoder interface for RAR 3.0 compression (unpack version 29)
|
||||
// Decode input is broken up into 1 or more blocks. The start of each block specifies
|
||||
// the decoding algorithm (ppm or lz) and optional data to initialize with.
|
||||
// Block length is not stored, it is determined only after decoding an end of file and/or
|
||||
// block marker in the data.
|
||||
type decoder29 struct {
|
||||
br *rarBitReader
|
||||
eof bool // at file eof
|
||||
fnum int // current filter number (index into filters)
|
||||
flen []int // filter block length history
|
||||
filters []v3Filter // list of current filters used by archive encoding
|
||||
|
||||
// current decode function (lz or ppm).
|
||||
// When called it should perform a single decode operation, and either apply the
|
||||
// data to the window or return they raw bytes for a filter.
|
||||
decode func(w *window) ([]byte, error)
|
||||
|
||||
lz lz29Decoder // lz decoder
|
||||
ppm ppm29Decoder // ppm decoder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// init intializes the decoder for decoding a new file.
|
||||
func (d *decoder29) init(r io.ByteReader, reset bool) error {
|
||||
if d.br == nil {
|
||||
d.br = newRarBitReader(r)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
d.br.reset(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.eof = false
|
||||
if reset {
|
||||
d.initFilters()
|
||||
d.lz.reset()
|
||||
d.ppm.reset()
|
||||
d.decode = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if d.decode == nil {
|
||||
return d.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder29) initFilters() {
|
||||
d.fnum = 0
|
||||
d.flen = nil
|
||||
d.filters = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readVMCode reads the raw bytes for the code/commands used in a vm filter
|
||||
func readVMCode(br *rarBitReader) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
n, err := br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > maxCodeSize || n == 0 {
|
||||
return nil, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, n)
|
||||
err = br.readFull(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
var x byte
|
||||
for _, c := range buf[1:] {
|
||||
x ^= c
|
||||
}
|
||||
// simple xor checksum on data
|
||||
if x != buf[0] {
|
||||
return nil, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder29) parseVMFilter(buf []byte) (*filterBlock, error) {
|
||||
flags := buf[0]
|
||||
br := newRarBitReader(bytes.NewReader(buf[1:]))
|
||||
fb := new(filterBlock)
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the filter number which is an index into d.filters.
|
||||
// If filter number == len(d.filters) it is a new filter to be added.
|
||||
if flags&0x80 > 0 {
|
||||
n, err := br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
d.initFilters()
|
||||
fb.reset = true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n--
|
||||
if n > maxUniqueFilters {
|
||||
return nil, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
if int(n) > len(d.filters) {
|
||||
return nil, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.fnum = int(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// filter offset
|
||||
n, err := br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&0x40 > 0 {
|
||||
n += 258
|
||||
}
|
||||
fb.offset = int(n)
|
||||
|
||||
// filter length
|
||||
if d.fnum == len(d.flen) {
|
||||
d.flen = append(d.flen, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&0x20 > 0 {
|
||||
n, err = br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fb.length = int(n)
|
||||
d.flen[d.fnum] = int(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
fb.length = d.flen[d.fnum]
|
||||
|
||||
// initial register values
|
||||
r := make(map[int]uint32)
|
||||
if flags&0x10 > 0 {
|
||||
bits, err := br.readBits(vmRegs - 1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < vmRegs-1; i++ {
|
||||
if bits&1 > 0 {
|
||||
r[i], err = br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits >>= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// filter is new so read the code for it
|
||||
if d.fnum == len(d.filters) {
|
||||
code, err := readVMCode(br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
f, err := getV3Filter(code)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.filters = append(d.filters, f)
|
||||
d.flen = append(d.flen, fb.length)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// read global data
|
||||
var g []byte
|
||||
if flags&0x08 > 0 {
|
||||
n, err := br.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > vmGlobalSize-vmFixedGlobalSize {
|
||||
return nil, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
g = make([]byte, n)
|
||||
err = br.readFull(g)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// create filter function
|
||||
f := d.filters[d.fnum]
|
||||
fb.filter = func(buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
return f(r, g, buf, offset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return fb, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readBlockHeader determines and initializes the current decoder for a new decode block.
