make DiB_fileStats skip invalid files (fileSize <= 0) to prevent negative totals and bogus allocation
Command Line Interface for Zstandard library
Command Line Interface (CLI) can be created using the make command without any additional parameters.
There are however other Makefile targets that create different variations of CLI:
zstd: default CLI supporting gzip-like arguments; includes dictionary builder, benchmark, and supports decompression of legacy zstd formatszstd_nolegacy: Same aszstdbut without support for legacy zstd formatszstd-small: CLI optimized for minimal size; no dictionary builder, no benchmark, and no support for legacy zstd formatszstd-compress: version of CLI which can only compress into zstd formatzstd-decompress: version of CLI which can only decompress zstd format
Compilation variables
zstd scope can be altered by modifying the following make variables :
-
HAVE_THREAD : multithreading is automatically enabled when
pthreadis detected. It's possible to disable multithread support, by settingHAVE_THREAD=0. Example :make zstd HAVE_THREAD=0It's also possible to force multithread support, usingHAVE_THREAD=1. In which case, linking stage will fail if neitherpthreadnorwindows.hlibrary can be found. This is useful to ensure this feature is not silently disabled. -
ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT :
zstdcan decompress files compressed by older versions ofzstd. Starting v0.8.0, all versions ofzstdproduce frames compliant with the specification, and are therefore compatible. But older versions (< v0.8.0) produced different, incompatible, frames. By default,zstdsupports decoding legacy formats >= v0.4.0 (ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT=4). This can be altered by modifying this compilation variable.ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT=1means "support all formats >= v0.1.0".ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT=2means "support all formats >= v0.2.0", and so on.ZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT=0means DO NOT support any legacy format. ifZSTD_LEGACY_SUPPORT >= 8, it's the same as0, since there is no legacy format after7. Note :zstdonly supports decoding older formats, and cannot generate any legacy format. -
HAVE_ZLIB :
zstdcan compress and decompress files in.gzformat. This is ordered through command--format=gzip. Alternatively, symlinks namedgziporgunzipwill mimic intended behavior..gzsupport is automatically enabled whenzliblibrary is detected at build time. It's possible to disable.gzsupport, by settingHAVE_ZLIB=0. Example :make zstd HAVE_ZLIB=0It's also possible to force compilation with zlib support, usingHAVE_ZLIB=1. In which case, linking stage will fail ifzliblibrary cannot be found. This is useful to prevent silent feature disabling. -
HAVE_LZMA :
zstdcan compress and decompress files in.xzand.lzmaformats. This is ordered through commands--format=xzand--format=lzmarespectively. Alternatively, symlinks namedxz,unxz,lzma, orunlzmawill mimic intended behavior..xzand.lzmasupport is automatically enabled whenlzmalibrary is detected at build time. It's possible to disable.xzand.lzmasupport, by settingHAVE_LZMA=0. Example :make zstd HAVE_LZMA=0It's also possible to force compilation with lzma support, usingHAVE_LZMA=1. In which case, linking stage will fail iflzmalibrary cannot be found. This is useful to prevent silent feature disabling. -
HAVE_LZ4 :
zstdcan compress and decompress files in.lz4formats. This is ordered through commands--format=lz4. Alternatively, symlinks namedlz4, orunlz4will mimic intended behavior..lz4support is automatically enabled whenlz4library is detected at build time. It's possible to disable.lz4support, by settingHAVE_LZ4=0. Example :make zstd HAVE_LZ4=0It's also possible to force compilation with lz4 support, usingHAVE_LZ4=1. In which case, linking stage will fail iflz4library cannot be found. This is useful to prevent silent feature disabling. -
ZSTD_NOBENCH :
zstdcli will be compiled without its integrated benchmark module. This can be useful to produce smaller binaries. In this case, the corresponding unit can also be excluded from compilation target. -
ZSTD_NODICT :
zstdcli will be compiled without support for the integrated dictionary builder. This can be useful to produce smaller binaries. In this case, the corresponding unit can also be excluded from compilation target. -
ZSTD_NOCOMPRESS :
zstdcli will be compiled without support for compression. The resulting binary will only be able to decompress files. This can be useful to produce smaller binaries. A correspondingMakefiletarget using this ability iszstd-decompress. -
ZSTD_NODECOMPRESS :
zstdcli will be compiled without support for decompression. The resulting binary will only be able to compress files. This can be useful to produce smaller binaries. A correspondingMakefiletarget using this ability iszstd-compress. -
BACKTRACE :
zstdcan display a stack backtrace when execution generates a runtime exception. By default, this feature may be degraded/disabled on some platforms unless additional compiler directives are applied. When triaging a runtime issue, enabling this feature can provide more context to determine the location of the fault. Example :make zstd BACKTRACE=1
Aggregation of parameters
CLI supports aggregation of parameters i.e. -b1, -e18, and -i1 can be joined into -b1e18i1.
