# Accelerate inference of text-to-image diffusion models
Diffusion models are known to be slower than their counter parts, GANs, because of the iterative and sequential reverse diffusion process. Recent works try to address limitation with:
* progressive timestep distillation (such as [LCM LoRA](../using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm_lora.md))
* model compression (such as [SSD-1B](https://huggingface.co/segmind/SSD-1B))
* reusing adjacent features of the denoiser (such as [DeepCache](https://github.com/horseee/DeepCache))
In this tutorial, we focus on leveraging the power of PyTorch 2 to accelerate the inference latency of text-to-image diffusion pipeline, instead. We will use [Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](../using-diffusers/sdxl.md) as a case study, but the techniques we will discuss should extend to other text-to-image diffusion pipelines.
## Setup
Make sure you're on the latest version of `diffusers`:
```bash
pip install -U diffusers
```
Then upgrade the other required libraries too:
```bash
pip install -U transformers accelerate peft
```
To benefit from the fastest kernels, use PyTorch nightly. You can find the installation instructions [here](https://pytorch.org/).
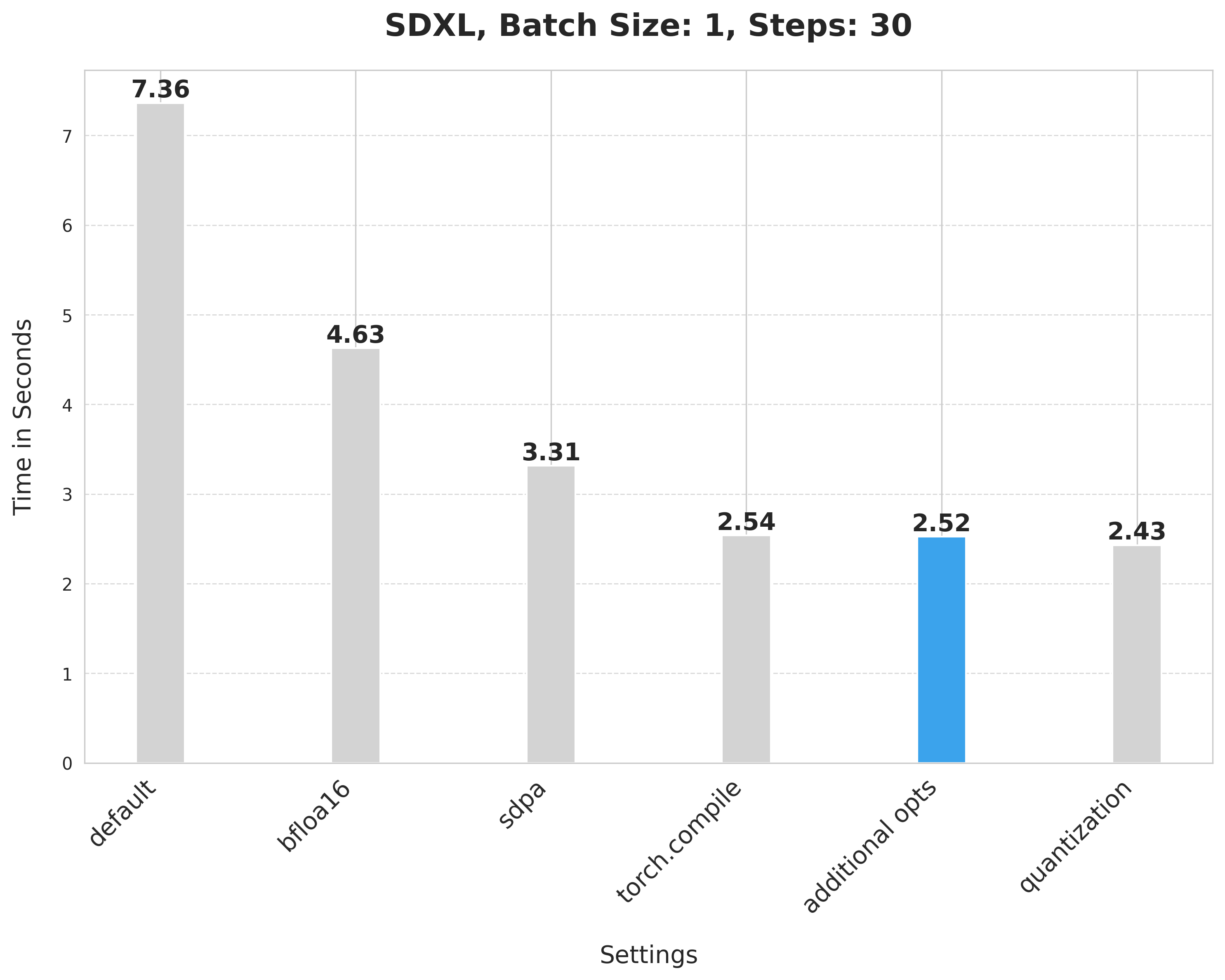
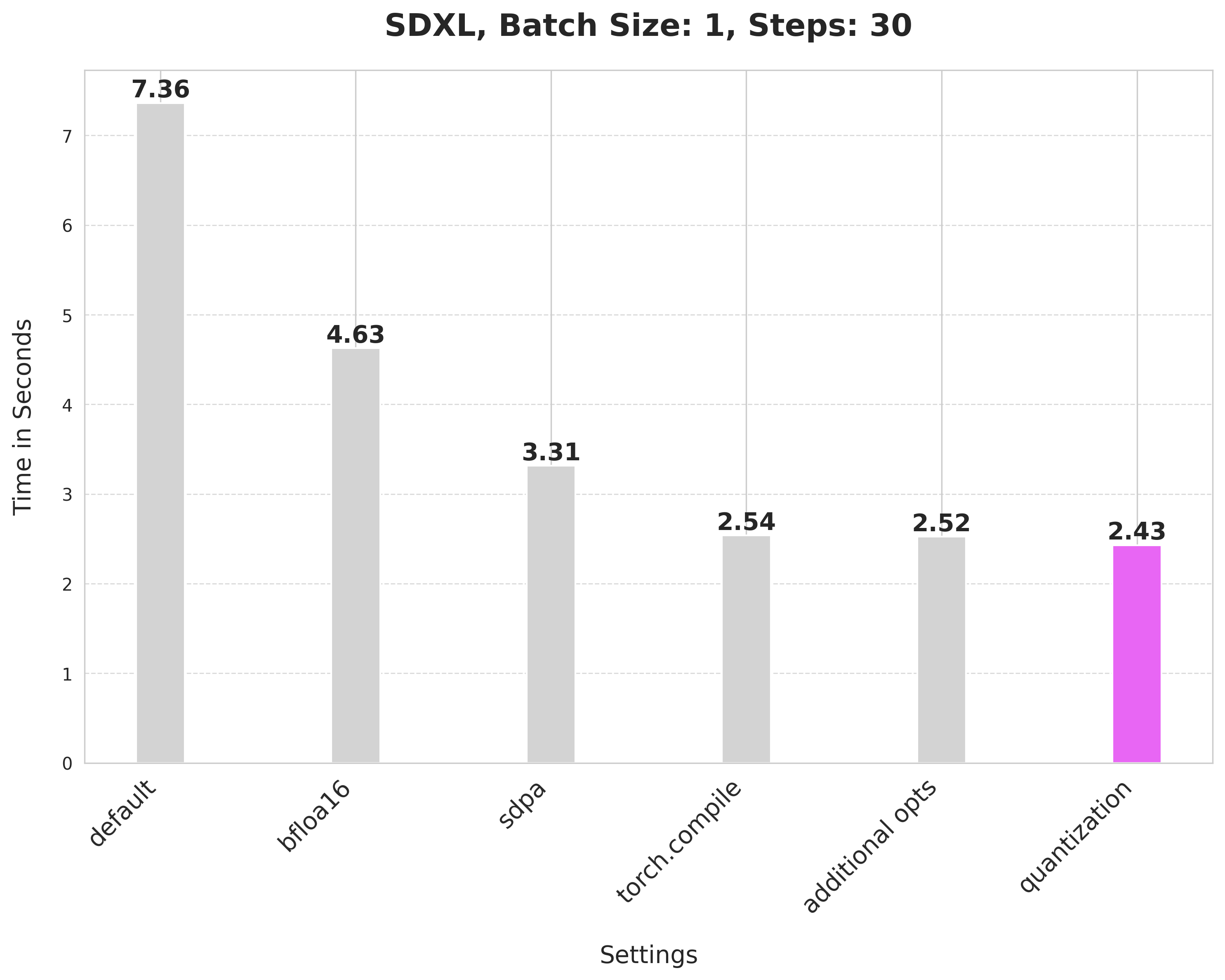
To report the numbers shown below, we used an 80GB 400W A100 with its clock rate set to the maximum.