|
||||
func (d *decoder29) readBlockHeader() error {
|
||||
d.br.alignByte()
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(1)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
d.decode = d.ppm.decode
|
||||
err = d.ppm.init(d.br)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
d.decode = d.lz.decode
|
||||
err = d.lz.init(d.br)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = errDecoderOutOfData
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder29) fill(w *window) ([]*filterBlock, error) {
|
||||
if d.eof {
|
||||
return nil, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var fl []*filterBlock
|
||||
|
||||
for w.available() > 0 {
|
||||
b, err := d.decode(w) // perform a single decode operation
|
||||
if len(b) > 0 && err == nil {
|
||||
// parse raw data for filter and add to list of filters
|
||||
var f *filterBlock
|
||||
f, err = d.parseVMFilter(b)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
// make offset relative to read index (from write index)
|
||||
f.offset += w.buffered()
|
||||
fl = append(fl, f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch err {
|
||||
case nil:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case endOfBlock:
|
||||
err = d.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
case endOfFile:
|
||||
d.eof = true
|
||||
err = io.EOF
|
||||
case endOfBlockAndFile:
|
||||
d.eof = true
|
||||
d.decode = nil // clear decoder, it will be setup by next init()
|
||||
err = io.EOF
|
||||
case io.EOF:
|
||||
err = errDecoderOutOfData
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fl, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// return filters
|
||||
return fl, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
247
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29_lz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
247
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29_lz.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,247 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
mainSize = 299
|
||||
offsetSize = 60
|
||||
lowOffsetSize = 17
|
||||
lengthSize = 28
|
||||
tableSize = mainSize + offsetSize + lowOffsetSize + lengthSize
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
lengthBase = [28]int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20,
|
||||
24, 28, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 80, 96, 112, 128, 160, 192, 224}
|
||||
lengthExtraBits = [28]uint{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2,
|
||||
2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5}
|
||||
|
||||
offsetBase = [60]int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48, 64, 96,
|
||||
128, 192, 256, 384, 512, 768, 1024, 1536, 2048, 3072, 4096,
|
||||
6144, 8192, 12288, 16384, 24576, 32768, 49152, 65536, 98304,
|
||||
131072, 196608, 262144, 327680, 393216, 458752, 524288,
|
||||
589824, 655360, 720896, 786432, 851968, 917504, 983040,
|
||||
1048576, 1310720, 1572864, 1835008, 2097152, 2359296, 2621440,
|
||||
2883584, 3145728, 3407872, 3670016, 3932160}
|
||||
offsetExtraBits = [60]uint{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6,
|
||||
6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10, 10, 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 14, 14,
|
||||
15, 15, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16,
|
||||
18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18, 18}
|
||||
|
||||
shortOffsetBase = [8]int{0, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 192}
|
||||
shortOffsetExtraBits = [8]uint{2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 6}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type lz29Decoder struct {
|
||||
codeLength [tableSize]byte
|
||||
|
||||
mainDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
offsetDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
lowOffsetDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
lengthDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
|
||||
offset [4]int // history of previous offsets
|
||||
length int // previous length
|
||||
lowOffset int
|
||||
lowOffsetRepeats int
|
||||
|
||||
br *rarBitReader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *lz29Decoder) reset() {
|
||||
for i := range d.offset {
|
||||
d.offset[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length = 0
|
||||
for i := range d.codeLength {
|
||||
d.codeLength[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *lz29Decoder) init(br *rarBitReader) error {
|
||||
d.br = br
|
||||
d.lowOffset = 0
|
||||
d.lowOffsetRepeats = 0
|
||||
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
addOld := n > 0
|
||||
|
||||
cl := d.codeLength[:]
|
||||
if err = readCodeLengthTable(d.br, cl, addOld); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
d.mainDecoder.init(cl[:mainSize])
|
||||
cl = cl[mainSize:]
|
||||
d.offsetDecoder.init(cl[:offsetSize])
|
||||
cl = cl[offsetSize:]
|
||||
d.lowOffsetDecoder.init(cl[:lowOffsetSize])
|
||||
cl = cl[lowOffsetSize:]
|
||||
d.lengthDecoder.init(cl)
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *lz29Decoder) readFilterData() (b []byte, err error) {
|
||||
flags, err := d.br.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n := (int(flags) & 7) + 1
|
||||
switch n {
|
||||
case 7:
|
||||
n, err = d.br.readBits(8)
|
||||
n += 7
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 8:
|
||||
n, err = d.br.readBits(16)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, n+1)
|
||||
buf[0] = flags
|
||||
err = d.br.readFull(buf[1:])
|
||||
|
||||
return buf, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *lz29Decoder) readEndOfBlock() error {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
return endOfBlock
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err = d.br.readBits(1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
return endOfBlockAndFile
|
||||
}
|
||||
return endOfFile
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *lz29Decoder) decode(win *window) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
sym, err := d.mainDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case sym < 256:
|
||||
// literal
|
||||
win.writeByte(byte(sym))
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
case sym == 256:
|
||||
return nil, d.readEndOfBlock()
|
||||
case sym == 257:
|
||||
return d.readFilterData()
|
||||
case sym == 258:
|
||||
// use previous offset and length
|
||||
case sym < 263:
|
||||
i := sym - 259
|
||||
offset := d.offset[i]
|
||||
copy(d.offset[1:i+1], d.offset[:i])
|
||||
d.offset[0] = offset
|
||||
|
||||
i, err := d.lengthDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length = lengthBase[i] + 2
|
||||
bits := lengthExtraBits[i]
|
||||
if bits > 0 {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
case sym < 271:
|
||||
i := sym - 263
|
||||
copy(d.offset[1:], d.offset[:])
|
||||
offset := shortOffsetBase[i] + 1
|
||||
bits := shortOffsetExtraBits[i]
|
||||
if bits > 0 {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.offset[0] = offset
|
||||
|
||||
d.length = 2
|
||||
default:
|
||||
i := sym - 271
|
||||
d.length = lengthBase[i] + 3
|
||||
bits := lengthExtraBits[i]
|
||||
if bits > 0 {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i, err = d.offsetDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset := offsetBase[i] + 1
|
||||
bits = offsetExtraBits[i]
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case bits >= 4:
|
||||
if bits > 4 {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits - 4)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n << 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if d.lowOffsetRepeats > 0 {
|
||||
d.lowOffsetRepeats--
|
||||
offset += d.lowOffset