Symlink shortcuts
It's possible to invoke zstd through a symlink.
When the name of the symlink has a specific value, it triggers an associated behavior.
zstdmt: compress using all cores available on local system.zcat: will decompress and output target file using any of the supported formats.gzcatandzstdcatare also equivalent.gzip: if zlib support is enabled, will mimicgzipby compressing file using.gzformat, removing source file by default (use--keepto preserve). If zlib is not supported, triggers an error.xz: if lzma support is enabled, will mimicxzby compressing file using.xzformat, removing source file by default (use--keepto preserve). If xz is not supported, triggers an error.lzma: if lzma support is enabled, will mimiclzmaby compressing file using.lzmaformat, removing source file by default (use--keepto preserve). If lzma is not supported, triggers an error.lz4: if lz4 support is enabled, will mimiclz4by compressing file using.lz4format. If lz4 is not supported, triggers an error.unzstdandunlz4will decompress any of the supported format.ungz,unxzandunlzmawill do the same, and will also remove source file by default (use--keepto preserve).
Dictionary builder in Command Line Interface
Zstd offers a training mode, which can be used to tune the algorithm for a selected
type of data, by providing it with a few samples. The result of the training is stored
in a file selected with the -o option (default name is dictionary),
which can be loaded before compression and decompression.
Using a dictionary, the compression ratio achievable on small data improves dramatically. These compression gains are achieved while simultaneously providing faster compression and decompression speeds. Dictionary work if there is some correlation in a family of small data (there is no universal dictionary). Hence, deploying one dictionary per type of data will provide the greater benefits. Dictionary gains are mostly effective in the first few KB. Then, the compression algorithm will rely more and more on previously decoded content to compress the rest of the file.
Usage of the dictionary builder and created dictionaries with CLI:
- Create the dictionary :
zstd --train PathToTrainingSet/* -o dictionaryName - Compress with the dictionary:
zstd FILE -D dictionaryName - Decompress with the dictionary:
zstd --decompress FILE.zst -D dictionaryName
Benchmark in Command Line Interface
CLI includes in-memory compression benchmark module for zstd.
The benchmark is conducted using given filenames. The files are read into memory and joined together.
It makes benchmark more precise as it eliminates I/O overhead.
Multiple filenames can be supplied, as multiple parameters, with wildcards,
or directory names can be used with -r option.
If no file is provided, the benchmark will use a procedurally generated "lorem ipsum" content.
The benchmark measures ratio, compressed size, compression and decompression speed.
One can select compression levels starting from -b and ending with -e.
The -i parameter selects minimal time used for each of tested levels.
The benchmark can also be used to test specific parameters,
such as number of threads (-T#), or advanced parameters (--zstd=#), or dictionary compression (-D DICTIONARY),
and many others available on command for regular compression and decompression.
Usage of Command Line Interface
The full list of options can be obtained with -h or -H parameter:
*** Zstandard CLI (64-bit) v1.5.6, by Yann Collet ***
Compress or decompress the INPUT file(s); reads from STDIN if INPUT is `-` or not provided.
Usage: zstd [OPTIONS...] [INPUT... | -] [-o OUTPUT]
Options:
-o OUTPUT Write output to a single file, OUTPUT.
-k, --keep Preserve INPUT file(s). [Default]
--rm Remove INPUT file(s) after successful (de)compression to file.
-# Desired compression level, where `#` is a number between 1 and 19;
lower numbers provide faster compression, higher numbers yield
better compression ratios. [Default: 3]
-d, --decompress Perform decompression.
-D DICT Use DICT as the dictionary for compression or decompression.
-f, --force Disable input and output checks. Allows overwriting existing files,
receiving input from the console, printing output to STDOUT, and
operating on links, block devices, etc. Unrecognized formats will be
passed-through through as-is.
-h Display short usage and exit.
-H, --help Display full help and exit.
-V, --version Display the program version and exit.
Advanced options:
-c, --stdout Write to STDOUT (even if it is a console) and keep the INPUT file(s).
-v, --verbose Enable verbose output; pass multiple times to increase verbosity.