_This tutorial doesn't present the benchmarking code and focuses on how to perform the optimizations, instead. For the full benchmarking code, refer to: [https://github.com/huggingface/diffusion-fast](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusion-fast)._
## Baseline
Let's start with a baseline. Disable the use of a reduced precision and [`scaled_dot_product_attention`](../optimization/torch2.0.md):
```python
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
# Load the pipeline in full-precision and place its model components on CUDA.
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
).to("cuda")
# Run the attention ops without efficiency.
pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
pipe.vae.set_default_attn_processor()
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
```
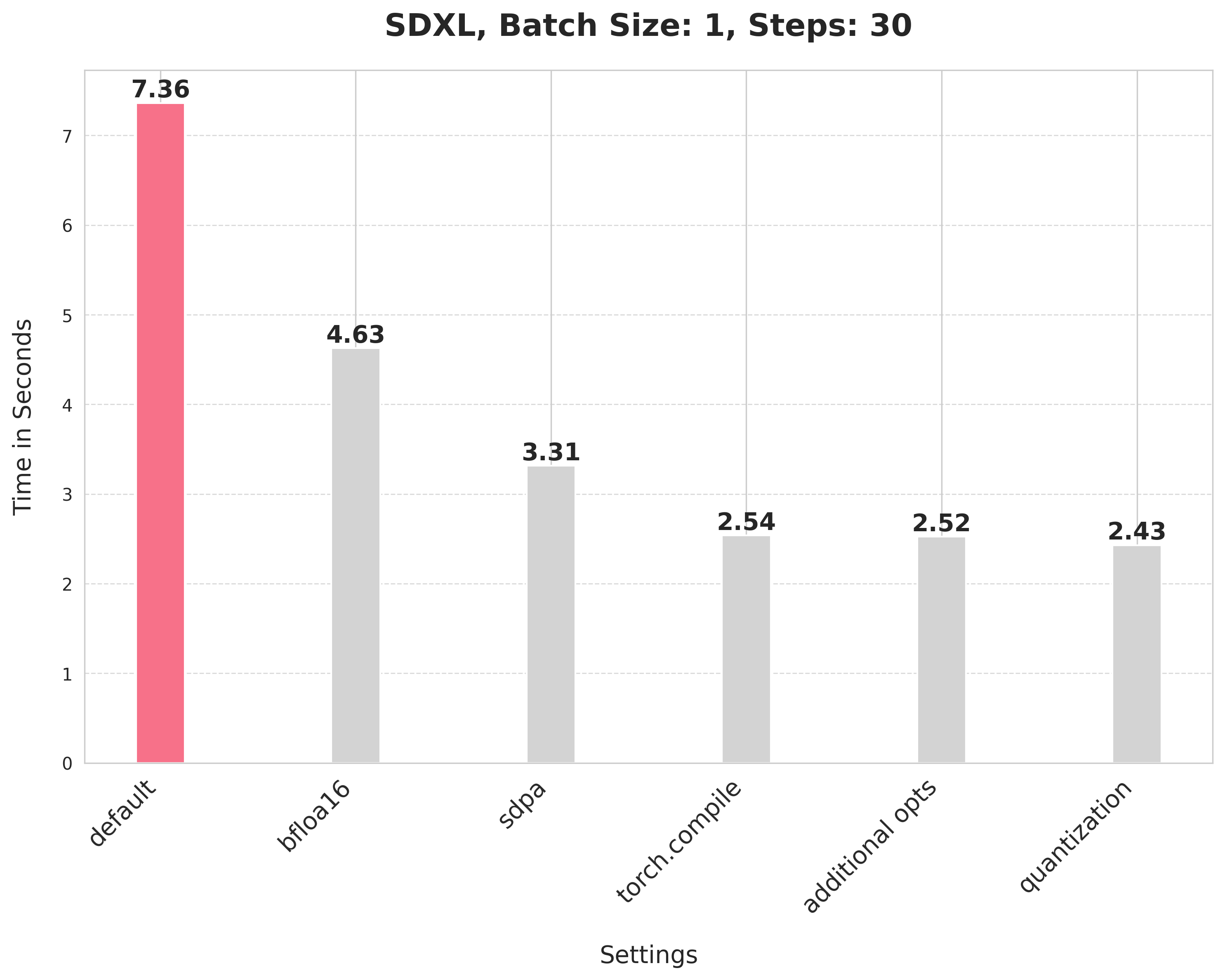
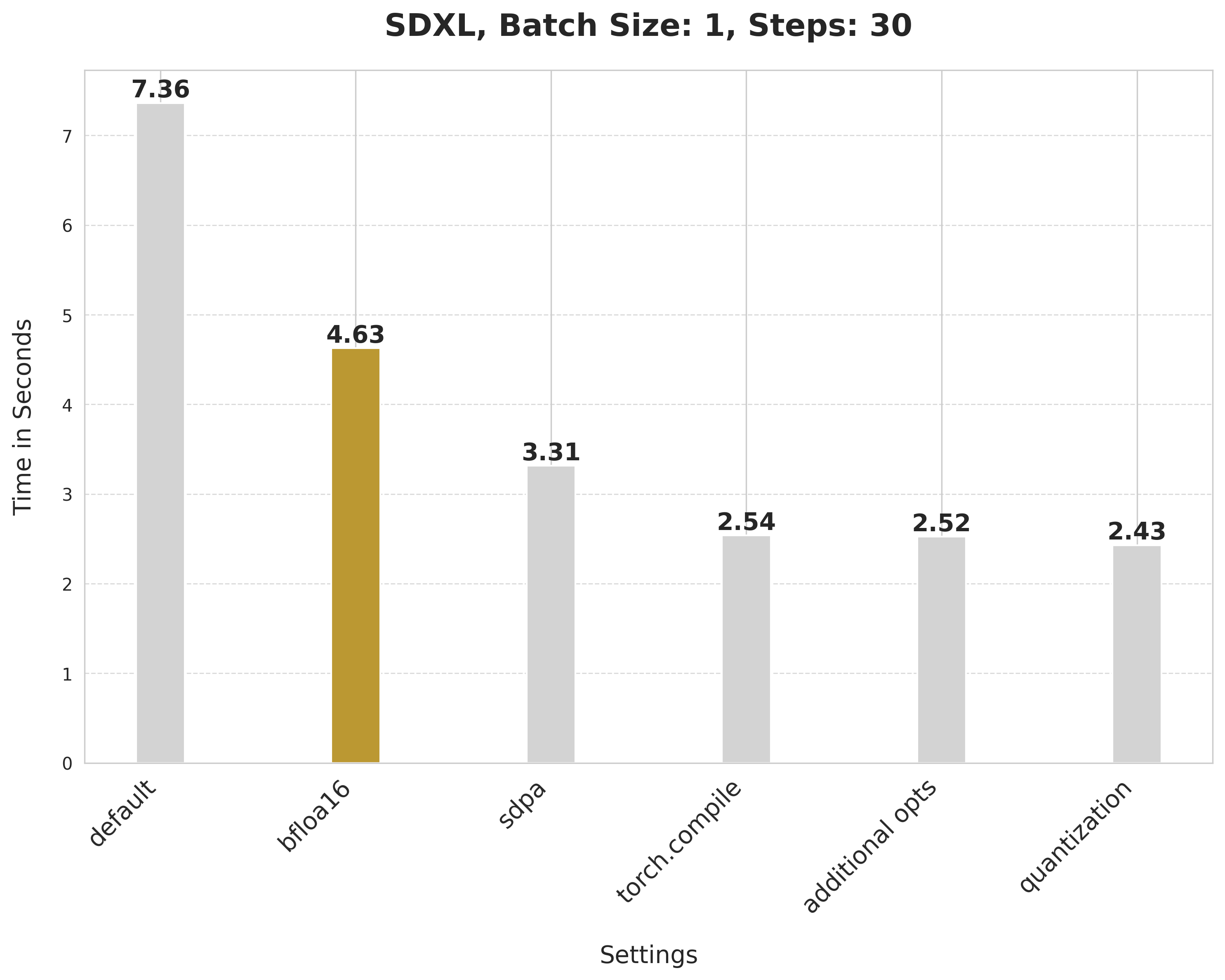
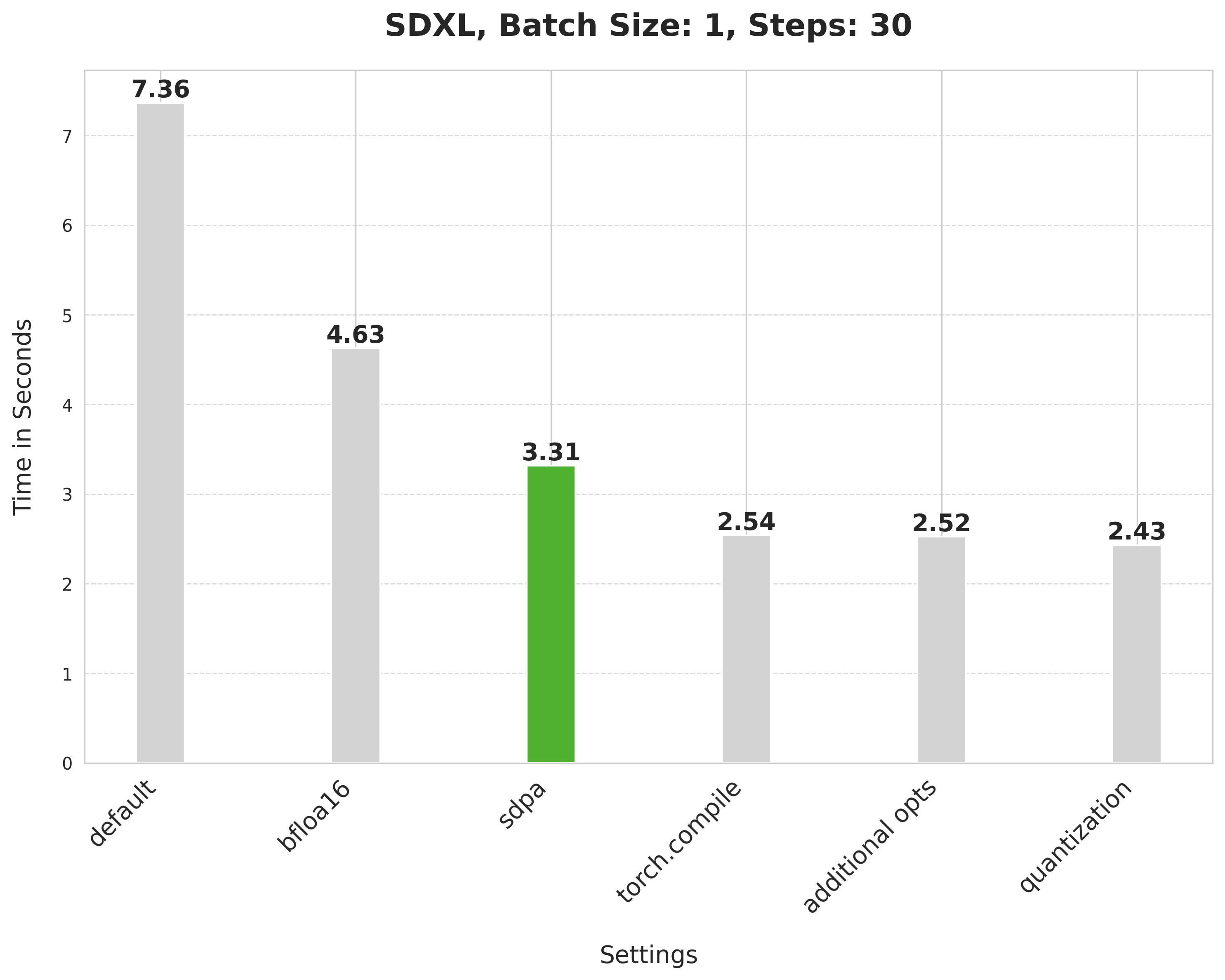
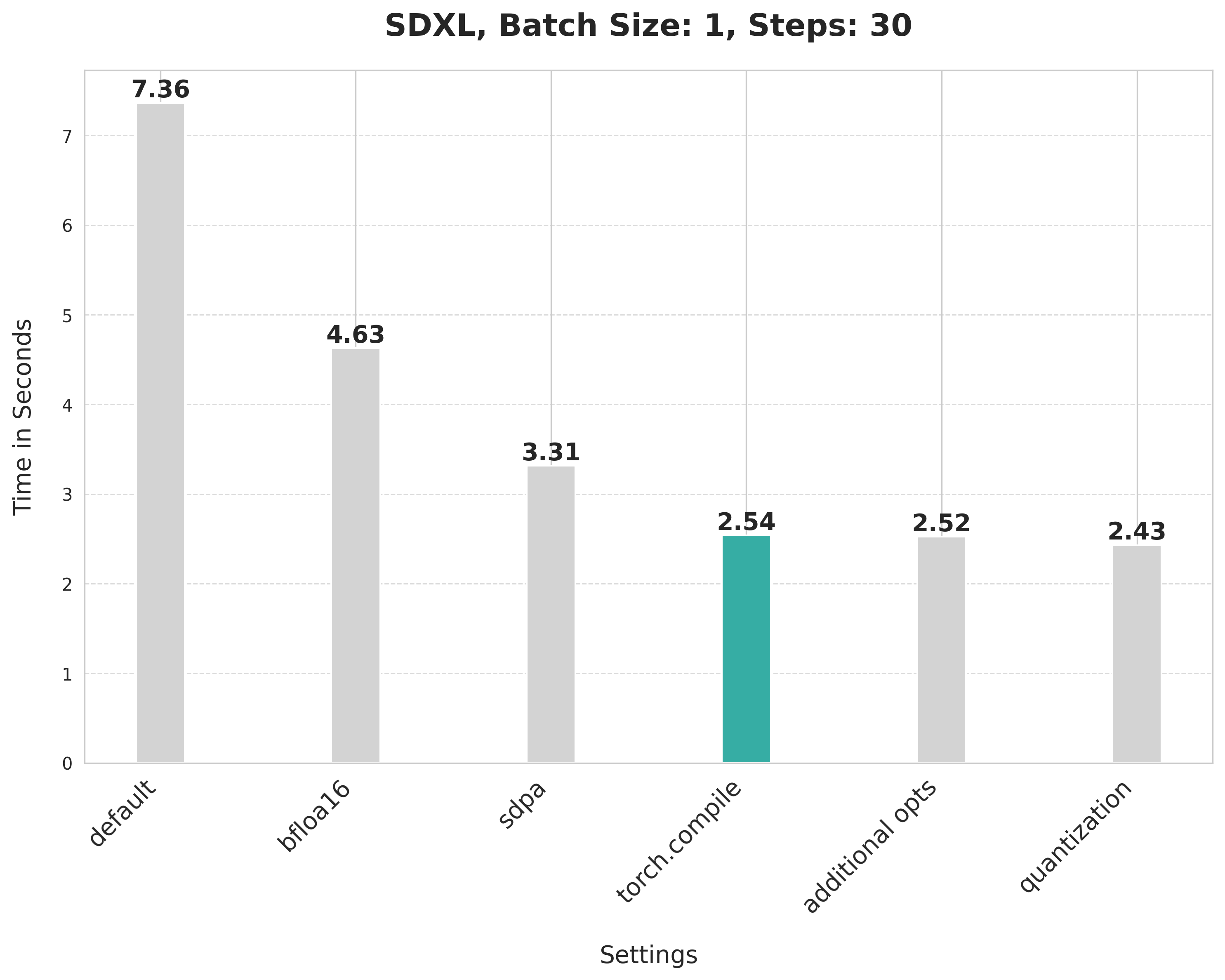
This takes 7.36 seconds:
## Running inference in bfloat16
Enable the first optimization: use a reduced precision to run the inference.