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n, err := d.lowOffsetDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n == 16 {
|
||||
d.lowOffsetRepeats = 15
|
||||
offset += d.lowOffset
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
offset += n
|
||||
d.lowOffset = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case bits > 0:
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if offset >= 0x2000 {
|
||||
d.length++
|
||||
if offset >= 0x40000 {
|
||||
d.length++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(d.offset[1:], d.offset[:])
|
||||
d.offset[0] = offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
win.copyBytes(d.length, d.offset[0])
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
132
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29_ppm.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
132
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode29_ppm.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import "io"
|
||||
|
||||
type ppm29Decoder struct {
|
||||
m model // ppm model
|
||||
esc byte // escape character
|
||||
br io.ByteReader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *ppm29Decoder) init(br *rarBitReader) error {
|
||||
maxOrder, err := br.readBits(7)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
reset := maxOrder&0x20 > 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Should have flushed all unread bits from bitReader by now,
|
||||
// use underlying ByteReader
|
||||
d.br = br.r
|
||||
|
||||
var maxMB int
|
||||
if reset {
|
||||
c, err := d.br.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
maxMB = int(c) + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if maxOrder&0x40 > 0 {
|
||||
d.esc, err = d.br.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
maxOrder = (maxOrder & 0x1f) + 1
|
||||
if maxOrder > 16 {
|
||||
maxOrder = 16 + (maxOrder-16)*3
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return d.m.init(d.br, reset, maxOrder, maxMB)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *ppm29Decoder) reset() {
|
||||
d.esc = 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *ppm29Decoder) readFilterData() ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
c, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := int(c&7) + 1
|
||||
if n == 7 {
|
||||
b, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n += int(b)
|
||||
} else if n == 8 {
|
||||
b, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n = int(b) << 8
|
||||
b, err = d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n |= int(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n++
|
||||
buf := make([]byte, n)
|
||||
buf[0] = byte(c)
|
||||
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
buf[i], err = d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *ppm29Decoder) decode(w *window) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
c, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c != d.esc {
|
||||
w.writeByte(c)
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
c, err = d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return nil, endOfBlock
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
return nil, endOfBlockAndFile
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
return d.readFilterData()
|
||||
case 4:
|
||||
offset := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
|
||||
c, err = d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset = offset<<8 | int(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
len, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.copyBytes(int(len)+32, offset+2)
|
||||
case 5:
|
||||
len, err := d.m.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.copyBytes(int(len)+4, 1)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
w.writeByte(d.esc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
294
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode50.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
294
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode50.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,294 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
mainSize5 = 306
|
||||
offsetSize5 = 64
|
||||
lowoffsetSize5 = 16
|
||||
lengthSize5 = 44
|
||||
tableSize5 = mainSize5 + offsetSize5 + lowoffsetSize5 + lengthSize5
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errUnknownFilter = errors.New("rardecode: unknown V5 filter")
|
||||
errCorruptDecodeHeader = errors.New("rardecode: corrupt decode header")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// decoder50 implements the decoder interface for RAR 5 compression.
|
||||
// Decode input it broken up into 1 or more blocks. Each block starts with
|
||||
// a header containing block length and optional code length tables to initialize
|
||||
// the huffman decoders with.
|
||||
type decoder50 struct {
|
||||
r io.ByteReader
|
||||
br bitReader // bit reader for current data block
|
||||
codeLength [tableSize5]byte
|
||||
|
||||
lastBlock bool // current block is last block in compressed file
|
||||
|
||||
mainDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
offsetDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
lowoffsetDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
lengthDecoder huffmanDecoder
|
||||
|
||||
offset [4]int
|
||||
length int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder50) init(r io.ByteReader, reset bool) error {
|
||||
d.r = r
|
||||
d.lastBlock = false
|
||||
|
||||
if reset {
|
||||
for i := range d.offset {
|
||||
d.offset[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length = 0
|
||||
for i := range d.codeLength {
|
||||
d.codeLength[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := d.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
return errDecoderOutOfData
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder50) readBlockHeader() error {
|
||||
flags, err := d.r.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bytecount := (flags>>3)&3 + 1
|
||||
if bytecount == 4 {
|
||||
return errCorruptDecodeHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
hsum, err := d.r.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
blockBits := int(flags)&0x07 + 1
|
||||
blockBytes := 0
|
||||
sum := 0x5a ^ flags
|
||||
for i := byte(0); i < bytecount; i++ {
|
||||
n, err := d.r.ReadByte()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
sum ^= n
|
||||
blockBytes |= int(n) << (i * 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if sum != hsum { // bad header checksum
|
||||
return errCorruptDecodeHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
blockBits += (blockBytes - 1) * 8
|
||||
|
||||
// create bit reader for block
|
||||
d.br = limitBitReader(newRarBitReader(d.r), blockBits, errDecoderOutOfData)
|
||||
d.lastBlock = flags&0x40 > 0
|
||||
|
||||
if flags&0x80 > 0 {
|
||||
// read new code length tables and reinitialize huffman decoders
|
||||
cl := d.codeLength[:]
|
||||
err = readCodeLengthTable(d.br, cl, false)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.mainDecoder.init(cl[:mainSize5])
|
||||
cl = cl[mainSize5:]
|
||||
d.offsetDecoder.init(cl[:offsetSize5])
|
||||
cl = cl[offsetSize5:]
|
||||
d.lowoffsetDecoder.init(cl[:lowoffsetSize5])
|
||||
cl = cl[lowoffsetSize5:]
|
||||
d.lengthDecoder.init(cl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func slotToLength(br bitReader, n int) (int, error) {
|
||||
if n >= 8 {
|
||||
bits := uint(n/4 - 1)
|
||||
n = (4 | (n & 3)) << bits
|
||||
if bits > 0 {
|
||||
b, err := br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n |= b
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
n += 2
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readFilter5Data reads an encoded integer used in V5 filters.
