6.3 KiB
Diffusers
Definitions
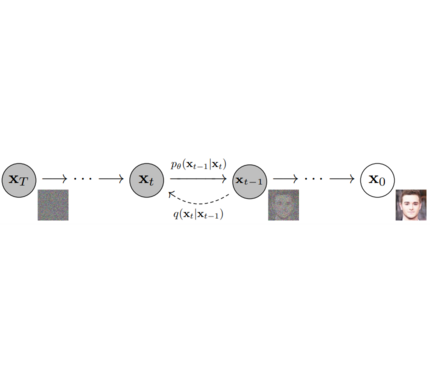
Models: Single neural network that models p_θ(x_t-1|x_t) and is trained to “denoise” to image Examples: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
Schedulers: Algorithm to sample noise schedule for both training and inference. Defines alpha and beta schedule, timesteps, etc.. Example: Gaussian DDPM, DDIM, PMLS, DEIN
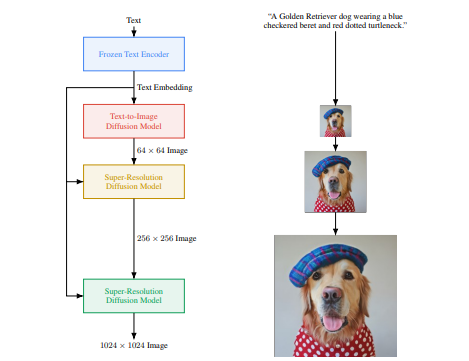
Diffusion Pipeline: End-to-end pipeline that includes multiple diffusion models, possible text encoders, CLIP Example: GLIDE,CompVis/Latent-Diffusion, Imagen, DALL-E
1. diffusers as a central modular diffusion and sampler library
diffusers is more modularized than transformers. The idea is that researchers and engineers can use only parts of the library easily for the own use cases.
It could become a central place for all kinds of models, schedulers, training utils and processors that one can mix and match for one's own use case.
Both models and scredulers should be load- and saveable from the Hub.
Example:
import torch
from diffusers import UNetModel, GaussianDDPMScheduler
import PIL
import numpy as np
generator = torch.Generator()
generator = generator.manual_seed(6694729458485568)
torch_device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 1. Load models
scheduler = GaussianDDPMScheduler.from_config("fusing/ddpm-lsun-church")
model = UNetModel.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-lsun-church").to(torch_device)
# 2. Sample gaussian noise
image = scheduler.sample_noise((1, model.in_channels, model.resolution, model.resolution), device=torch_device, generator=generator)
# 3. Denoise
for t in reversed(range(len(scheduler))):
# i) define coefficients for time step t
clipped_image_coeff = 1 / torch.sqrt(scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t))
clipped_noise_coeff = torch.sqrt(1 / scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t) - 1)
image_coeff = (1 - scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t - 1)) * torch.sqrt(scheduler.get_alpha(t)) / (1 - scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t))
clipped_coeff = torch.sqrt(scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t - 1)) * scheduler.get_beta(t) / (1 - scheduler.get_alpha_prod(t))
# ii) predict noise residual
with torch.no_grad():
noise_residual = model(image, t)
# iii) compute predicted image from residual
# See 2nd formula at https://github.com/hojonathanho/diffusion/issues/5#issue-896554416 for comparison
pred_mean = clipped_image_coeff * image - clipped_noise_coeff * noise_residual
pred_mean = torch.clamp(pred_mean, -1, 1)
prev_image = clipped_coeff * pred_mean + image_coeff * image
# iv) sample variance
prev_variance = scheduler.sample_variance(t, prev_image.shape, device=torch_device, generator=generator)
# v) sample x_{t-1} ~ N(prev_image, prev_variance)
sampled_prev_image = prev_image + prev_variance
image = sampled_prev_image
# process image to PIL
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
# save image
image_pil.save("test.png")
2. diffusers as a collection of most important Diffusion systems (GLIDE, Dalle, ...)
models directory in repository hosts the complete code necessary for running a diffusion system as well as to train it. A DiffusionPipeline class allows to easily run the diffusion model in inference:
Example:
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import PIL.Image
import numpy as np
# load model and scheduler
ddpm = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("fusing/ddpm-lsun-bedroom")
# run pipeline in inference (sample random noise and denoise)
image = ddpm()
# process image to PIL
image_processed = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
# save image
image_pil.save("test.png")
Library structure:
├── models
│ ├── audio
│ │ └── fastdiff
│ │ ├── modeling_fastdiff.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_fastdiff.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── vision
│ ├── dalle2
│ │ ├── modeling_dalle2.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_dalle2.py
│ ├── ddpm
│ │ ├── example.py
│ │ ├── modeling_ddpm.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_ddpm.py
│ ├── glide
│ │ ├── modeling_glide.py
│ │ ├── modeling_vqvae.py.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_glide.py
│ ├── imagen
│ │ ├── modeling_dalle2.py
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ └── run_dalle2.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── latent_diffusion
│ ├── modeling_latent_diffusion.py
│ ├── README.md
│ └── run_latent_diffusion.py
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
├── setup.cfg
├── setup.py
├── src
│ └── diffusers
│ ├── configuration_utils.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── modeling_utils.py
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── unet_glide.py
│ │ └── unet.py
│ ├── pipeline_utils.py
│ └── schedulers
│ ├── gaussian_ddpm.py
│ ├── __init__.py
├── tests
│ └── test_modeling_utils.py