```python
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
).to("cuda")
# Run the attention ops without efficiency.
pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
pipe.vae.set_default_attn_processor()
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
```
bfloat16 reduces the latency from 7.36 seconds to 4.63 seconds:
_(We later ran the experiments in float16 and found out that the recent versions of torchao do not incur numerical problems from float16.)_
**Why bfloat16?**
* Using a reduced numerical precision (such as float16, bfloat16) to run inference doesn’t affect the generation quality but significantly improves latency.
* The benefits of using the bfloat16 numerical precision as compared to float16 are hardware-dependent. Modern generations of GPUs tend to favor bfloat16.
* Furthermore, in our experiments, we bfloat16 to be much more resilient when used with quantization in comparison to float16.
We have a [dedicated guide](../optimization/fp16.md) for running inference in a reduced precision.
## Running attention efficiently
Attention blocks are intensive to run. But with PyTorch's [`scaled_dot_product_attention`](../optimization/torch2.0.md), we can run them efficiently.
```python
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
).to("cuda")
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
```
`scaled_dot_product_attention` improves the latency from 4.63 seconds to 3.31 seconds.
## Use faster kernels with torch.compile
Compile the UNet and the VAE to benefit from the faster kernels. First, configure a few compiler flags:
```python
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
torch._inductor.config.conv_1x1_as_mm = True
torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_tuning = True
torch._inductor.config.epilogue_fusion = False
torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_check_all_directions = True
```
For the full list of compiler flags, refer to [this file](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/torch/_inductor/config.py).
It is also important to change the memory layout of the UNet and the VAE to “channels_last” when compiling them. This ensures maximum speed:
```python
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
pipe.vae.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
```
Then, compile and perform inference:
```python
# Compile the UNet and VAE.
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
pipe.vae.decode = torch.compile(pipe.vae.decode, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
# First call to `pipe` will be slow, subsequent ones will be faster.
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
```
`torch.compile` offers different backends and modes. As we’re aiming for maximum inference speed, we opt for the inductor backend using the “max-autotune”. “max-autotune” uses CUDA graphs and optimizes the compilation graph specifically for latency. Specifying fullgraph to be True ensures that there are no graph breaks in the underlying model, ensuring the fullest potential of `torch.compile`.
Using SDPA attention and compiling both the UNet and VAE reduces the latency from 3.31 seconds to 2.54 seconds.
## Combine the projection matrices of attention
Both the UNet and the VAE used in SDXL make use of Transformer-like blocks. A Transformer block consists of attention blocks and feed-forward blocks.
In an attention block, the input is projected into three sub-spaces using three different projection matrices – Q, K, and V. In the naive implementation, these projections are performed separately on the input. But we can horizontally combine the projection matrices into a single matrix and perform the projection in one shot. This increases the size of the matmuls of the input projections and improves the impact of quantization (to be discussed next).
Enabling this kind of computation in Diffusers just takes a single line of code:
```python
pipe.fuse_qkv_projections()
```
It provides a minor boost from 2.54 seconds to 2.52 seconds.
Support for `fuse_qkv_projections()` is limited and experimental. As such, it's not available for many non-SD pipelines such as [Kandinsky](../using-diffusers/kandinsky.md). You can refer to [this PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/6179) to get an idea about how to support this kind of computation.
## Dynamic quantization
Aapply [dynamic int8 quantization](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/recipes/dynamic_quantization.html) to both the UNet and the VAE. This is because quantization adds additional conversion overhead to the model that is hopefully made up for by faster matmuls (dynamic quantization). If the matmuls are too small, these techniques may degrade performance.