|
||||
func readFilter5Data(br bitReader) (int, error) {
|
||||
// TODO: should data really be uint? (for 32bit ints).
|
||||
// It will be masked later anyway by decode window mask.
|
||||
bytes, err := br.readBits(2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
bytes++
|
||||
|
||||
var data int
|
||||
for i := 0; i < bytes; i++ {
|
||||
n, err := br.readBits(8)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
data |= n << (uint(i) * 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return data, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readFilter(br bitReader) (*filterBlock, error) {
|
||||
fb := new(filterBlock)
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
|
||||
fb.offset, err = readFilter5Data(br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
fb.length, err = readFilter5Data(br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
ftype, err := br.readBits(3)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch ftype {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
n, err := br.readBits(5)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
fb.filter = func(buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) { return filterDelta(n+1, buf) }
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
fb.filter = func(buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) { return filterE8(0xe8, true, buf, offset) }
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
fb.filter = func(buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) { return filterE8(0xe9, true, buf, offset) }
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
fb.filter = filterArm
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, errUnknownFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fb, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder50) decodeSym(win *window, sym int) (*filterBlock, error) {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case sym < 256:
|
||||
// literal
|
||||
win.writeByte(byte(sym))
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
case sym == 256:
|
||||
f, err := readFilter(d.br)
|
||||
f.offset += win.buffered()
|
||||
return f, err
|
||||
case sym == 257:
|
||||
// use previous offset and length
|
||||
case sym < 262:
|
||||
i := sym - 258
|
||||
offset := d.offset[i]
|
||||
copy(d.offset[1:i+1], d.offset[:i])
|
||||
d.offset[0] = offset
|
||||
|
||||
sl, err := d.lengthDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.length, err = slotToLength(d.br, sl)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
length, err := slotToLength(d.br, sym-262)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
offset := 1
|
||||
slot, err := d.offsetDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if slot < 4 {
|
||||
offset += slot
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
bits := uint(slot/2 - 1)
|
||||
offset += (2 | (slot & 1)) << bits
|
||||
|
||||
if bits >= 4 {
|
||||
if bits > 4 {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits - 4)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n << 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err := d.lowoffsetDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n, err := d.br.readBits(bits)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += n
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if offset > 0x100 {
|
||||
length++
|
||||
if offset > 0x2000 {
|
||||
length++
|
||||
if offset > 0x40000 {
|
||||
length++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(d.offset[1:], d.offset[:])
|
||||
d.offset[0] = offset
|
||||
d.length = length
|
||||
}
|
||||
win.copyBytes(d.length, d.offset[0])
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder50) fill(w *window) ([]*filterBlock, error) {
|
||||
var fl []*filterBlock
|
||||
|
||||
for w.available() > 0 {
|
||||
sym, err := d.mainDecoder.readSym(d.br)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
var f *filterBlock
|
||||
f, err = d.decodeSym(w, sym)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
fl = append(fl, f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
// reached end of the block
|
||||
if d.lastBlock {
|
||||
return fl, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = d.readBlockHeader()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
return fl, errDecoderOutOfData
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fl, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fl, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
290
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
290
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decode_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
minWindowSize = 0x40000
|
||||
maxQueuedFilters = 8192
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errTooManyFilters = errors.New("rardecode: too many filters")
|
||||
errInvalidFilter = errors.New("rardecode: invalid filter")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// filter functions take a byte slice, the current output offset and
|
||||
// returns transformed data.
|
||||
type filter func(b []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error)
|
||||
|
||||
// filterBlock is a block of data to be processed by a filter.
|
||||
type filterBlock struct {
|
||||
length int // length of block
|
||||
offset int // bytes to be read before start of block
|
||||
reset bool // drop all existing queued filters
|
||||
filter filter // filter function
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// decoder is the interface for decoding compressed data
|
||||
type decoder interface {
|
||||
init(r io.ByteReader, reset bool) error // initialize decoder for current file
|
||||
fill(w *window) ([]*filterBlock, error) // fill window with decoded data, returning any filters
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// window is a sliding window buffer.
|
||||
type window struct {
|
||||
buf []byte
|
||||
mask int // buf length mask
|
||||
r int // index in buf for reads (beginning)
|
||||
w int // index in buf for writes (end)
|
||||
l int // length of bytes to be processed by copyBytes
|
||||
o int // offset of bytes to be processed by copyBytes
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffered returns the number of bytes yet to be read from window
|
||||
func (w *window) buffered() int { return (w.w - w.r) & w.mask }
|
||||
|
||||
// available returns the number of bytes that can be written before the window is full
|
||||
func (w *window) available() int { return (w.r - w.w - 1) & w.mask }
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *window) reset(log2size uint, clear bool) {
|
||||
size := 1 << log2size
|
||||
if size < minWindowSize {
|
||||
size = minWindowSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
if size > len(w.buf) {
|
||||
b := make([]byte, size)
|
||||
if clear {
|
||||
w.w = 0
|
||||
} else if len(w.buf) > 0 {
|
||||
n := copy(b, w.buf[w.w:])
|
||||
n += copy(b[n:], w.buf[:w.w])
|
||||
w.w = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.buf = b
|
||||
w.mask = size - 1
|
||||
} else if clear {
|
||||
for i := range w.buf {
|
||||
w.buf[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.w = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.r = w.w
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// writeByte writes c to the end of the window
|
||||
func (w *window) writeByte(c byte) {
|
||||
w.buf[w.w] = c
|
||||
w.w = (w.w + 1) & w.mask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copyBytes copies len bytes at off distance from the end
|
||||
// to the end of the window.