-q, --quiet Suppress warnings; pass twice to suppress errors.
--trace LOG Log tracing information to LOG.
--[no-]progress Forcibly show/hide the progress counter. NOTE: Any (de)compressed
output to terminal will mix with progress counter text.
-r Operate recursively on directories.
--filelist LIST Read a list of files to operate on from LIST.
--output-dir-flat DIR Store processed files in DIR.
--output-dir-mirror DIR Store processed files in DIR, respecting original directory structure.
--[no-]asyncio Use asynchronous IO. [Default: Enabled]
--[no-]check Add XXH64 integrity checksums during compression. [Default: Add, Validate]
If `-d` is present, ignore/validate checksums during decompression.
-- Treat remaining arguments after `--` as files.
Advanced compression options:
--ultra Enable levels beyond 19, up to 22; requires more memory.
--fast[=#] Use to very fast compression levels. [Default: 1]
--adapt Dynamically adapt compression level to I/O conditions.
--long[=#] Enable long distance matching with window log #. [Default: 27]
--patch-from=REF Use REF as the reference point for Zstandard's diff engine.
-T# Spawn # compression threads. [Default: 1; pass 0 for core count.]
--single-thread Share a single thread for I/O and compression (slightly different than `-T1`).
--auto-threads={physical|logical}
Use physical/logical cores when using `-T0`. [Default: Physical]
-B# Set job size to #. [Default: 0 (automatic)]
--rsyncable Compress using a rsync-friendly method (`-B` sets block size).
--exclude-compressed Only compress files that are not already compressed.
--stream-size=# Specify size of streaming input from STDIN.
--size-hint=# Optimize compression parameters for streaming input of approximately size #.
--target-compressed-block-size=#
Generate compressed blocks of approximately # size.
--no-dictID Don't write `dictID` into the header (dictionary compression only).
--[no-]compress-literals Force (un)compressed literals.
--[no-]row-match-finder Explicitly enable/disable the fast, row-based matchfinder for
the 'greedy', 'lazy', and 'lazy2' strategies.
--format=zstd Compress files to the `.zst` format. [Default]
--[no-]mmap-dict Memory-map dictionary file rather than mallocing and loading all at once
--format=gzip Compress files to the `.gz` format.
--format=xz Compress files to the `.xz` format.
--format=lzma Compress files to the `.lzma` format.
--format=lz4 Compress files to the `.lz4` format.
Advanced decompression options:
-l Print information about Zstandard-compressed files.
--test Test compressed file integrity.
-M# Set the memory usage limit to # megabytes.
--[no-]sparse Enable sparse mode. [Default: Enabled for files, disabled for STDOUT.]
--[no-]pass-through Pass through uncompressed files as-is. [Default: Disabled]
Dictionary builder:
--train Create a dictionary from a training set of files.
--train-cover[=k=#,d=#,steps=#,split=#,shrink[=#]]
Use the cover algorithm (with optional arguments).
--train-fastcover[=k=#,d=#,f=#,steps=#,split=#,accel=#,shrink[=#]]
Use the fast cover algorithm (with optional arguments).
--train-legacy[=s=#] Use the legacy algorithm with selectivity #. [Default: 9]
-o NAME Use NAME as dictionary name. [Default: dictionary]
--maxdict=# Limit dictionary to specified size #. [Default: 112640]
--dictID=# Force dictionary ID to #. [Default: Random]
Benchmark options:
-b# Perform benchmarking with compression level #. [Default: 3]
-e# Test all compression levels up to #; starting level is `-b#`. [Default: 1]
-i# Set the minimum evaluation to time # seconds. [Default: 3]
-B# Cut file into independent chunks of size #. [Default: No chunking]
-S Output one benchmark result per input file. [Default: Consolidated result]
-D dictionary Benchmark using dictionary
--priority=rt Set process priority to real-time.
Passing parameters through Environment Variables
There is no "generic" way to pass "any kind of parameter" to zstd in a pass-through manner.
Using environment variables for this purpose has security implications.
Therefore, this avenue is intentionally restricted and only supports ZSTD_CLEVEL and ZSTD_NBTHREADS.
ZSTD_CLEVEL can be used to modify the default compression level of zstd
(usually set to 3) to another value between 1 and 19 (the "normal" range).
ZSTD_NBTHREADS can be used to specify a number of threads
that zstd will use for compression, which by default is 1.
This functionality only exists when zstd is compiled with multithread support.
0 means "use as many threads as detected cpu cores on local system".