Through experimentation, we found that certain linear layers in the UNet and the VAE don’t benefit from dynamic int8 quantization. You can check out the full code for filtering those layers [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusion-fast/blob/0f169640b1db106fe6a479f78c1ed3bfaeba3386/utils/pipeline_utils.py#L16) (referred to as `dynamic_quant_filter_fn` below).
You will leverage the ultra-lightweight pure PyTorch library [torchao](https://github.com/pytorch-labs/ao) to use its user-friendly APIs for quantization.
First, configure all the compiler tags:
```python
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
# Notice the two new flags at the end.
torch._inductor.config.conv_1x1_as_mm = True
torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_tuning = True
torch._inductor.config.epilogue_fusion = False
torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_check_all_directions = True
torch._inductor.config.force_fuse_int_mm_with_mul = True
torch._inductor.config.use_mixed_mm = True
```
Define the filtering functions:
```python
def dynamic_quant_filter_fn(mod, *args):
return (
isinstance(mod, torch.nn.Linear)
and mod.in_features > 16
and (mod.in_features, mod.out_features)
not in [
(1280, 640),
(1920, 1280),
(1920, 640),
(2048, 1280),
(2048, 2560),
(2560, 1280),
(256, 128),
(2816, 1280),
(320, 640),
(512, 1536),
(512, 256),
(512, 512),
(640, 1280),
(640, 1920),
(640, 320),
(640, 5120),
(640, 640),
(960, 320),
(960, 640),
]
)
def conv_filter_fn(mod, *args):
return (
isinstance(mod, torch.nn.Conv2d) and mod.kernel_size == (1, 1) and 128 in [mod.in_channels, mod.out_channels]
)
```
Then apply all the optimizations discussed so far:
```python
# SDPA + bfloat16.
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
).to("cuda")
# Combine attention projection matrices.
pipe.fuse_qkv_projections()
# Change the memory layout.
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
pipe.vae.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
```
Since this quantization support is limited to linear layers only, we also turn suitable pointwise convolution layers into linear layers to maximize the benefit.
```python
from torchao import swap_conv2d_1x1_to_linear
swap_conv2d_1x1_to_linear(pipe.unet, conv_filter_fn)
swap_conv2d_1x1_to_linear(pipe.vae, conv_filter_fn)
```
Apply dynamic quantization:
```python
from torchao import apply_dynamic_quant
apply_dynamic_quant(pipe.unet, dynamic_quant_filter_fn)
apply_dynamic_quant(pipe.vae, dynamic_quant_filter_fn)
```
Finally, compile and perform inference:
```python
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
pipe.vae.decode = torch.compile(pipe.vae.decode, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
```
Applying dynamic quantization improves the latency from 2.52 seconds to 2.43 seconds.
## Misc
### No graph breaks during torch.compile
Ensuring that the underlying model/method can be fully compiled is crucial for performance (torch.compile with fullgraph=True). This means having no graph breaks. We did this for the UNet and VAE by changing how we access the returning variables. Consider the following example:
```diff
- latents = unet(
- latents, timestep=timestep, encoder_hidden_states=prompt_embeds
-).sample
+ latents = unet(
+ latents, timestep=timestep, encoder_hidden_states=prompt_embeds, return_dict=False
+)[0]
```
### Getting rid of GPU syncs after compilation
During the iterative reverse diffusion process, we [call](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1d686bac8146037e97f3fd8c56e4063230f71751/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion_xl/pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl.py#L1228) `step()` on the scheduler each time after the denoiser predicts the less noisy latent embeddings. Inside `step()`, the `sigmas` variable is [indexed](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1d686bac8146037e97f3fd8c56e4063230f71751/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_euler_discrete.py#L476). If the `sigmas` array is placed on the GPU, indexing causes a communication sync between the CPU and GPU. This causes a latency, and it becomes more evident when the denoiser has already been compiled.
But if the `sigmas` array always stays on the CPU (refer to [this line](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/35a969d297cba69110d175ee79c59312b9f49e1e/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_euler_discrete.py#L240)), this sync doesn’t take place, hence improved latency. In general, any CPU <-> GPU communication sync should be none or be kept to a bare minimum as it can impact inference latency.