|
||||
func (w *window) copyBytes(len, off int) {
|
||||
len &= w.mask
|
||||
|
||||
n := w.available()
|
||||
if len > n {
|
||||
// if there is not enough space availaible we copy
|
||||
// as much as we can and save the offset and length
|
||||
// of the remaining data to be copied later.
|
||||
w.l = len - n
|
||||
w.o = off
|
||||
len = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i := (w.w - off) & w.mask
|
||||
for ; len > 0; len-- {
|
||||
w.buf[w.w] = w.buf[i]
|
||||
w.w = (w.w + 1) & w.mask
|
||||
i = (i + 1) & w.mask
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// read reads bytes from the beginning of the window into p
|
||||
func (w *window) read(p []byte) (n int) {
|
||||
if w.r > w.w {
|
||||
n = copy(p, w.buf[w.r:])
|
||||
w.r = (w.r + n) & w.mask
|
||||
p = p[n:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if w.r < w.w {
|
||||
l := copy(p, w.buf[w.r:w.w])
|
||||
w.r += l
|
||||
n += l
|
||||
}
|
||||
if w.l > 0 && n > 0 {
|
||||
// if we have successfully read data, copy any
|
||||
// leftover data from a previous copyBytes.
|
||||
l := w.l
|
||||
w.l = 0
|
||||
w.copyBytes(l, w.o)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// decodeReader implements io.Reader for decoding compressed data in RAR archives.
|
||||
type decodeReader struct {
|
||||
win window // sliding window buffer used as decode dictionary
|
||||
dec decoder // decoder being used to unpack file
|
||||
tot int64 // total bytes read
|
||||
buf []byte // filter input/output buffer
|
||||
outbuf []byte // filter output not yet read
|
||||
err error
|
||||
filters []*filterBlock // list of filterBlock's, each with offset relative to previous in list
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) init(r io.ByteReader, dec decoder, winsize uint, reset bool) error {
|
||||
if reset {
|
||||
d.filters = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = nil
|
||||
d.outbuf = nil
|
||||
d.tot = 0
|
||||
d.win.reset(winsize, reset)
|
||||
d.dec = dec
|
||||
return d.dec.init(r, reset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) readErr() error {
|
||||
err := d.err
|
||||
d.err = nil
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// queueFilter adds a filterBlock to the end decodeReader's filters.
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) queueFilter(f *filterBlock) error {
|
||||
if f.reset {
|
||||
d.filters = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(d.filters) >= maxQueuedFilters {
|
||||
return errTooManyFilters
|
||||
}
|
||||
// offset & length must be < window size
|
||||
f.offset &= d.win.mask
|
||||
f.length &= d.win.mask
|
||||
// make offset relative to previous filter in list
|
||||
for _, fb := range d.filters {
|
||||
if f.offset < fb.offset {
|
||||
// filter block must not start before previous filter
|
||||
return errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.offset -= fb.offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.filters = append(d.filters, f)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// processFilters processes any filters valid at the current read index
|
||||
// and stores the output in outbuf.
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) processFilters() (err error) {
|
||||
f := d.filters[0]
|
||||
if f.offset > 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.filters = d.filters[1:]
|
||||
if d.win.buffered() < f.length {
|
||||
// fill() didn't return enough bytes
|
||||
err = d.readErr()
|
||||
if err == nil || err == io.EOF {
|
||||
return errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if cap(d.buf) < f.length {
|
||||
d.buf = make([]byte, f.length)
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.outbuf = d.buf[:f.length]
|
||||
n := d.win.read(d.outbuf)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// run filter passing buffer and total bytes read so far
|
||||
d.outbuf, err = f.filter(d.outbuf, d.tot)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cap(d.outbuf) > cap(d.buf) {
|
||||
// Filter returned a bigger buffer, save it for future filters.
|
||||
d.buf = d.outbuf
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(d.filters) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
f = d.filters[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if f.offset != 0 {
|
||||
// next filter not at current offset
|
||||
f.offset -= n
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f.length != len(d.outbuf) {
|
||||
return errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.filters = d.filters[1:]
|
||||
|
||||
if cap(d.outbuf) < cap(d.buf) {
|
||||
// Filter returned a smaller buffer. Copy it back to the saved buffer
|
||||
// so the next filter can make use of the larger buffer if needed.
|
||||
d.outbuf = append(d.buf[:0], d.outbuf...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fill fills the decodeReader's window
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) fill() {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var fl []*filterBlock
|
||||
fl, d.err = d.dec.fill(&d.win) // fill window using decoder
|
||||
for _, f := range fl {
|
||||
err := d.queueFilter(f)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
d.err = err
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read decodes data and stores it in p.
|
||||
func (d *decodeReader) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) {
|
||||
if len(d.outbuf) == 0 {
|
||||
// no filter output, see if we need to create more
|
||||
if d.win.buffered() == 0 {
|
||||
// fill empty window
|
||||
d.fill()
|
||||
if d.win.buffered() == 0 {
|
||||
return 0, d.readErr()
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if len(d.filters) > 0 {
|
||||
f := d.filters[0]
|
||||
if f.offset == 0 && f.length > d.win.buffered() {
|
||||
d.fill() // filter at current offset needs more data
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(d.filters) > 0 {
|
||||
if err := d.processFilters(); err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(d.outbuf) > 0 {
|
||||
// copy filter output into p
|
||||
n = copy(p, d.outbuf)
|
||||
d.outbuf = d.outbuf[n:]
|
||||
} else if len(d.filters) > 0 {
|
||||
f := d.filters[0]
|
||||
if f.offset < len(p) {
|
||||
// only read data up to beginning of next filter
|
||||
p = p[:f.offset]
|
||||
}
|
||||
n = d.win.read(p) // read directly from window
|
||||
f.offset -= n // adjust first filter offset by bytes just read
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n = d.win.read(p) // read directly from window
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.tot += int64(n)
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
126
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decrypt_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
126
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/decrypt_reader.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"crypto/aes"
|
||||
"crypto/cipher"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// cipherBlockReader implements Block Mode decryption of an io.Reader object.