The max # of threads is capped at ZSTDMT_NBWORKERS_MAX,
which is either 64 in 32-bit mode, or 256 for 64-bit environments.
This functionality can be useful when zstd CLI is invoked in a way that doesn't allow passing arguments.
One such scenario is tar --zstd.
As ZSTD_CLEVEL and ZSTD_NBTHREADS only replace the default compression level
and number of threads respectively, they can both be overridden by corresponding command line arguments:
-# for compression level and -T# for number of threads.
Long distance matching mode
The long distance matching mode, enabled with --long, is designed to improve
the compression ratio for files with long matches at a large distance (up to the
maximum window size, 128 MiB) while still maintaining compression speed.
Enabling this mode sets the window size to 128 MiB and thus increases the memory
usage for both the compressor and decompressor. Performance in terms of speed is
dependent on long matches being found. Compression speed may degrade if few long
matches are found. Decompression speed usually improves when there are many long
distance matches.
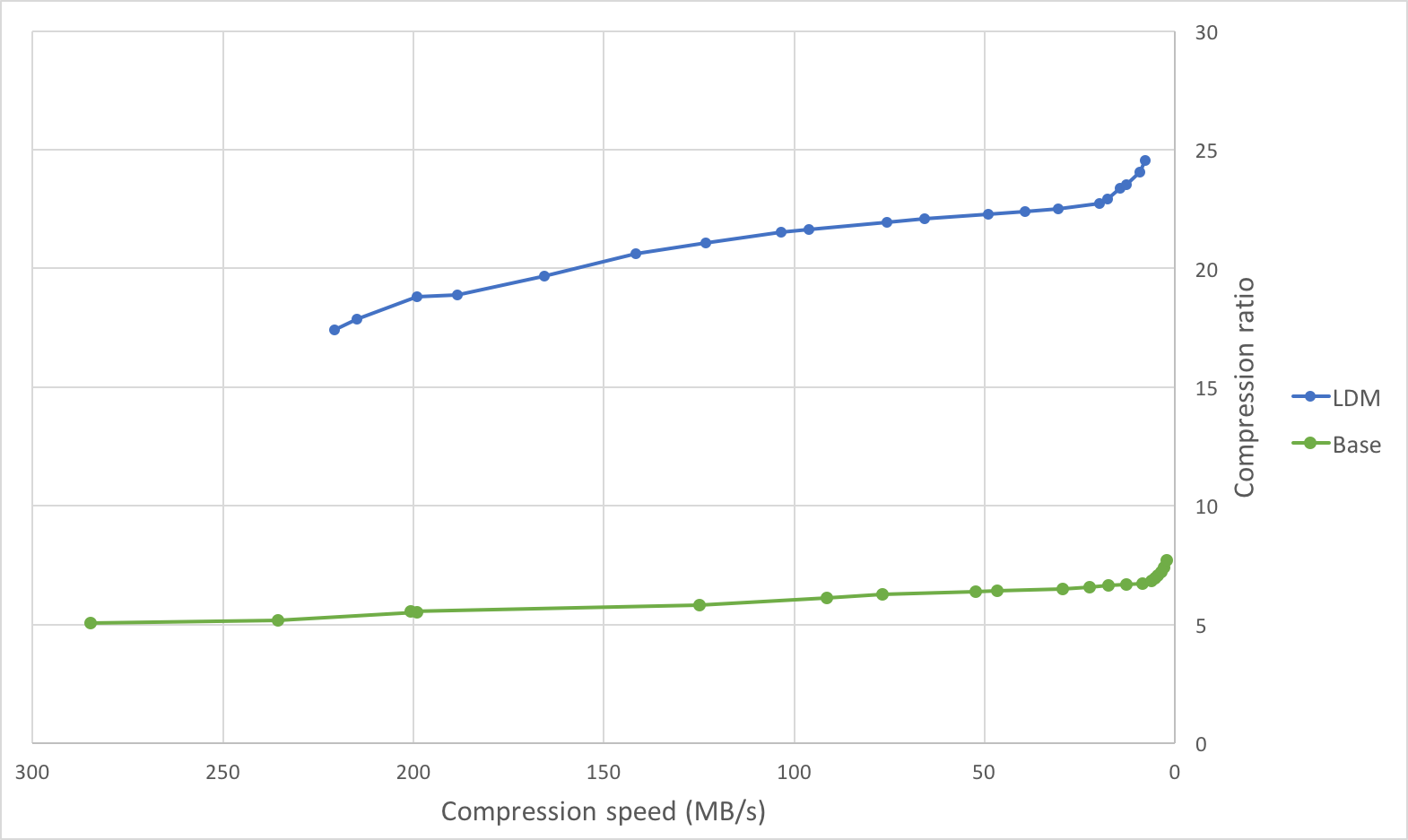
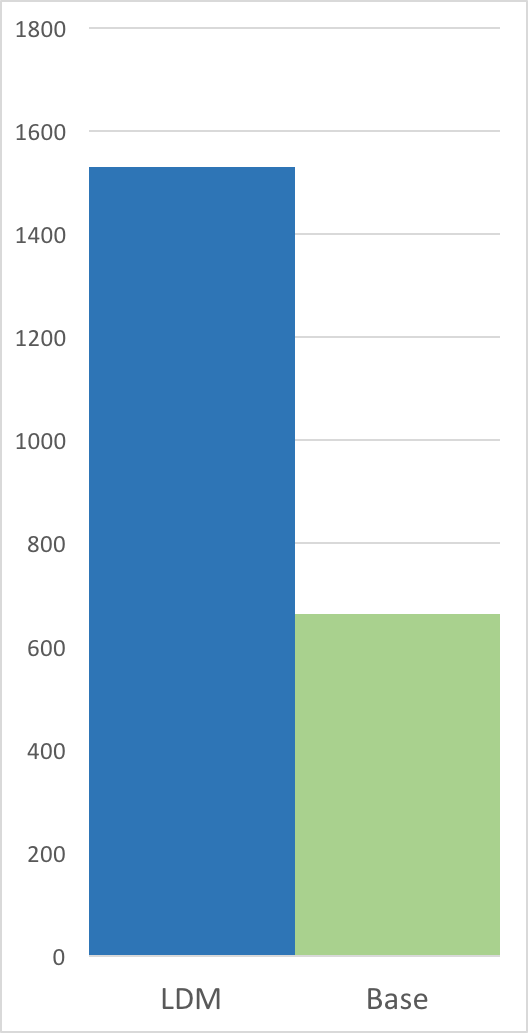
Below are graphs comparing the compression speed, compression ratio, and
decompression speed with and without long distance matching on an ideal use
case: a tar of four versions of clang (versions 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.5.0,
3.5.1) with a total size of 244889600 B. This is an ideal use case as there
are many long distance matches within the maximum window size of 128 MiB (each
version is less than 128 MiB).