|
||||
type cipherBlockReader struct {
|
||||
r io.Reader
|
||||
mode cipher.BlockMode
|
||||
inbuf []byte // input buffer for partial data block
|
||||
outbuf []byte // output buffer used when output slice < block size
|
||||
n int // bytes read from outbuf
|
||||
err error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// read reads and decrypts one or more input blocks into p.
|
||||
// len(p) must be >= cipher block size.
|
||||
func (cr *cipherBlockReader) read(p []byte) (n int, err error) {
|
||||
bs := cr.mode.BlockSize()
|
||||
// round p down to a multiple of the block size
|
||||
l := len(p) - len(p)%bs
|
||||
p = p[:l]
|
||||
|
||||
l = len(cr.inbuf)
|
||||
if l > 0 {
|
||||
// copy any buffered input into p
|
||||
copy(p, cr.inbuf)
|
||||
cr.inbuf = cr.inbuf[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// read data for at least one block
|
||||
n, err = io.ReadAtLeast(cr.r, p[l:], bs-l)
|
||||
n += l
|
||||
p = p[:n]
|
||||
|
||||
l = n % bs
|
||||
// check if p is a multiple of the cipher block size
|
||||
if l > 0 {
|
||||
n -= l
|
||||
// save trailing partial block to process later
|
||||
cr.inbuf = append(cr.inbuf, p[n:]...)
|
||||
p = p[:n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.ErrUnexpectedEOF || err == io.ErrShortBuffer {
|
||||
// ignore trailing bytes < block size length
|
||||
err = io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
cr.mode.CryptBlocks(p, p) // decrypt block(s)
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read reads and decrypts data into p.
|
||||
// If the input is not a multiple of the cipher block size,
|
||||
// the trailing bytes will be ignored.
|
||||
func (cr *cipherBlockReader) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if cr.n < len(cr.outbuf) {
|
||||
// return buffered output
|
||||
n = copy(p, cr.outbuf[cr.n:])
|
||||
cr.n += n
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cr.err != nil {
|
||||
err = cr.err
|
||||
cr.err = nil
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(p) >= cap(cr.outbuf) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
// p is not large enough to process a block, use outbuf instead
|
||||
n, cr.err = cr.read(cr.outbuf[:cap(cr.outbuf)])
|
||||
cr.outbuf = cr.outbuf[:n]
|
||||
cr.n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
// read blocks into p
|
||||
return cr.read(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadByte returns the next decrypted byte.
|
||||
func (cr *cipherBlockReader) ReadByte() (byte, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if cr.n < len(cr.outbuf) {
|
||||
c := cr.outbuf[cr.n]
|
||||
cr.n++
|
||||
return c, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cr.err != nil {
|
||||
err := cr.err
|
||||
cr.err = nil
|
||||
return 0, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// refill outbuf
|
||||
var n int
|
||||
n, cr.err = cr.read(cr.outbuf[:cap(cr.outbuf)])
|
||||
cr.outbuf = cr.outbuf[:n]
|
||||
cr.n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newCipherBlockReader returns a cipherBlockReader that decrypts the given io.Reader using
|
||||
// the provided block mode cipher.
|
||||
func newCipherBlockReader(r io.Reader, mode cipher.BlockMode) *cipherBlockReader {
|
||||
cr := &cipherBlockReader{r: r, mode: mode}
|
||||
cr.outbuf = make([]byte, 0, mode.BlockSize())
|
||||
cr.inbuf = make([]byte, 0, mode.BlockSize())
|
||||
return cr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newAesDecryptReader returns a cipherBlockReader that decrypts input from a given io.Reader using AES.
|
||||
// It will panic if the provided key is invalid.
|
||||
func newAesDecryptReader(r io.Reader, key, iv []byte) *cipherBlockReader {
|
||||
block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
mode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, iv)
|
||||
|
||||
return newCipherBlockReader(r, mode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
416
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/filters.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
416
vendor/github.com/nwaples/rardecode/filters.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,416 @@
|
||||
package rardecode
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"hash/crc32"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
fileSize = 0x1000000
|
||||
|
||||
vmGlobalAddr = 0x3C000
|
||||
vmGlobalSize = 0x02000
|
||||
vmFixedGlobalSize = 0x40
|
||||
|
||||
maxUint32 = 1<<32 - 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// v3Filter is the interface type for RAR V3 filters.
|
||||
// v3Filter performs the same function as the filter type, except that it also takes
|
||||
// the initial register values r, and global data as input for the RAR V3 VM.
|
||||
type v3Filter func(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// standardV3Filters is a list of known filters. We can replace the use of a vm
|
||||
// filter with a custom filter function.
|
||||
standardV3Filters = []struct {
|
||||
crc uint32 // crc of code byte slice for filter
|
||||
len int // length of code byte slice for filter
|
||||
f v3Filter // replacement filter function
|
||||
}{
|
||||
{0xad576887, 53, e8FilterV3},
|
||||
{0x3cd7e57e, 57, e8e9FilterV3},
|
||||
{0x3769893f, 120, itaniumFilterV3},
|
||||
{0x0e06077d, 29, deltaFilterV3},
|
||||
{0x1c2c5dc8, 149, filterRGBV3},
|
||||
{0xbc85e701, 216, filterAudioV3},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// itanium filter byte masks
|
||||
byteMask = []int{4, 4, 6, 6, 0, 0, 7, 7, 4, 4, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, 0}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func filterE8(c byte, v5 bool, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
off := int32(offset)
|
||||
for b := buf; len(b) >= 5; {
|
||||
ch := b[0]
|
||||
b = b[1:]
|
||||
off++
|
||||
if ch != 0xe8 && ch != c {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v5 {
|
||||
off %= fileSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
addr := int32(binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(b))
|
||||
if addr < 0 {
|
||||
if addr+off >= 0 {
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(b, uint32(addr+fileSize))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if addr < fileSize {
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(b, uint32(addr-off))
|
||||
}
|
||||
off += 4
|
||||
b = b[4:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func e8FilterV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
return filterE8(0xe8, false, buf, offset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func e8e9FilterV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
return filterE8(0xe9, false, buf, offset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getBits(buf []byte, pos, count uint) uint32 {
|
||||
n := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buf[pos/8:])
|
||||
n >>= pos & 7
|
||||
mask := uint32(maxUint32) >> (32 - count)
|
||||
return n & mask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func setBits(buf []byte, pos, count uint, bits uint32) {
|
||||
mask := uint32(maxUint32) >> (32 - count)
|
||||
mask <<= pos & 7
|
||||
bits <<= pos & 7
|
||||
n := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buf[pos/8:])
|
||||
n = (n & ^mask) | (bits & mask)
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(buf[pos/8:], n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func itaniumFilterV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
fileOffset := uint32(offset) >> 4
|
||||
|
||||
for b := buf; len(b) > 21; b = b[16:] {
|
||||
c := int(b[0]&0x1f) - 0x10
|
||||
if c >= 0 {
|
||||
mask := byteMask[c]
|
||||
if mask != 0 {
|
||||
for i := uint(0); i <= 2; i++ {
|
||||
if mask&(1<<i) == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos := i*41 + 18
|
||||
if getBits(b, pos+24, 4) == 5 {
|
||||
n := getBits(b, pos, 20)
|
||||
n -= fileOffset
|
||||
setBits(b, pos, 20, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
fileOffset++
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func filterDelta(n int, buf []byte) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
var res []byte
|
||||
l := len(buf)
|
||||
if cap(buf) >= 2*l {
|
||||
res = buf[l : 2*l] // use unused capacity
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res = make([]byte, l, 2*l)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
|
||||
var c byte
|
||||
for k := j; k < len(res); k += n {
|
||||
c -= buf[i]
|
||||
i++
|
||||
res[k] = c
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func deltaFilterV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
return filterDelta(int(r[0]), buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func abs(n int) int {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = -n
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func filterRGBV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
width := int(r[0] - 3)
|
||||
posR := int(r[1])
|
||||
if posR < 0 || width < 0 {
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var res []byte
|
||||
l := len(buf)
|
||||
if cap(buf) >= 2*l {
|
||||
res = buf[l : 2*l] // use unused capacity
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res = make([]byte, l, 2*l)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for c := 0; c < 3; c++ {
|
||||
var prevByte int
|
||||
for i := c; i < len(res); i += 3 {
|
||||
var predicted int
|
||||
upperPos := i - width
|
||||
if upperPos >= 3 {
|
||||
upperByte := int(res[upperPos])
|
||||
upperLeftByte := int(res[upperPos-3])
|
||||
predicted = prevByte + upperByte - upperLeftByte
|
||||
pa := abs(predicted - prevByte)
|
||||
pb := abs(predicted - upperByte)
|
||||
pc := abs(predicted - upperLeftByte)
|
||||
if pa <= pb && pa <= pc {
|
||||
predicted = prevByte
|
||||
} else if pb <= pc {
|
||||
predicted = upperByte
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
predicted = upperLeftByte
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
predicted = prevByte
|
||||
}
|
||||
prevByte = (predicted - int(buf[0])) & 0xFF
|
||||
res[i] = uint8(prevByte)
|
||||
buf = buf[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := posR; i < len(res)-2; i += 3 {
|
||||
c := res[i+1]
|
||||
res[i] += c
|
||||
res[i+2] += c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func filterAudioV3(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
var res []byte
|
||||
l := len(buf)
|
||||
if cap(buf) >= 2*l {
|
||||
res = buf[l : 2*l] // use unused capacity
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res = make([]byte, l, 2*l)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
chans := int(r[0])
|
||||
for c := 0; c < chans; c++ {
|
||||
var prevByte, byteCount int
|
||||
var diff [7]int
|
||||
var d, k [3]int
|
||||
|
||||
for i := c; i < len(res); i += chans {
|
||||
predicted := prevByte<<3 + k[0]*d[0] + k[1]*d[1] + k[2]*d[2]
|
||||