| Compression Speed vs Ratio | Decompression Speed |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Method | Compression ratio | Compression speed | Decompression speed |
|---|---|---|---|
zstd -1 |
5.065 |
284.8 MB/s |
759.3 MB/s |
zstd -5 |
5.826 |
124.9 MB/s |
674.0 MB/s |
zstd -10 |
6.504 |
29.5 MB/s |
771.3 MB/s |
zstd -1 --long |
17.426 |
220.6 MB/s |
1638.4 MB/s |
zstd -5 --long |
19.661 |
165.5 MB/s |
1530.6 MB/s |
zstd -10 --long |
21.949 |
75.6 MB/s |
1632.6 MB/s |
On this file, the compression ratio improves significantly with minimal impact on compression speed, and the decompression speed doubles.
On the other extreme, compressing a file with few long distance matches (such as the Silesia compression corpus) will likely lead to a deterioration in compression speed (for lower levels) with minimal change in compression ratio.
The below table illustrates this on the Silesia compression corpus.
| Method | Compression ratio | Compression speed | Decompression speed |
|---|---|---|---|
zstd -1 |
2.878 |
231.7 MB/s |
594.4 MB/s |
zstd -1 --long |
2.929 |
106.5 MB/s |
517.9 MB/s |
zstd -5 |
3.274 |
77.1 MB/s |
464.2 MB/s |
zstd -5 --long |
3.319 |
51.7 MB/s |
371.9 MB/s |
zstd -10 |
3.523 |
16.4 MB/s |
489.2 MB/s |
zstd -10 --long |
3.566 |
16.2 MB/s |
415.7 MB/s |
zstdgrep
zstdgrep is a utility which makes it possible to grep directly a .zst compressed file.
It's used the same way as normal grep, for example :
zstdgrep pattern file.zst
zstdgrep is not compatible with dictionary compression.
To search into a file compressed with a dictionary,
it's necessary to decompress it using zstd or zstdcat,
and then pipe the result to grep. For example :
zstdcat -D dictionary -qc -- file.zst | grep pattern