predicted = int(int8(predicted >> 3))
|
||||
|
||||
curByte := int(int8(buf[0]))
|
||||
buf = buf[1:]
|
||||
predicted -= curByte
|
||||
res[i] = uint8(predicted)
|
||||
|
||||
dd := curByte << 3
|
||||
diff[0] += abs(dd)
|
||||
diff[1] += abs(dd - d[0])
|
||||
diff[2] += abs(dd + d[0])
|
||||
diff[3] += abs(dd - d[1])
|
||||
diff[4] += abs(dd + d[1])
|
||||
diff[5] += abs(dd - d[2])
|
||||
diff[6] += abs(dd + d[2])
|
||||
|
||||
prevDelta := int(int8(predicted - prevByte))
|
||||
prevByte = predicted
|
||||
d[2] = d[1]
|
||||
d[1] = prevDelta - d[0]
|
||||
d[0] = prevDelta
|
||||
|
||||
if byteCount&0x1f == 0 {
|
||||
min := diff[0]
|
||||
diff[0] = 0
|
||||
n := 0
|
||||
for j := 1; j < len(diff); j++ {
|
||||
if diff[j] < min {
|
||||
min = diff[j]
|
||||
n = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
diff[j] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
n--
|
||||
if n >= 0 {
|
||||
m := n / 2
|
||||
if n%2 == 0 {
|
||||
if k[m] >= -16 {
|
||||
k[m]--
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if k[m] < 16 {
|
||||
k[m]++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
byteCount++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func filterArm(buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
for i := 0; len(buf)-i > 3; i += 4 {
|
||||
if buf[i+3] == 0xeb {
|
||||
n := uint(buf[i])
|
||||
n += uint(buf[i+1]) * 0x100
|
||||
n += uint(buf[i+2]) * 0x10000
|
||||
n -= (uint(offset) + uint(i)) / 4
|
||||
buf[i] = byte(n)
|
||||
buf[i+1] = byte(n >> 8)
|
||||
buf[i+2] = byte(n >> 16)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type vmFilter struct {
|
||||
execCount uint32
|
||||
global []byte
|
||||
static []byte
|
||||
code []command
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// execute implements v3filter type for VM based RAR 3 filters.
|
||||
func (f *vmFilter) execute(r map[int]uint32, global, buf []byte, offset int64) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
if len(buf) > vmGlobalAddr {
|
||||
return buf, errInvalidFilter
|
||||
}
|
||||
v := newVM(buf)
|
||||
|
||||
// register setup
|
||||
v.r[3] = vmGlobalAddr
|
||||
v.r[4] = uint32(len(buf))
|
||||
v.r[5] = f.execCount
|
||||
for i, n := range r {
|
||||
v.r[i] = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// vm global data memory block
|
||||
vg := v.m[vmGlobalAddr : vmGlobalAddr+vmGlobalSize]
|
||||
|
||||
// initialize fixed global memory
|
||||
for i, n := range v.r[:vmRegs-1] {
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(vg[i*4:], n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(vg[0x1c:], uint32(len(buf)))
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(vg[0x24:], uint64(offset))
|
||||
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(vg[0x2c:], f.execCount)
|
||||
|
||||
// registers
|
||||
v.r[6] = uint32(offset)
|
||||
|
||||
// copy program global memory
|
||||
var n int
|
||||
if len(f.global) > 0 {
|
||||
n = copy(vg[vmFixedGlobalSize:], f.global) // use saved global instead
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n = copy(vg[vmFixedGlobalSize:], global)
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(vg[vmFixedGlobalSize+n:], f.static)
|
||||
|
||||
v.execute(f.code)
|
||||
|
||||
f.execCount++
|
||||
|
||||
// keep largest global buffer
|
||||
if cap(global) > cap(f.global) {
|
||||
f.global = global[:0]
|
||||
} else if len(f.global) > 0 {
|
||||
f.global = f.global[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check for global data to be saved for next program execution
|
||||
globalSize := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(vg[0x30:])
|
||||
if globalSize > 0 {
|
||||
if globalSize > vmGlobalSize-vmFixedGlobalSize {
|
||||
globalSize = vmGlobalSize - vmFixedGlobalSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cap(f.global) < int(globalSize) {
|
||||
f.global = make([]byte, globalSize)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
f.global = f.global[:globalSize]
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy(f.global, vg[vmFixedGlobalSize:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// find program output
|
||||
length := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(vg[0x1c:]) & vmMask
|
||||
start := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(vg[0x20:]) & vmMask
|
||||
if start+length > vmSize {
|
||||
// TODO: error
|
||||
start = 0
|
||||
length = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if start != 0 && cap(v.m) > cap(buf) {
|
||||
// Initial buffer was to small for vm.
|
||||
// Copy output to beginning of vm memory so that decodeReader
|
||||
// will re-use the newly allocated vm memory and we will not
|
||||
// have to reallocate again next time.
|
||||
copy(v.m, v.m[start:start+length])
|
||||
start = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.m[start : start+length], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getV3Filter returns a V3 filter function from a code byte slice.
|
||||
func getV3Filter(code []byte) (v3Filter, error) {
|
||||
// check if filter is a known standard filter
|
||||
c := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(code)
|
||||
for _, f := range standardV3Filters {
|
||||
if f.crc == c && f.len == len(code) {
|
||||
return f.f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// create new vm filter
|
||||
f := new(vmFilter)
|
||||
r := newRarBitReader(bytes.NewReader(code[1:])) // skip first xor byte check
|
||||
|
||||
// read static data
|
||||
n, err := r.readBits(1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
m, err := r.readUint32()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.static = make([]byte, m+1)
|
||||
err = r.readFull(f.static)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.code, err = readCommands(r)
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
err = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return f.execute, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user